
- The History of Investment Banking
- Role of Investment Banks in M&A
- Equity and Debt Capital markets
- Role in the Financial Market
- Core Functions of Investment Banks
- Industry Coverage Groups
- Debt Capital Markets (DCM)
- Regulatory Landscape
- Major Global and Indian Players
- Technology in Investment Banking
- Financial Modeling and Analytics
- Conclusion
The History of Investment Banking
Investment banking sector is a key part of the financial services industry. It supports capital formation, corporate finance restructuring, and complex financial transactions around the world. This article explores the basics, roles, functions, historical background, rules, and future trends affecting investment banking. Investment banking is a specific area of banking that helps individuals, businesses, and governments raise capital and offers financial consulting services. Unlike commercial banks, which take deposits and give loans, Business Analyst Training banks mainly underwrite securities, facilitate mergers and acquisitions, and provide financial services strategy advice.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Role of Investment Banks in M&A
- They provide valuations and fairness opinions.
- They structure deals and negotiate terms.
- They coordinate due diligence, regulatory approvals, and financing. Impact on Economy
- They help companies raise equity or debt capital for growth, operations, or acquisitions.
- They underwrite initial public offerings (IPOs) and bond issuances.
- Investment banks trade securities, providing liquidity and helping with price discovery. Their market-making roles ensure ongoing buying and selling of securities.
- They offer strategic advice on mergers, acquisitions, divestitures, and restructuring.
- They help clients manage financial risks using derivatives and hedging strategies.
- Investment banks publish equity and credit research to help investors make informed choices.
- They contribute to the efficient functioning of markets.
- They underwrite debt and equity issuance.
- They structure and execute capital raising transactions.
- They provide advisory services for mergers and acquisitions and corporate restructuring.
- Investment banks assist companies in accessing public and private capital markets.
- Equity Capital Markets (ECM)
- They manage IPOs, follow-on offerings, and private placements.
- They price shares using book building or fixed-price methods.
- Technology, Media, and Telecommunications (TMT)
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
- financial services Institutions
- Consumer and Retail
- Energy and Natural Resources
- Industrials
- They issue: corporate finance bonds, convertible debentures, and syndicated loans.
- They advise: On optimal capital structures that balance cost and risk.
- They help: Clients access diverse investor groups, including pension funds and insurance companies.
- Strategic Advisory: They develop growth strategies including expansions, joint ventures, and market entry.
- Capital Structure: They help with optimization and refinancing options.
- Risk Advisory: They assist in hedging interest rate, currency, and commodity risks.
- Derivatives Strategy: They design strategies that match client risk preferences.
- Restructuring and Turnaround: They support financially troubled companies with debt restructuring.
- Bankruptcy Support: They offer advice during bankruptcy proceedings and asset sales.
- Proprietary Trading: They trade securities using the bank’s own capital to make profits.
- Trading Strategies: They engage in arbitrage, market making, and algorithmic trading.
- Brokerage Services: They execute trades for institutional and retail clients.
- Market Access: They provide access to global exchanges and electronic trading platforms.
- They publish earnings estimates, buy/sell recommendations, and sector reports. Their work influences investor sentiment and assists portfolio managers.
- They analyze debt instruments and assess issuer creditworthiness.
- Their research supports fixed income sales and trading operations.
- They offer economic forecasts and risk modeling.
- Their insights improve trading strategies and client advisory.
- Basel III: Sets requirements for capital adequacy and liquidity.
- Dodd-Frank Act: Post-crisis reforms in the U.S. focused on transparency and risk management.
- MiFID II: European rules for market transparency and investor protection.
- SEBI Regulations: In India, SEBI regulates securities markets, including IPOs and disclosures.
- Banks have compliance teams to handle anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC), and insider trading laws.
- They must conduct regular audits and stress tests to check their resilience.
- Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, Morgan Stanley, Bank of America Merrill Lynch, and Citi lead the global investment banking sector market due to their wide range of services. European firms like Barclays, Deutsche Bank, and Credit Suisse also hold significant market shares.
- ICICI Securities, Kotak Mahindra Capital, Axis Capital, HDFC Bank, and JM Financial are top investment banks in India.
- Growing cross-border deals and regulatory changes have boosted market growth.
- Mergers between banks and partnerships with fintech firms are changing the competitive landscape.
- High-frequency trading algorithms and AI-powered market making.
- Cloud computing supports large-scale data processing.
- Digital platforms simplify client onboarding, portfolio management, and communication.
- Blockchain and smart contracts speed up settlement and reduce fraud.
- Automation: Routine tasks are increasingly taken over by AI and robotic process automation (RPA).
- Sustainability Finance: There is a growing focus on ESG investing and green bonds.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Finance built on blockchain is challenging traditional models.
- Client-Centric Models: Products are becoming more tailored with transparent fee structures.
- Talent Evolution: There is a rising demand for tech-savvy bankers with varied skills.
M&A activities can lead to industry consolidation, improve efficiency, and create shareholder value.
However, they also face challenges like regulatory scrutiny and cultural integration.
Equity and Debt Capital markets
19th Century Growth: The industrial revolution and the growth of capital markets led to the need for formal investment banking services. In the U.S., firms like J.P. Morgan & Co. led the way by underwriting railroad bonds and industrial projects. 20th Century Expansion: After the Great Depression, reforms such as the Glass-Steagall Act separated commercial and investment banking sector in the U.S., shaping how the industry trends was regulated. Deregulation and Globalization: The late 20th century saw deregulation, the repeal of Glass-Steagall in 1999, and globalization, which created large investment banks offering various services. Post-2008 Financial Crisis: The financial crisis in 2008 led to increased regulatory scrutiny, including the Dodd-Frank Act in the U.S. and Basel III norms globally, affecting risk management and capital needs.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Role in the Financial Market
Investment banks are important intermediaries in markets. They perform several key roles:
Capital Formation
Market Liquidity
Advisory and Risk Management
Price Discovery and Research
Core Functions of Investment Banks
Investment banks carry out a wide range of activities grouped into three main areas:
Corporate Finance
Sales and Trading markets
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Industry Coverage Groups
Investment banks are divided into industry coverage groups specializing in Business Analyst Training sectors such as:
Analysts typically join an industry trends group where they develop sector-specific expertise, allowing deeper understanding of company fundamentals and Capital markets exposure
Debt Capital Markets (DCM)
Advisory Services
Trading and Brokerage Arms
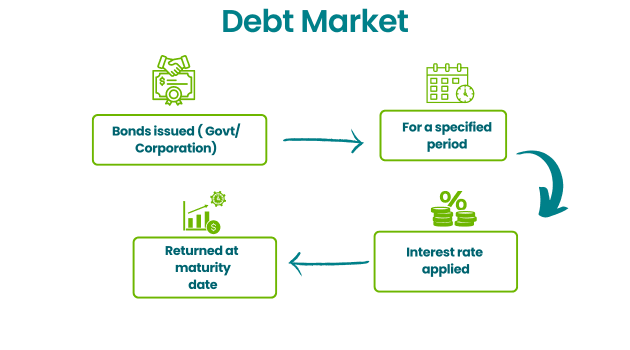
Equity Research
Credit Research
Macroeconomic and Quantitative Research
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Regulatory Landscape
Investment banks work within strict regulatory frameworks designed to maintain financial stability and protect investors.
Key Regulations
Compliance and Risk Management
Major Global and Indian Players
Global Giants
Indian Market Leaders
Market Consolidation
Technology in Investment Banking
Technology is changing how investment banks operate. It improves efficiency, cuts costs, and sparks innovation.
Trading Technology
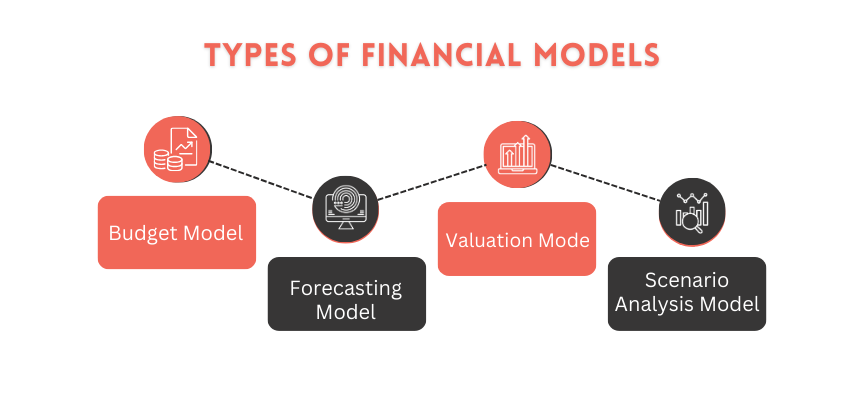
Financial Modeling and Analytics
Advanced modeling tools use machine learning for scenario analysis. Real-time risk management dashboards enhance decision-making.
Client Engagement
Cybersecurity
There is a stronger focus on safeguarding sensitive data from cyber threats.
Future of Investment Banking
The industry trends is undergoing major changes because of regulatory pressures, technology, and evolving client needs.
Trends to Watch
Challenges
Regulatory complexity and global risks remain significant.
Competition from fintech startups is intense.
There is a need to balance innovation with compliance.
Conclusion
Investment banking is essential to the global financial system. It enables capital flows, corporate finance growth, and market efficiency. While it evolves with new technologies and regulations, its main role of connecting those seeking capital with those providing it, and advising on complex Business Analyst Training decisions, remains the same. Both aspiring professionals and investors benefit from understanding the many aspects of investment banking, including its history, functions, and future opportunities.




