
- Hadoop Clusters
- Single Node vs Multi-Node Setup
- Hadoop Installation Prerequisites
- Setting Up HDFS
- Configuring YARN
- DataNode and NameNode Configuration
- Networking and SSH Setup
- Conclusion
Hadoop Clusters
Hadoop clusters are collections of computers, known as nodes, that work together to store and process massive amounts of data in a distributed computing environment. These clusters form the core of Hadoop’s ability to handle big data workloads efficiently and reliably. By distributing data and tasks across multiple machines, Hadoop clusters ensure both fault tolerance and scalability.Hadoop clusters are primarily composed of two types of nodes: master nodes, which manage and coordinate tasks Data Science Training, and worker nodes, which store data and perform computations. Understanding how to set up and manage a Hadoop cluster is essential for any big data engineer or data scientist aiming to work in enterprise-level data environments DataNode and NameNode. Hadoop clusters are collections of computers working together to store and process large datasets using the Hadoop framework. They use a distributed computing model, with data spread across nodes for fault tolerance and scalability. Key components include HDFS for storage and MapReduce or YARN for processing and resource management.
Single Node vs Multi-Node Setup
Single Node Setup
- All Hadoop daemons run on a single machine.
- Suitable for development, testing, and learning.
- No data distribution or real parallel processing.
- Limited storage and computing capacity An ETL Audit Process .
- No fault tolerance if the node fails, the system stops.
- Easy to install and manage.
- Hadoop daemons are distributed across multiple machines.
- Ideal for production environments and large datasets.
- Enables real parallel processing and data distribution.
- High scalability adds more nodes as needed.
- Built-in fault tolerance and high availability.
- More complex to configure and manage.
Multi-Node Setup
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Hadoop Installation Prerequisites
BeforeHadoop Installation Prerequisites , ensure the following prerequisites are met: Operating System: Linux (Ubuntu/CentOS) is preferred.
- Java: Hadoop requires Java 8 or above.
- SSH Configuration: Password-less SSH should be configured among cluster nodes Apache Hive vs HBase Guide
- Hostname Configuration: Each node must have a static IP and a recognizable hostname.
- Sufficient Disk Space and RAM: Each node should meet the required resource threshold for HDFS and MapReduce operations.
Installing Hadoop also involves downloading the appropriate version from the Apache Hadoop website and unpacking it on all nodes.
To Explore Data Science in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Data Science Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Setting Up HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System)
HDFS is Hadoop’s primary storage system. It splits large files into blocks and distributes them across different nodes in the cluster. Elasticsearch Nested Mapping Here’s how to configure it:
- core-site.xml: Configure the default file system and temporary directories.
- hdfs-site.xml: Set replication factors, name directories for NameNode and DataNode, and permission settings.
- namenode format: Run hdfs namenode -format on the master node to format the filesystem.
- Start HDFS services: Use start-dfs.sh to launch NameNode and DataNode daemons.
Proper HDFS configuration ensures data redundancy, reliability, and fault tolerance.
Configuring YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator)
YARN manages computing resources in Hadoop. It separates resource management from job scheduling, enabling better scalability and performance.
- yarn-site.xml: Configure resource manager hostname, auxiliary services, and log aggregation settings.
- mapred-site.xml: Define the MapReduce framework to use YARN Data Science Training.
- Start YARN services: Use start-yarn.sh to start ResourceManager and NodeManager services.
YARN provides the abstraction layer for Hadoop jobs to efficiently use cluster resources.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science Training by Enrolling in Our Data Science Master Program Training Course Now!
DataNode and NameNode Configuration
- Stores metadata: Keeps directory tree, file names, blocks, and locations.
- Runs on Master Node: It is the central manager of HDFS.
- Highly available setup: Usually supported with standby NameNode for fault tolerance What is Splunk Rex .
- Configuration file: hdfs-site.xml – set properties like dfs.namenode.name.dir.
- High memory usage: Stores all metadata in RAM for fast access.
- Critical component: If NameNode fails (without backup), HDFS becomes inaccessible.
- Stores actual data: Saves data blocks on the local file system.
- Runs on Worker Nodes: Multiple DataNodes across the cluster.
- Reports to NameNode: Sends heartbeat and block reports regularly.
- Configuration file: hdfs-site.xml – set properties like dfs.datanode.data.dir.
- Can be scaled: More DataNodes = more storage and performance.
- Failure handling: If one fails, data is replicated from others (based on replication factor) Apache Pig.
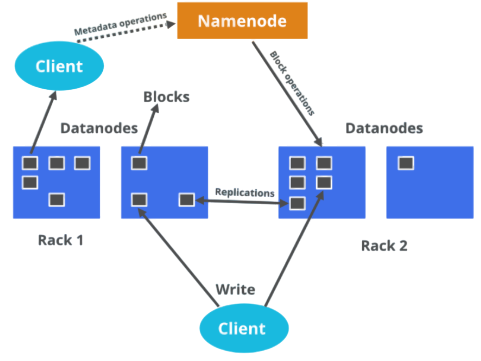
DataNode Configuration
Are You Preparing for Data Science Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Science Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Networking and SSH Setup
In a Hadoop cluster, proper networking and SSH setup are essential for seamless communication between nodes. All nodes must be connected through a reliable network and assigned static IP addresses or hostnames, which are typically defined in the /etc/hosts file for name resolution. Secure Shell (SSH) is used for remote access and to allow the Hadoop master node (usually the NameNode)What is Azure Data Lake to execute commands on slave nodes (DataNodes) without requiring a password. This is achieved by generating an SSH key pair on the master node and copying the public key to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file of each slave node. Ensuring password-less SSH access is a key step in automating the Hadoop daemon startup across the cluster. SSH ensures Hadoop scripts can remotely start and manage services across nodes.
Conclusion
Setting up and managing a Hadoop cluster involves several moving parts from proper configuration and resource allocation to ensuring robust networking and security protocols. While the initial setup can seem complex, understanding each component’s role makes it manageable and scalable. Once configured, a Hadoop cluster empowers businesses to derive insights from petabytes of data, making it a cornerstone of modern big data analytics. Whether you’re a systems administrator or a data engineer Data Science Training, mastering Hadoop cluster management is a valuable skill for the data-driven world. Understanding the roles of DataNode and NameNode, choosing between single-node and multi-node setups, and ensuring proper SSH and network configurations are crucial for a stable and scalable system. A well-configured Hadoop cluster enables efficient, Single Node distributed processing of big data, making it a powerful tool for modern data-driven applications.


