
- Introduction to Corporate Restructuring
- Reasons for Restructuring
- Types of Restructuring
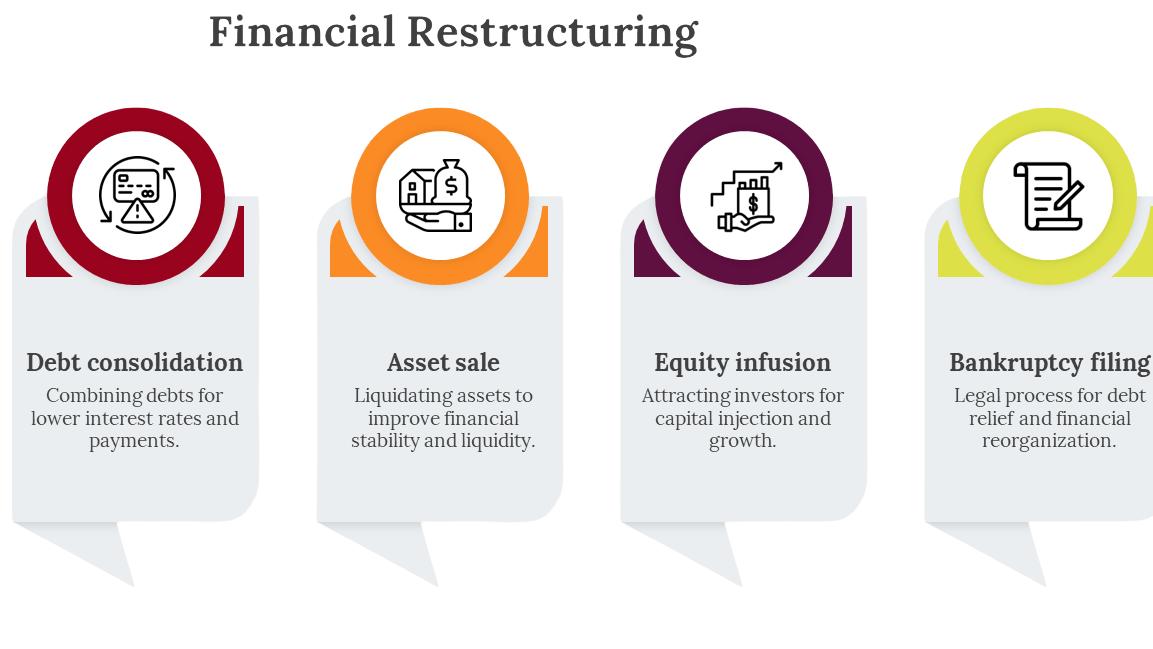
- Financial Restructuring
- Operational Restructuring
- Workforce Restructuring
- Legal and Regulatory Aspects
- Valuation Techniques
- Impact on Shareholders
- Conclusion
Introduction to Corporate Restructuring
Corporate restructuring refers to the process through which a company makes significant changes to its organizational, operational, or financial structures to improve overall performance, address financial difficulties, respond to market shifts, or pursue new strategic directions. This process may involve altering ownership patterns, reconfiguring assets and liabilities, reshaping management, or revising business models. Restructuring is often a critical step in turning around struggling companies but can also be a proactive strategy for growth or optimization. The primary goal of corporate restructuring is to increase shareholder value, improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and position the company better for long-term sustainability. It involves complex decision-making and coordination across various departments and stakeholders, including investors, creditors, employees, and regulators. Restructuring can be voluntary, initiated by management to optimize the company’s structure, or forced, triggered by financial distress or external pressures such as regulatory changes or market downturns.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Reasons for Restructuring
Companies undertake restructuring for a variety of reasons, each driven by specific challenges or opportunities:
- Financial Distress: One of the most common triggers is financial distress, where a company struggles to meet its debt obligations, faces liquidity shortages, or experiences declining profitability. Restructuring helps restore financial stability by renegotiating debt, cutting costs, or raising new capital.
- Changing Market Conditions: Shifts in market dynamics, such as increased competition, technological disruption, or changing customer preferences, may require companies to adapt their business models or operations to remain competitive.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Following mergers or acquisitions, companies often restructure to integrate operations, eliminate redundancies, and streamline management for improved synergy and cost savings.
- Regulatory and Legal Changes: New regulations or compliance requirements can necessitate structural changes to ensure adherence, reduce legal risks, or exploit new business opportunities created by regulatory shifts.
- Strategic Refocusing: Companies may restructure to focus on core competencies, divest non-core businesses, or enter new markets. This strategic refocusing can help improve resource allocation and long-term profitability.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Persistent inefficiencies in processes, production, or supply chains can drive restructuring to improve productivity, reduce costs, and enhance quality.
- Technology Upgrades: Adoption of new technologies often requires reorganization of workflows, teams, and business units to leverage digital transformation effectively.
Types of Restructuring
Corporate restructuring can take several forms, broadly classified into financial, operational, and workforce restructuring. Each type targets different aspects of the business.
- Financial Restructuring: Financial restructuring involves changes to the company’s capital structure, its mix of debt and equity and aims to improve liquidity, solvency, and access to capital.
- Operational Restructuring: Operational restructuring focuses on improving business processes, organizational efficiency, and product or service delivery. It may involve reorganizing departments, outsourcing, or process reengineering.
- Workforce Restructuring: Workforce restructuring entails changes in human resources, such as layoffs, redeployments, or retraining, to align staffing levels and skills with business needs.
- Asset Restructuring: This includes selling, spinning off, or acquiring assets or business units to optimize the asset base and enhance strategic focus.
- Debt Restructuring: Companies renegotiate terms with creditors to extend maturities, reduce interest rates, or convert debt into equity. This can alleviate immediate cash flow pressures and reduce the risk of bankruptcy.
- Equity Restructuring: Issuing new shares, buybacks, or recapitalizations can alter the ownership base and improve the balance sheet. Equity restructuring may dilute existing shareholders but can provide necessary capital infusion.
- Refinancing: Replacing existing debt with new loans at better terms can reduce costs and improve financial flexibility.
- Capital Raising: Issuing new equity or debt to fund operations, pay down liabilities, or finance growth initiatives.
- Debt-for-Equity Swaps: Creditors agree to exchange debt claims for ownership stakes, reducing debt burden while increasing equity capital.
- Compliance: Ensuring adherence to securities laws, labor regulations, antitrust rules, and tax laws.
- Bankruptcy and Insolvency Laws: Restructuring may involve court-supervised processes such as Chapter 11 in the U.S. or administration in the U.K.
- Contractual Obligations: Managing covenants, leases, and supplier agreements during changes.
- Disclosure and Reporting: Meeting transparency requirements for investors and regulators.
- Shareholder Approvals: Gaining consent for significant transactions or changes in governance.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF): Projecting future cash flows and discounting them to present value.
- Comparable Company Analysis: Valuing based on metrics of similar companies in the market.
- Precedent Transactions: Analyzing prices paid in recent comparable deals.
- Asset-Based Valuation: Calculating the net asset value by subtracting liabilities from assets.
- Market Capitalization: Using current stock price and shares outstanding as an indicator.
- Share Dilution: New equity issuance can reduce existing shareholders’ percentage ownership.
- Share Price Volatility: Restructuring announcements often lead to stock price fluctuations.
- Dividends and Earnings: Operational improvements or asset sales can affect dividend payments and earnings per share.
- Control Changes: Debt-to-equity swaps or mergers can shift control among shareholders.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Financial Restructuring
Financial restructuring is critical for companies facing liquidity problems or seeking to optimize their capital structure. The key components include:
Operational Restructuring
Operational restructuring is a strategy for improving business performance by transforming organizational processes and structures. By implementing focused initiatives like business process reengineering, companies can eliminate workflow redundancies and reduce operational cycle times. This transformation often extends to key areas such as technology integration, where IT systems and automation tools are used to improve productivity and support better decision-making. At the same time, organizations aim to optimize their supply chains by building stronger supplier relationships and refining logistics to enhance cost-efficiency and market responsiveness. Strategic management restructuring is important in this process. It may involve realigning leadership, flattening hierarchies, and creating more agile divisions within the organization. Companies also often streamline their product and service offerings, focusing resources on high-margin products and discontinuing those that underperform. By carefully outsourcing and offshoring certain functions, businesses can further streamline operations. This approach allows them to transfer non-core activities to outside vendors, leading to cost reductions and improved operational performance.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Workforce Restructuring
Workforce restructuring is a way for companies to realign their staff with changing business goals and financial situations. Organizations usually use a mix of strategies that include targeted layoffs, employee redeployment, and voluntary separation programs. By managing these transitions carefully, companies can lower their workforce, control expenses, and keep operations running smoothly. At the same time, forward-thinking organizations invest in retraining and reskilling to help their workforce stay flexible and competitive. Good labor relations management is important during these times; it requires careful negotiations with unions and support for employee morale. Besides adjusting the workforce, companies often look for ways to sell assets, create spin-offs, or make carve-outs to raise funds and sharpen their focus. They also form joint ventures and strategic alliances to share risks and use each other’s strengths, which helps them build more resilient and agile business models that can handle complex market challenges.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Corporate restructuring must navigate a complex legal and regulatory environment.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Valuation Techniques
Accurate valuation is crucial for restructuring decisions, including asset sales, mergers, and equity changes.
Impact on Shareholders
Restructuring decisions directly affect shareholder value and rights.
Conclusion
Corporate restructuring is a multifaceted process that involves significant changes to a company’s financial and operational frameworks. When executed well, it can revitalize struggling companies, unlock new growth opportunities, and increase shareholder value. However, it requires careful planning, expert execution, and ongoing management to navigate legal complexities, align stakeholder interests, and achieve desired outcomes. Understanding the different types of restructuring, the reasons behind them, and the best practices for implementation is essential for business leaders, investors, and advisors aiming to successfully guide companies through transformative periods.



