
- Definition and Scope
- Role of Investment Managers
- Types of Investment Firms
- Investment Mandates
- Portfolio Strategies
- Passive vs Active Management
- Risk and Performance Metrics
- Institutional vs Retail Management
- Conclusion
Definition and Scope
Investment management refers to the professional management of various securities (stocks, bonds, etc.) and assets (real estate, precious metals, etc.) to meet specific investment goals for the benefit of investors. These investors may be individuals or institutions such as pension funds, insurance companies, investment strategies charities, and corporations. The process includes activities such as asset selection, portfolio construction, monitoring, and rebalancing. It also involves strategies to optimize returns and manage risks. Investment management is the professional process of managing various financial assets such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, mutual funds and other securities on behalf of individuals, institutions, Passive vs active management or governments to help them achieve specific financial goals. It involves not only the buying and selling of investments but also ongoing strategies to grow and preserve wealth over time.The scope of investment management is broad and includes key functions such as portfolio management, where investments are selected and balanced based on an investor’s objectives and risk tolerance. Asset allocation is a crucial component, ensuring a strategic mix of asset classes to optimize returns while managing risk. Investment managers also perform in-depth market research and financial analysis to support decision-making, monitor portfolio performance, and adjust strategies as needed. Risk management is integral, helping protect against potential losses due to market volatility or other financial threats. Additionally, investment managers provide tailored advice to clients, mutual funds, investors,investment strategies ensure compliance with financial regulations, and produce detailed reports to maintain transparency and accountability.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Role of Investment Managers
Portfolio Construction and Management: Build and manage investment portfolios tailored to clients’ financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Asset Allocation: Determine the optimal mix of asset classes (e.g., equities, bonds, real estate) to balance risk and return.
- Investment Research and Analysis: Conduct market, industry, and security-level research to inform investment decisions.
- Risk Management: Identify, assess, and mitigate risks to protect client capital and maintain portfolio stability.
- Performance Monitoring: Track portfolio management performance against benchmarks and adjust strategies when needed.
- Client Advisory: Communicate with clients to understand their needs and provide personalized investment advice.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure all investment activities comply with legal, ethical, and industry standards.
- Reporting and Documentation: Prepare and present performance reports, financial statements, and regulatory disclosures.
- Market Forecasting: Anticipate market trends and economic shifts to proactively manage investment strategies.
- Sustainable/ESG Investing: Incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions (if applicable).
Types of Investment Firms
Investment management is conducted by various types of firms, including:
- Asset Management Firms: Handle large-scale portfolios for institutional clients
- Wealth Management Firms: Offer personalized services to high-net-worth individuals
- Robo-Advisors: Use algorithms to manage investments with minimal human intervention
- Boutique Firms: Focus on niche markets or asset classes
Hedge Funds and Private Equity Firms: Use alternative strategies to generate higher returns
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Investment Mandates
An investment mandate is a set of guidelines or instructions that define how a portfolio manager should invest a client’s funds. It outlines the investment objectives, risk tolerance, financial goals, asset allocation limits, time horizon, scope and any specific restrictions or preferences the client may have. These mandates serve as a framework for decision-making and ensure that investment strategies align with the client’s goals whether they are focused on growth, income, capital preservation, or ethical investing. Investment mandates are typically formalized in a legal agreement between the asset manager and the client, and they are critical in maintaining consistency, Passive vs active Management transparency, mutual funds and accountability in portfolio management. Adherence to the mandate helps protect both parties and ensures that role of investment managers are managed according to agreed-upon principles.
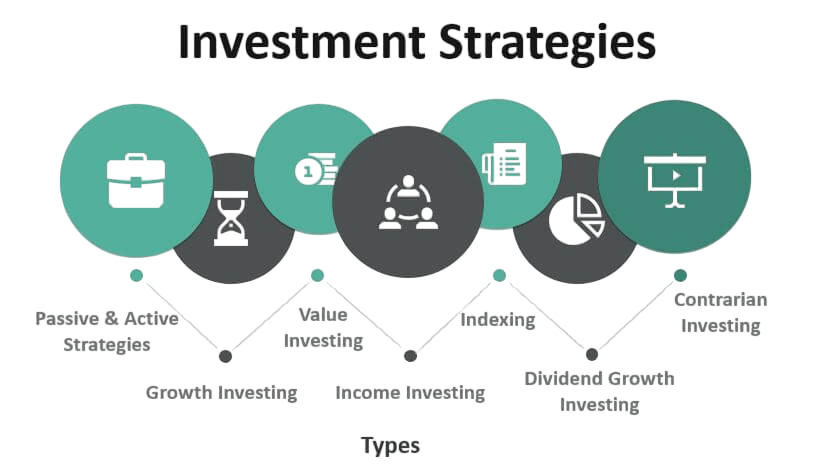
Portfolio Strategies
Portfolio strategies guide the composition and risk level of an investment portfolio. Common strategies include:
- Growth Investing: Focuses on stocks with strong potential for capital appreciation, targeting companies expected to grow faster than the market.
- Value Investing: Targets undervalued stocks trading below their intrinsic value, aiming for gains as the market corrects the price.
- Income Investing: Seeks stable income through dividends or interest payments, ideal for investors wanting regular cash flow.
- Indexing: Mirrors the performance of a specific market index (e.g., S&P 500) to provide broad market exposure with low costs.
- Thematic Investing: Invests in emerging trends or sectors like artificial intelligence, green energy, or other transformative industries.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Passive vs Active Management
Passive Management involves replicating a market index. It’s cost-effective, transparent, financial goals and tax-efficient.
Active Management involves making specific investments with the goal of outperforming the market. It requires:
- Extensive research
- Market timing
- Security selection
Both approaches have merits: passive vs active management generally performs well in efficient markets, while active management can generate alpha in volatile or emerging markets.
Risk and Performance Metrics
Evaluating the success of an investment strategy requires performance and risk metrics:
- Alpha: Measures the excess return of an investment compared to a benchmark, indicating how much value the manager added.
- Beta: Reflects the sensitivity of an investment’s returns to market movements, showing its market-related risk.
- Sharpe Ratio: Adjusts an investment’s return by its risk, helping assess risk-adjusted performance.
- Standard Deviation: Measures the volatility or variability of an investment’s returns over time.
- Tracking Error: Quantifies how much an investment’s returns deviate from its benchmark, indicating consistency in following the index.
Performance analysis must be adjusted for role of investment managers and market conditions to provide an accurate assessment.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Institutional vs Retail Management
Institutional Investment Management involves managing large pools of capital for organizations. Characteristics include:
- Larger average deal sizes
- More sophisticated strategies
- Emphasis on fiduciary responsibility
Retail Investment Management caters to individual investors and typically involves:
- More educational support
- Customization
- Smaller portfolios
Firms may serve one or both segments, depending on their expertise and infrastructure.
Conclusion
Investment management is a dynamic and multifaceted industry that combines analytical rigor, market insight, and client service. Whether managing a pension fund or a personal portfolio management role of investment managers, investment managers must align strategies with objectives while navigating market complexities. As the industry evolves with technology and global trends, Scope understanding the fundamentals and staying informed are crucial for success both for professionals and investors alike.In summary, understanding the fundamentals of investment management from different investing styles and portfolio management metrics to the roles of investment managers is essential for making informed financial decisions. Whether you are an individual investor or a professional, mutual funds a clear grasp of these concepts helps align investment strategies with your financial goals while managing risk effectively. With the right knowledge and approach, investment management can be a powerful tool to grow and preserve wealth over time.




