
- Introduction to Investment Banking
- Core Functions and Services
- Role in the Financial Markets
- Key Skills Required
- Career Path and Growth
- Compensation and Perks
- Challenges and Demands
- Investment Banking vs Commercial Banking
- Conclusion
Introduction to Investment Banking
Investment banking is a specialized segment of the financial services industry that focuses on helping individuals, capital seekers corporations, and governments raise capital and provide advisory services for mergers, acquisitions, and other complex financial transactions. Unlike commercial banking, which deals primarily with deposit-taking and loan provision, investment banks operate at the intersection of capital markets, role in the financial markets and corporate finance. Historically rooted in the role of underwriting securities, investment banking has evolved to encompass a broad array of activities that support the function of the financial markets and enable companies to grow, restructure, and expand globally. Investment banks act as intermediaries between investors and companies, facilitating capital seekers flows and ensuring market liquidity. In essence, investment banking is the engine that drives large-scale financial activity and economic development by connecting capital seekers with capital providers through structured financial solutions.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Core Functions and Services
Investment banking covers a wide spectrum of financial services. The core functions can be broadly categorized as follows:
Raising Capital
Investment banks assist companies in raising capital through:
- Equity Financing: Managing initial public offerings (IPOs), follow-on public offerings (FPOs), and private placements to raise equity capital.
- Debt Financing: Issuance of bonds, debentures, and other debt instruments in the primary market.
They underwrite these securities, function of the financial markets, guaranteeing the sale of shares or bonds to investors and assuming the associated risks.
Advisory Services
Investment banks provide expert advice on:
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A): Assisting companies in buying, selling, or merging with other firms, including deal structuring, valuation, due diligence, and negotiations.
- Restructuring: Advising on financial restructuring, including debt refinancing, recapitalization, and turnaround strategies.
- Spin-offs and Divestitures: Helping companies separate parts of their business or divest non-core assets.
- Sales and Trading: Investment banks operate sales and trading desks that facilitate the buying and selling of securities in secondary markets. They provide liquidity and price discovery for various asset classes, function of the financial markets, including equities, bonds, commodities, and derivatives.
- Research: Equity and credit research teams analyze companies, sectors, and markets to provide investment recommendations,financial services, valuations, and market forecasts that guide both internal trading desks and external clients.
- Asset Management: Some investment banks also offer asset management services to institutional and high-net-worth clients, managing portfolios across various asset classes.
Role in the Financial Markets
Investment banks are crucial intermediaries in financial markets, serving as:
- Market Makers: They facilitate liquidity by buying and selling securities and maintaining orderly markets.
- Capital Market Facilitators: By underwriting and distributing securities, they connect issuers with investors efficiently.
- Advisors: Their specialized knowledge helps corporations make informed strategic decisions that affect market valuations and economic growth.
- Risk Managers: They assist clients in hedging financial risks using derivatives and structured products.
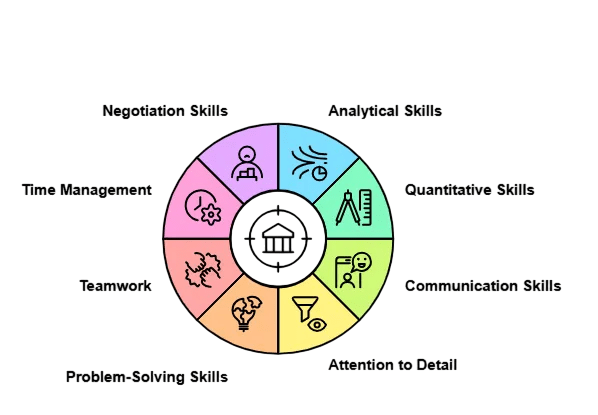
- Financial Modeling and Valuation: Proficiency in Excel and other tools to build complex models that project company performance, value assets, and assess deal feasibility.
- Accounting and Financial Statement Analysis: Understanding financial statements and accounting principles to interpret company health and profitability.
- Market Knowledge: Awareness of economic trends, industry dynamics, and regulatory environments to provide relevant advice.
- Communication and Presentation: Ability to articulate complex financial concepts clearly to clients, stakeholders, and internal teams through reports, pitch books, and presentations.
- Negotiation and Salesmanship: Persuasive skills to negotiate deals and convince clients.
- Attention to Detail and Analytical Thinking: Accuracy and rigorous analysis are vital to avoid costly errors.
- Stress Management and Work Ethic: High-pressure environments require stamina, resilience, and long working hours.
- Analyst: Typically a 2-3 year role post-undergraduate degree, involving financial modeling, market research, and preparing presentation materials.
- Associate: Usually requires an MBA or promotion from Analyst, with greater client interaction and deal execution responsibilities.
- Vice President (VP): Manages deal teams, client relationships, and business development.
- Director/Executive Director: Focuses on sourcing deals, strategic client advisory, and leading transactions.
- Managing Director (MD): Senior leadership, driving firm revenue, and high-level client negotiations.
- Base Salary: Competitive fixed pay, increasing with seniority.
- Bonuses: Significant performance-based bonuses can be multiples of the base salary.
- Perks: Include health insurance, retirement plans, wellness programs, travel allowances, and sometimes stock options.
- Long-term Incentives: Senior bankers may receive profit-sharing or equity stakes.
- Long Working Hours: 70-100 hours per week during deal cycles.
- High Stress: Deadlines, client demands, and market volatility create pressure.
- Work-Life Balance: Often compromised, especially at junior levels.
- Competitive Environment: Intense rivalry within firms and against other banks.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Navigating conflicts of interest and regulatory compliance.
- Burnout Risk: Due to sustained stress and workload.
The presence of investment banks enhances the efficiency, transparency, and stability of role in the Financial Markets. Their operations impact the flow of capital, pricing of securities, and allocation of resources across the economy.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Key Skills Required
Working in investment banking demands a unique blend of technical, analytical, and interpersonal skills:
Career Path and Growth
Entry-Level Roles
Mid to Senior-Level Roles
Career progression depends on performance,function of the financial markets, financial services, deal success, networking, and sometimes internal firm dynamics.
Compensation and Perks
Investment banking is known for lucrative compensation packages, especially in global financial hubs:
However, compensation is closely tied to individual and firm performance, making the role demanding yet rewarding.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Investment Banking vs Commercial Banking
| Aspect | Investment Banking | Commercial Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Capital markets, advisory, M&A, underwriting | Deposits, loans, payments, retail banking |
| Clients | Corporations, governments, institutional investors | Individuals, SMEs, corporations |
| Revenue Model | Fees, commissions, trading profits | Interest income, fees from loans and services |
| Risk Profile | Market and underwriting risk | Credit risk, liquidity risk |
| Regulation | Regulated but less restrictive | Highly regulated to protect depositors |
Challenges and Demands
While rewarding, investment banking careers come with challenges:
Successful bankers develop coping strategies and focus on career longevity
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Investment banking stands at the heart of global finance, connecting capital seekers with investors, capital seekers advising on transformative deals, and driving economic growth. It offers lucrative and prestigious career paths for those with strong analytical abilities, resilience, and a passion for markets. Despite the challenges of long hours and intense pressure, commercial banking, investment banking rewards dedication with financial benefits, learning opportunities, and the chance to shape industries. With rapid technological advancements, increasing focus on ESG, role in the Financial Markets and evolving regulatory landscapes, function of the financial markets, investment banking continues to transform, financial services demanding adaptability and continuous skill development. For aspiring professionals, breaking into this field requires commitment, preparation, and networking but offers unmatched exposure to the world of high finance and deal-making.




