
- What are Short-Term Investments?
- Types of Short-Term Investments
- Treasury Bills and Commercial Papers
- Certificates of Deposit
- Money Market Funds
- Short-Term Bonds and ETFs
- Risk vs Return Comparison
- Liquidity Considerations
- Conclusion
What are Short-Term Investments?
Short-term investments, also known as temporary investments or marketable securities, are financial investments that can be easily converted into cash within a short period typically within one year. These investments offer investors a way to earn a return on idle cash while maintaining liquidity. They are usually characterized by lower risk, shorter duration, and moderate returns. Companies and individuals use types of short-term investments to manage cash flows efficiently and meet short-term financial obligations. These investments serve multiple purposes such as capital preservation, income generation, and portfolio diversification. They are ideal for conservative investors or those who anticipate needing access to their funds within a short time frame.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Types of Short-Term Investments
Several financial instruments fall under the umbrella of short-term investments. These include:
- Treasury Bills (T-Bills): Issued by the government, considered one of the safest short-term instruments.
- Commercial Papers: Unsecured promissory notes issued by corporations to finance short-term liabilities.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): Time deposits offered by banks with a fixed maturity date and interest rate.
- Money Market Funds: Pooled funds that invest in a diversified portfolio of short-term debt instruments.
- Short-Term Bonds: Bonds with maturities of less than three years.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs that focus on short-term instruments for quick liquidity.
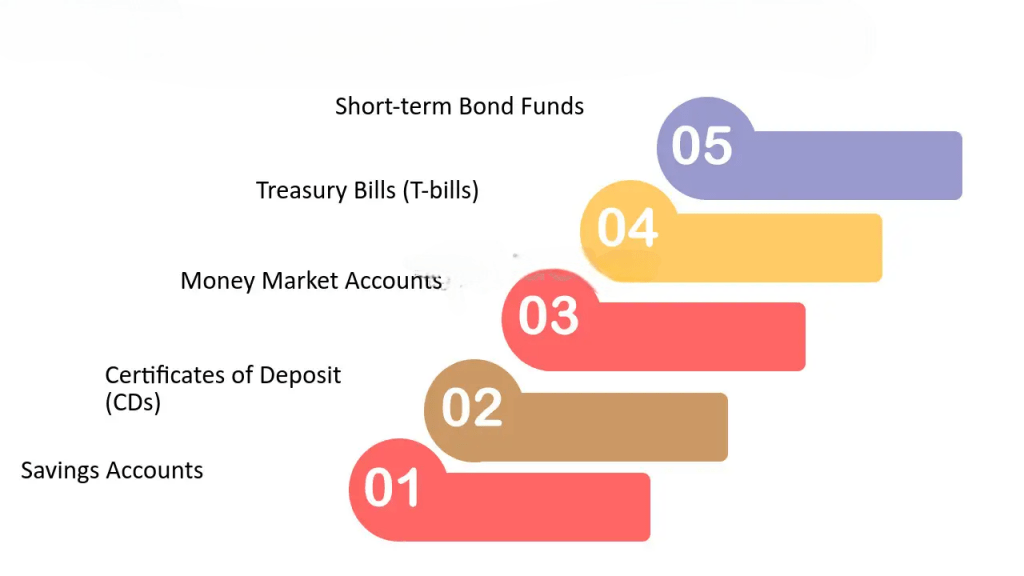
Each instrument has unique characteristics that suit different risk appetites and investment horizons.
Treasury Bills and Commercial Papers
Treasury Bills (T-Bills)
- Issuer: Government
- Tenure: Ranges from a few days to 52 weeks
- Returns: Offered at a discount; investors earn the difference between purchase price and face value
- Risk Level: Very low due to sovereign backing
Commercial Papers
- Issuer: Corporations
- Tenure: Generally up to 270 days
- Returns: Higher than T-bills due to greater risk
- Risk Level: Moderate to high; credit rating of the issuing company is crucial
T-bills are often the first choice for ultra-conservative investors, while commercial papers are suitable for those willing to accept slightly higher types of short-term investments for better returns.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Certificates of Deposit
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) are offered by banks and credit unions, providing a fixed interest rate over a specified period.
- Interest Rates: Usually higher than regular savings accounts
- Tenure: Can range from one month to five years
- Liquidity: Early withdrawal may incur penalties
- Risk: Insured by government schemes (e.g., FDIC in the U.S.)
CDs are suitable for investors looking for predictable returns without the volatility of market-linked instruments.
Money Market Funds
Money Market Funds (MMFs) are mutual funds that invest in short-term debt instruments.
- Portfolio: Includes T-bills, commercial papers, CDs
- NAV Stability: Generally stable around $1 per share
- Returns: Low to moderate
- Liquidity: High; often allows same-day redemptions
- Use Case: Ideal for temporary parking of funds
MMFs are widely used by both institutional and retail investors for their liquidity and safety.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Short-Term Bonds and ETFs
Short-term bonds have maturities of less than three years and offer a fixed interest income.
- Types: Government bonds, corporate bonds, municipal bonds
- Risk: Varies with issuer
- Liquidity: Generally good, especially for government bonds
Short-term bond ETFs provide diversification by investing in a portfolio of such bonds.
- Advantages: Lower cost, easier access, automatic diversification
- Examples: iShares Short Treasury Bond ETF, Vanguard Short-Term Bond ETF
- High Liquidity: T-bills, MMFs, and ETFs allow quick access to cash.
- Moderate Liquidity: Commercial papers and short-term bonds may need to be sold in secondary markets.
- Low Liquidity: CDs impose penalties for early withdrawals.
These are ideal for conservative investors seeking higher returns than savings accounts with limited interest rate risk.
Risk vs Return Comparison
| Instrument | Risk Level | Expected Return | Liquidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treasury Bills | Very Low | 3-5% | High |
| Commercial Papers | Moderate | 5-7% | Moderate |
| Certificates of Deposit | Low | 4-6% | Low (penalties) |
| Money Market Funds | Low | 3-6% | High |
| Short-Term Bonds | Low-Moderate | 4-7% | Moderate |
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Liquidity Considerations
Liquidity is a critical factor in short-term investing:
Investors should match their investment horizon with the liquidity profile of the instrument.
Conclusion
Short-term bonds investments play a vital role in financial planning, offering a blend of safety, liquidity, and modest returns. While they may not generate high yields, their stability makes them indispensable for risk-averse investors and as components of emergency funds. Understanding the characteristics, benefits, and limitations of each type of short-term investments empowers investors to make informed decisions that align with their financial goals. Whether for individual investors or institutions, short-term investments provide essential flexibility and control in an unpredictable financial landscape.




