
- Hadoop Basics
- Hadoop Ecosystem Overview
- Installation Basics
- Configuring Core Components
- Learning Path for Beginners
- Key Use Cases
- Tools to Learn with Hadoop
- MapReduce Basics
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
- Sample Projects
- Certification Guidance
- Conclusion
Hadoop Basics
Hadoop is an open-source framework developed by the Apache Software Foundation that allows for the distributed processing of large datasets across clusters of computers using simple programming models.It is designed to scale from a single server to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage, making it a vital skill to learn in Data Science Training. Hadoop is particularly well-suited for big data applications, as it can efficiently and cost-effectively process massive volumes of both structured and unstructured data. The framework is based on the principle of breaking down large tasks into smaller pieces that are executed across nodes in a cluster. Its fault-tolerant design ensures that data is not lost even if one or several nodes fail, making it a preferred solution for enterprises dealing with big data challenges.
Hadoop Ecosystem Overview
The Hadoop ecosystem includes a variety of tools and technologies that complement the core Hadoop modules. The primary components of the ecosystem are
- Hadoop Common: The utilities that support the other Hadoop modules.
- HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System): A distributed file system that stores data across multiple machines.
- YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): Manages and schedules computing resources in clusters.
- MapReduce: A programming model for processing large datasets.
“In addition to these core modules, the ecosystem includes tools like Hive (data warehousing), Pig (data flow scripting), HBase (NoSQL database), Sqoop (data import/export), Flume (log data collection), and Oozie (workflow scheduler), which, along with Apache Storm Instruction enhance the overall capability of the big data ecosystem. Together, these tools provide a comprehensive platform for processing, analyzing, and storing big data.
Installation Basics
Hadoop must be installed on a single-node server for testing or on a multi-node cluster for production settings before you can start utilising it. The machine should have enough RAM and disc space, be Linux-based (such as Ubuntu or CentOS), and have Java installed. First, go to the official Apache Hadoop website and download the most recent stable version of Hadoop.
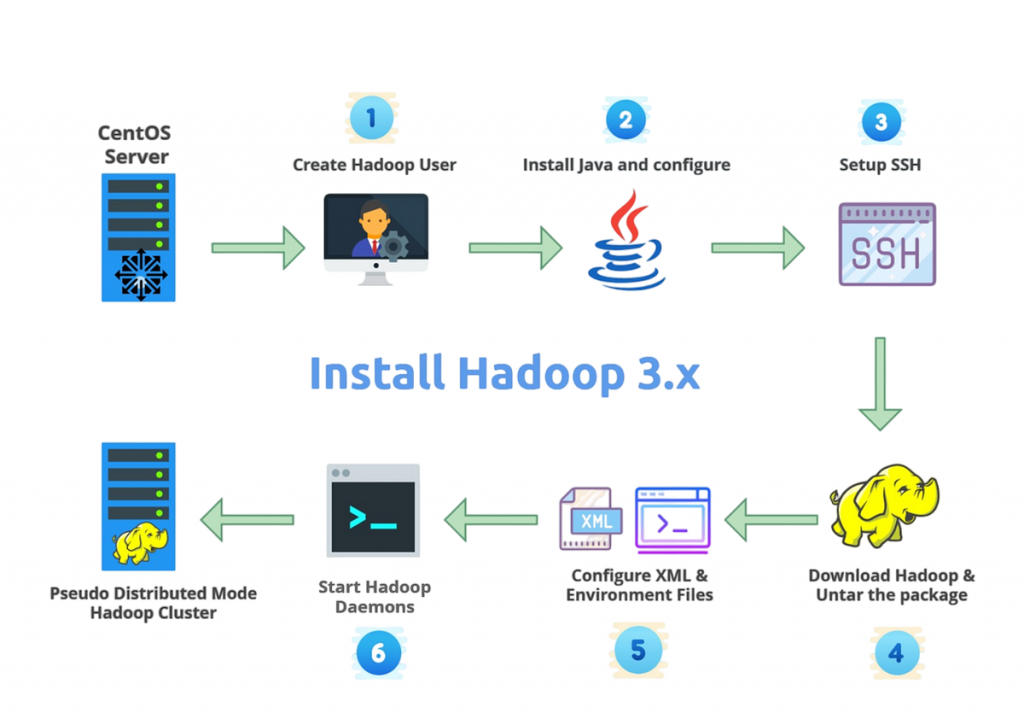
Once the files have been downloaded, unzip them and set up important environment variables like JAVA_HOME and HADOOP_HOME. Setting up SSH access is necessary even for a single-node setup because Hadoop needs SSH for node-to-node communication, a concept also emphasized in Cassandra Online Training For Next Gen Computing for understanding secure distributed environments. The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) should then be initialised by formatting the Namenode using the hdfs namenode -format command. Lastly, launch the file system and resource management components by starting the Hadoop services with the start-dfs.sh and start-yarn.sh scripts. Hadoop also offers Docker images and virtual machines (VMs) for faster deployment, particularly for testing and learning.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Configuring Core Components
The proper configuration of Hadoop is crucial for its efficient functioning. Key configuration files include:
- core-site.xml: Contains configuration settings for Hadoop Core, such as the default filesystem.
- hdfs-site.xml: Used to configure HDFS-specific settings like replication factor and Namenode/Datanode directories.
- mapred-site.xml:Contains MapReduce job configurations, including job history and the execution framework, making it a vital part of The New Black Now Is Hadoop ecosystem for efficient big data processing.
- yarn-site.xml: Specifies YARN resource management settings, including node manager resources and scheduler options.
Fine-tuning these settings helps Hadoop perform efficiently under varying loads and use cases. For production clusters, configuring memory allocations, replication factors, and block sizes is essential for optimized storage and performance.
To Explore Data Science in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Data Science Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Learning Path for Beginners
A planned learning route is crucial for novices wishing to learn Hadoop. Learn about the fundamentals of big data, including its traits, difficulties, and the necessity of Hadoop. Because Hadoop is Java-based and runs on Linux, learn the fundamentals of both Java programming and Linux commands. After that, practice setting up Hadoop on your local machine in pseudo-distributed mode to familiarise yourself with its components and configuration, which can later support projects like Market Basket Analysis for data-driven insights. Explore HDFS and MapReduce to learn about data processing and storage. After you’re at ease, practice using ecosystem tools like Hive, Pig, and HBase. Use MapReduce or Hive queries to create sample projects utilising real-world datasets to put your abilities to use. In order to comprehend scalability and performance, move on to deploying Hadoop on a multi-node cluster. This systematic learning process can be further supported by platforms such as edX, Udemy, and Coursera.
Tools to Learn with Hadoop
The Hadoop ecosystem is vast. Beginners should prioritize the following tools:
- Hive: A SQL-like querying language built on Hadoop, allowing users to run analytical queries.
- Pig: A scripting platform for exploring and analyzing large datasets.
- HBase: A NoSQL database that allows real-time read/write access to big data.
- Sqoop: Used for transferring data between Hadoop and relational databases.
- Flume: For collecting, aggregating, and moving large amounts of log data.
- Oozie: A workflow scheduler that helps manage Hadoop jobs.
- Zookeeper: Provides coordination services for distributed applications.
These tools simplify data ingestion, processing, storage, and job scheduling in Hadoop workflows, complementing enterprise solutions like IBM Big Data InfoSphere for efficient data management.
MapReduce Basics
MapReduce is a programming model in Hadoop that enables the processing of large datasets using a distributed algorithm across a cluster.
- Map Phase: The input data is split and mapped into key-value pairs.
- Shuffle and Sort:The data is grouped based on keys and sorted before the reduce phase, which can later support Data Visualization in Zepline for better analytical representation of results.
- Reduce Phase: Aggregates the key-value pairs and produces the final output.
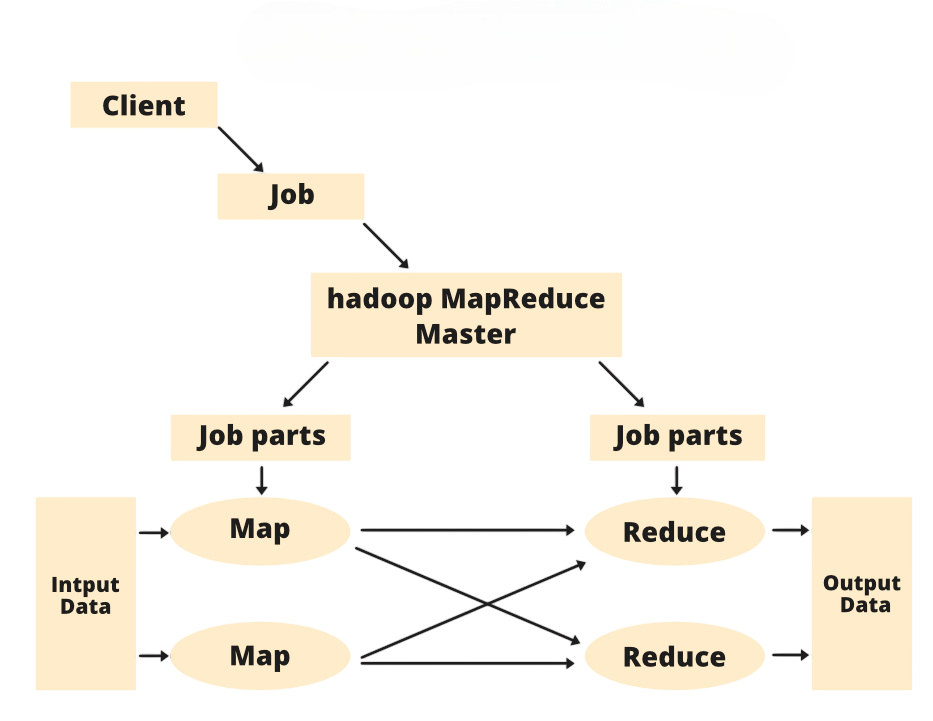
For example, in a word count program, the map function reads the input text and emits word and count pairs (e.g., “Hadoop,” 1), and the reduce function aggregates these counts to output the total frequency of each word. Understanding MapReduce is foundational for Hadoop and is often the first programming exercise for learners.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science Training by Enrolling in Our Data Science Master Program Training Course Now!
Key Use Cases
Hadoop is versatile and is used across various industries for different use cases:
- Retail and E-commerce: Companies like Amazon and Walmart utilize Hadoop to analyze customer behavior, manage inventory, and make product recommendations.
- Banking and Finance: Hadoop is employed for fraud detection, risk analysis, and real-time trading.
- Healthcare: Hospitals use Hadoop to process electronic medical records (EMRs) and genomic data for diagnosis and research.
- Telecommunications: Providers use Hadoop to analyze call records and improve network performance.
- Government and Public Sector: Governments leverage Hadoop for large-scale data analysis in areas such as census and tax fraud detection.
These use cases highlight Hadoop’s flexibility and ability to manage large, complex datasets across sectors, making it a valuable tool to explore in Data Science Training .
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
HDFS is the primary storage system of Hadoop. It splits large files into blocks (typically 128 MB or 256 MB) and distributes them across nodes in a cluster, which is often compared in discussions of BI vs Data Science to understand the different approaches to data processing and analysis. Key components of HDFS include
- Namenode: Manages the metadata and directory structure of HDFS.
- Datanode: Stores the actual data blocks on physical hardware.
- Secondary Namenode: Assists in checkpointing and reducing the load on the primary Namenode.
HDFS ensures data redundancy through replication (the default is three copies) and is therefore fault-tolerant. It is optimized for high-throughput and batch processing, making it ideal for storing and analyzing massive datasets.
Are You Preparing for Data Science Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Science Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Sample Projects
Project work is essential for hands-on Hadoop learning. Developing a Word Count programme, a straightforward MapReduce project to count word frequencies in a text file, is one of the beginner-friendly projects. Another approach is retail sales analysis, which uses Hive to examine sales patterns in retail datasets. With a Log File Analyser project, students can use Flume to gather and analyse web server logs. Twitter Sentiment Analysis is a social media analytics technique that uses Hadoop and Pig or Hive to analyze tweets, facilitating a Data Analytics Collabration to gain insights from large-scale social media data. Additionally, developing a movie recommendation system with collaborative filtering on movie datasets offers practical expertise with real-world data. In addition to strengthening theoretical understanding, these projects help students get ready for real-world data difficulties.
Certification Guidance
Earning a Hadoop certification validates your skills and boosts your job prospects. Popular certifications include
- Cloudera Certified Associate (CCA)-Data Analyst/Administrator.
- Hortonworks Certified Associate (HCA) – Now part of Cloudera.
- MapR Certified Hadoop Developer/Administrator.
- Microsoft Azure HDInsight Certification.
- Google Cloud Certified – Professional Data Engineer (includes Hadoop-related components).
When preparing for these certifications, focus on practical exercises and mock tests, and use official documentation and course material from respective vendors.
Conclusion
Hadoop remains a foundational technology in the big data landscape, and learning it provides a solid stepping stone for advanced data engineering and analytics roles. By understanding its architecture, installing and configuring it properly, and exploring its ecosystem tools and use cases, beginners can build a strong foundation. Certification and hands-on projects, combined with Data Science Training further validate skills and prepare learners for rewarding careers in data. Whether you’re a student, developer, or data enthusiast, mastering Hadoop opens up numerous career opportunities in data science, analytics, and engineering. Stay curious, keep building, and leverage the power of Hadoop to solve real-world data challenges.


