
- What is Financial Planning?
- Setting Financial Goals
- Budgeting Essentials
- Emergency Funds
- Saving vs Investing
- Understanding Credit and Debt
- Basics of Insurance
- Retirement Planning Basics
- Tax Planning Tips
- Choosing the Right Investment Tools
- Conclusion
What is Financial Planning?
Effective financial planning is crucial for achieving financial security, building wealth, and avoiding unnecessary debt or stress. For beginners, navigating the world of finance can seem overwhelming, but with the right strategies and tools, anyone can gain control of their financial future. This guide introduces the key principles and actionable steps for beginner-friendly financial planning. Financial planning is the process of evaluating your current financial situation, setting financial goals, and outlining strategies to achieve them. It encompasses budgeting, saving, investing, tax planning, insurance, and retirement. The aim is to make informed decisions about money that align with personal values and long-term aspirations. Whether you’re planning to buy a home, pay off debt, or retire comfortably, financial planning helps you get there.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Setting Financial Goals
Crafting a strong financial plan starts with setting clear, measurable, and realistic goals. These goals act as a guide for your financial journey. They cover different time frames. Short-term objectives include building an emergency fund or saving for a vacation (0-2 years). Medium-term goals involve buying a car or paying off debt (3-5 years). Long-term ambitions focus on retirement planning, funding children’s education, or buying a home (5+ years). Using the SMART criteria helps you make your goals Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound. This approach turns vague wishes into specific financial targets. Writing down your goals, along with their costs and timelines, motivates you. It increases personal accountability and changes financial planning from a vague idea into a practical strategy, guiding you toward long-term financial success.
Budgeting Essentials
- Implement the 50/30/20 Budget Rule: Allocate 50% of your income to needs (e.g., rent, groceries), 30% to wants (e.g., entertainment, travel), and 20% to savings and debt repayment. This promotes balanced financial decision-making and encourages disciplined spending.
- Track Every Money: Record all sources of income and every expense. Categorize transactions (e.g., utilities, subscriptions) to uncover spending patterns and identify areas where you can improve your financial habits.
- Choose the Right Budgeting Tool: Use spreadsheets for manual control, mobile apps for convenience, or envelope systems for hands-on budgeting. Select tools that match your style to make expense tracking consistent and engaging.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: At the end of each month, revisit your budget. Check if your spending aligns with goals, and tweak categories or limits to reflect changes in income, goals, or circumstances.
- Transform Budgeting Into a Strategic Practice: Budgeting isn’t just about restriction it’s a tool for financial clarity and empowerment. Use it to actively direct your finances toward long-term milestones like debt freedom, wealth-building, or early retirement.
- Financial Shield: An emergency fund is your personal safety net. It protects you from unexpected financial shocks like job loss, medical emergencies, or sudden repairs. Aim to cover 3–6 months of essential expenses for optimal protection.
- Strategic Savings Approach: Build your emergency fund gradually. Even small contributions like ₹500 or $50 monthly can accumulate into a meaningful financial buffer over time.
- Smart Storage Strategy: Store your emergency fund in a high-yield savings account to ensure liquidity and earn modest returns while retaining quick access for urgent needs.
- Psychological Comfort: Beyond monetary security, emergency funds offer peace of mind, reduce stress, and provide flexibility to handle life’s unpredictable events.
- Disciplined Financial Habit: Treat emergency fund contributions as non-negotiable monthly payments. Make it a savings priority and avoid using the fund for non-emergencies.
- Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses
- Life Insurance: Supports dependents in case of death
- Auto Insurance: Required in most regions
- Home/Renter’s Insurance: Protects property and belongings
- Time is Your Wealth Ally: Begin investing early even with modest amounts to leverage the power of compounding. Over time, small contributions can grow substantially and form the foundation for retirement security.
- Diversify Retirement Options: Strengthen your retirement plan by combining vehicles like EPF, PPF, 401(k), IRA, and NPS. Diversification enhances growth potential while optimizing tax advantages.
- Automate Your Financial Future: Set up automated paycheck deductions to consistently fund retirement investments. This reduces decision fatigue and ensures disciplined savings.
- Increase Contributions Strategically: Whenever your salary increases, raise your retirement savings rate. This incremental approach boosts your nest egg without straining your current lifestyle.
- Regular Financial Check-In: Reassess your retirement strategy periodically. Adjust plans based on income changes, life goals, market trends, and inflation to stay on track.
- Align Investment Tools to Personal Profile: Select investments that match your risk tolerance, financial goals, and time horizon. A tailored approach fosters more meaningful and sustainable wealth creation.
- Beginner-Friendly Investment Vehicles: Begin with accessible options such as Fixed Deposits, Public Provident Fund (PPF), and Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs). These offer low entry barriers and help develop consistent saving habits.
- Strategic Asset Class Diversification: Create a balanced portfolio by combining debt instruments for stability, equities for capital growth, and alternative assets like gold or REITs for inflation hedging and risk dispersion.
- Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies: Maximize post-tax returns with options like Equity Linked Saving Schemes (ELSS) and other Section 80C-compliant instruments. This enhances overall financial efficiency and tax savings.
- Long-Term Wealth Creation Approach: Emphasize passive investment routes such as Index Funds and ETFs. These options benefit from market-wide growth, carry low costs, and reduce dependence on active fund management.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Emergency Funds
Saving vs Investing
Understanding the difference between saving and investing is important for good financial planning. Saving means putting away money for short-term or predictable expenses. It usually involves low risk and minimal returns. Investing, on the other hand, is about putting money into assets like stocks, mutual funds, and bonds. These have the potential for higher returns over time.
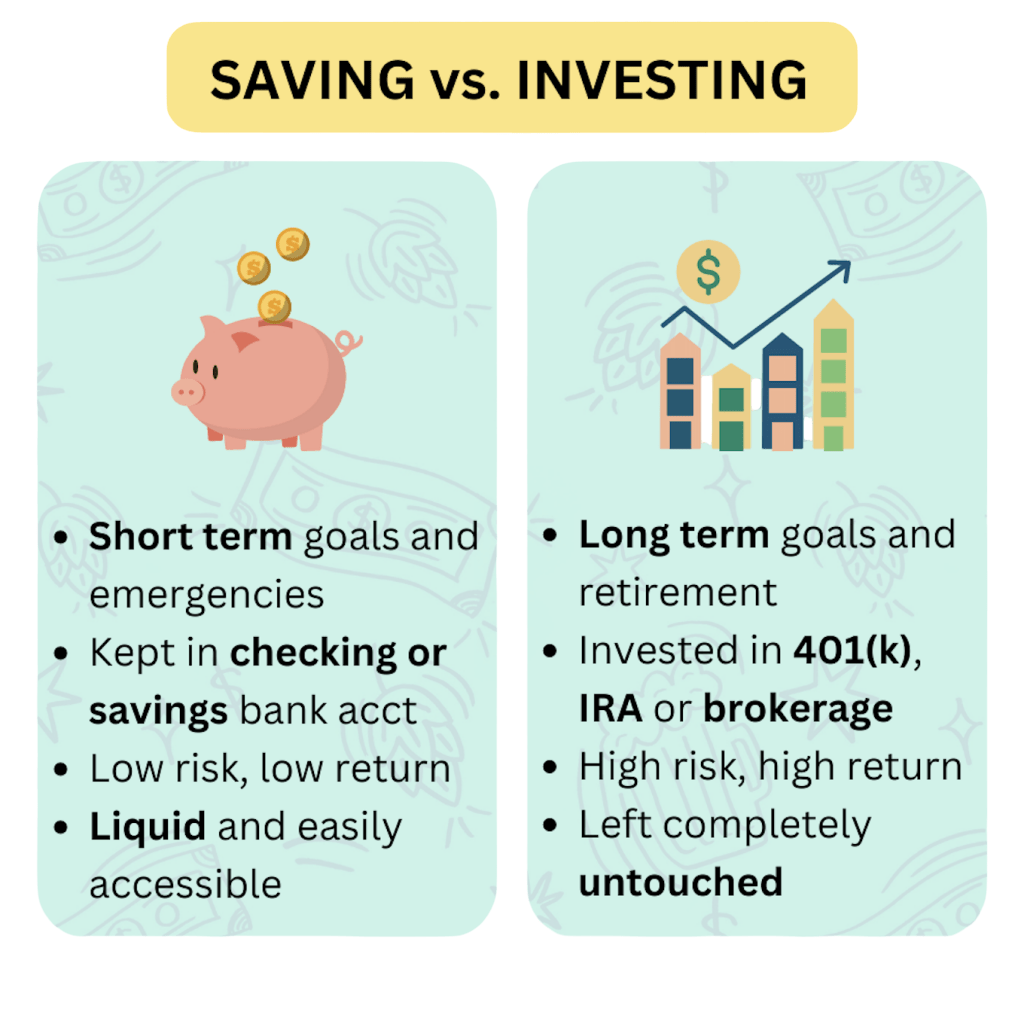
Good financial management requires knowing when to save. This includes building emergency funds or preparing for immediate financial needs. It also requires knowing when to invest, which is best for long-term goals like retirement, building wealth, and protecting against inflation. The key to financial growth is to diversify investments and carefully consider your personal risk tolerance. By distinguishing between saving and investing, and matching them with your financial goals, you can create a strong strategy that balances immediate security with future financial success.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Understanding Credit and Debt
Credit management is an important financial skill that needs a strategic understanding and a disciplined approach. Different types of credit, such as credit cards, personal loans, auto loans, student loans, and mortgages, provide financial flexibility when used wisely. Developing good credit habits is key to maintaining financial health. This means paying bills on time, keeping credit usage below 30%, and checking credit reports regularly. When dealing with debt, people can use effective methods to reduce it. The Snowball Method focuses on paying off the smallest debts first. The Avalanche Method targets high-interest debts to lessen the long-term financial burden. It’s also vital to avoid making only the minimum payments, as interest can quickly add up and trap consumers in a cycle of increasing debt. By understanding how credit works and following sound financial practices, people can use credit as a helpful tool for economic growth and stability, instead of letting it become a financial burden.
Basics of Insurance
Insurance protects you and your assets against unforeseen financial losses. Key types include:
Begin with term life and basic health insurance. As your income and assets grow, review and expand coverage. Always compare plans based on premium, coverage, and exclusions.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Retirement Planning Basics

Tax Planning Tips
Tax planning is a way to legally lower your tax bill and keep more of your income. By knowing your tax bracket and using specific strategies, you can improve your financial situation. Key techniques include using deductions like Section 80C in India, claiming exemptions such as House Rent Allowance (HRA) and Leave Travel Allowance (LTA), and investing in tax-efficient options like Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS), Public Provident Fund (PPF), and the National Pension System (NPS). It is important to file your tax return accurately and on time. You can make this process easier by consulting tax advisors or using online tools that help with documentation and submission. These steps not only reduce your tax burden but also encourage good financial habits and long-term wealth management.
Choosing the Right Investment Tools
Conclusion
True financial success depends not on your income but on how well you manage and grow your wealth. For those starting to handle money, small, steady actions are your best friends. Start by creating a simple budget. This means tracking where your money goes each month. You can use a notebook or a free app for this. Next, focus on saving. Even setting aside a small amount, like twenty dollars a week, builds momentum. This habit creates a safety net. Setting clear financial goals is also important. Do you want to buy a house? Pay off debt? Retire early? Knowing your goals fuels your motivation. These initial steps may seem small. However, they can have a big impact over time. They lay the groundwork for significant improvements in your overall financial health. Learning about money is essential. Read books or reliable online articles. Understand basic ideas like interest and investing. Use tools that are easy to find. Many banking apps offer budgeting features. There are also many free online calculators. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice. A financial advisor can provide personalized guidance. They can help you make complex decisions. The most important factor is discipline. Stick to your plan, even when it gets tough.



