
- Definition and Role of Stock Exchanges
- History of Stock Exchanges
- Major Global Stock Exchanges
- Indian Stock Exchanges (BSE/NSE)
- Listing Process
- Types of Orders
- Trading Mechanism
- Stock Indices and Benchmarks
- Conclusion
Definition and Role of Stock Exchanges
A stock exchange is a centralized marketplace where securities such as stocks, bonds, derivatives, and other financial instruments are bought and sold. It acts as a facilitator for trading between investors, ensuring transparency, liquidity, and price discovery.A stock exchange is a centralized and regulated marketplace where financial securities such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives are bought and sold. It acts as a key component of the financial system, world stock market enabling companies to raise capital from public investors by issuing shares through processes like initial public offerings (IPOs). Once listed, these securities can be traded among investors, providing liquidity and allowing for the efficient transfer of ownership.Stock exchanges play a vital role in maintaining transparency, order driven system, enforcing trading rules, and ensuring that all participants have access to accurate and timely information. This promotes fair trading practices and helps in accurate price discovery, where the market determines the value of a security based on supply and demand. Moreover, best trading platform exchanges support investor confidence by regulating participants and reducing systemic risk through oversight and compliance.For companies, being listed on a stock exchange increases visibility and credibility, which can attract more investors. For individuals and institutions, stock exchanges provide a convenient and structured environment to invest and grow wealth. By connecting savers and businesses, stock index, stock exchanges facilitate capital formation and contribute significantly to economic development and financial stability. In short, they are the backbone of modern capital markets.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
History of Stock Exchanges
The history of stock exchanges dates back to the late Middle Ages, evolving gradually with the growth of trade and commerce. The earliest form of a world stock market exchange can be traced to 13th-century Bruges, Belgium, where merchants gathered at the house of the Van der Beurze family to conduct business. This informal gathering eventually gave rise to the term “bourse,” a word still used today in parts of Europe to describe a stock market. The first official stock exchange was established in Amsterdam in 1602 by the Dutch East India Company, which issued the world’s first publicly traded shares. Investors could buy and sell shares in the company, making Amsterdam the birthplace of modern equity markets. The Amsterdam Stock Exchange laid the foundation for practices like continuous best trading platform, regulation, and the use of brokers. In the 18th century, the London world stock market Exchange was formed, followed by the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in 1792, when 24 brokers signed the Buttonwood Agreement on Wall Street. Over time, other global exchanges emerged, order driven system including those in Tokyo, Hong Kong, and Frankfurt. Today, stock exchanges are integral to the global financial system, facilitating billions in daily transactions and supporting economic growth through efficient capital allocation.
Major Global Stock Exchanges
Some of the largest and most influential stock index exchanges globally include:
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE): The largest by market capitalization, home to many blue-chip companies.
- NASDAQ: Known for its technology-heavy listings like Apple, Microsoft, and Google.
- London Stock Exchange (LSE): One of the oldest, with a broad international presence.
- Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE): The leading exchange in Japan and Asia.
- Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE): A major exchange representing the growing Chinese market.
- Euronext: Pan-European exchange operating in multiple countries.
- Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX): Gateway for investment into China.
Each exchange operates under its own regulatory framework but collaborates internationally to maintain market integrity.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Indian Stock Exchanges (BSE/NSE)
India’s stock market is primarily served by two major exchanges:
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE):
- Established in 1875, it is Asia’s oldest stock exchange. Known for the SENSEX, a benchmark index of 30 financially sound companies.
- Offers a wide range of products including equities, derivatives, debt instruments, and mutual funds.
National Stock Exchange (NSE):
- Founded in 1992 to bring a more modern and electronic trading system.
- Famous for the NIFTY 50 index, covering 50 major stocks.
- Pioneered electronic limit order book trading in India.
Both BSE and NSE have contributed significantly to India’s capital market growth, increasing accessibility and transparency.
Listing Process
Listing on a stock exchange involves a company offering its shares to the public via an Initial Public Offering (IPO). The general steps include:
- Preparation: The company prepares financial statements and other disclosures.
- Regulatory Approval: Submission of the Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP) to the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) for approval.
- IPO Pricing: Determination of share price through fixed price or book-building process.
- Public Offer: Shares are offered to investors.
- Listing: Shares begin trading on the exchange after the IPO closes.
Listing provides companies with access to the best public trading platform and enhances visibility and credibility.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
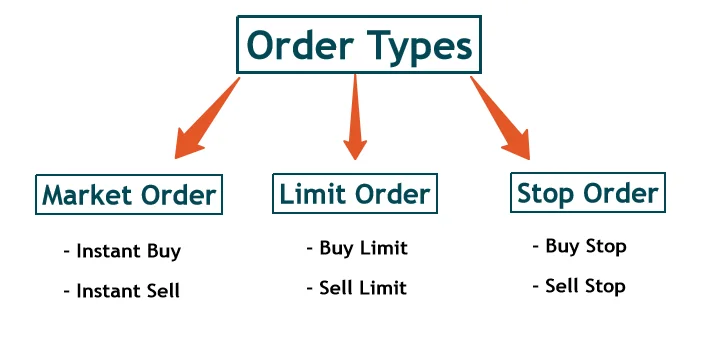
Types of Orders
Trading on stock exchanges involves different order types that specify how trades are executed:
- Market Order: Buy or sell immediately at the best available current price.
- Limit Order: Specifies a price limit; execution only occurs at that price or better.
- Stop Loss Order: An order to buy/sell once a specific price is reached, to limit losses.
- Stop Limit Order: Combination of stop loss and limit orders, triggered at a stop price but executed only within limit prices.
- Day Order: Valid only for the trading day.
- Good Till Cancelled (GTC): Remains active until executed or cancelled.
Understanding order types helps investors manage execution strategies and control risks.
Trading Mechanism
The best trading platform mechanism refers to the process through which securities are bought and sold on stock exchanges. It involves a set of rules and systems that ensure smooth, transparent,stock index and fair transactions between buyers and sellers. There are two main types of trading mechanisms: the order driven system and the quote driven system. In an order driven system, buy and sell orders from investors are matched based on price and time priority. This system is commonly used in most major stock exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE). Orders are entered into an electronic order book, and trades occur when matching orders are found. In contrast, a quote-driven system involves market makers who continuously provide buy and sell quotes for specific securities. They ensure liquidity by being ready to buy or sell at quoted prices, even when no matching orders are available from other investors. Modern trading is largely electronic, Benchmarks with investors placing orders through brokers or online platforms. Once an order is placed, it is routed to the stock exchange where it is matched and executed. After execution, trades are settled through clearinghouses, the world stock market ensuring the transfer of securities and payment. This entire process typically occurs within seconds, providing fast and efficient market access.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Stock Indices and Benchmarks
Stock indices track the performance of selected groups of stocks and serve as market benchmarks:
- Sensex (BSE): Tracks 30 financially strong, well-established companies.
- Nifty 50 (NSE): Represents 50 diversified companies across sectors.
- Global indices: Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), S&P 500, FTSE 100, Nikkei 225.
Indices help investors gauge overall market trends, compare fund performance, and make informed investment decisions.
Conclusion
Stock exchanges play a pivotal role in the financial ecosystem by enabling efficient capital allocation and economic growth. Understanding their structure, functioning, world stock market and participants helps investors navigate markets effectively. Indian exchanges like BSE and NSE have modernized trading and expanded access, order driven system stock index supported by robust regulation from SEBI.As technology advances and benchmarks evolve, stock exchanges will continue to innovate, best trading platform ensuring they meet the needs of a growing and diverse investor base.




