
- Data Management Challenges Today
- Introduction to Apache Hadoop
- How Hadoop Transforms Data Handling
- Key Components of Hadoop
- Big Data Analytics with Hadoop
- Integration with Other Technologies
- Real-Life Enterprise Case Studies
- Hadoop for Business Intelligence
- Virtual Training Features
- Skills Gained
- Summary
Data Management Challenges Today
In the modern digital era, organizations generate data at an unprecedented scale ranging from social media interactions and IoT sensors to e-commerce transactions and real-time business operations. Traditional data management systems struggle to handle the volume, velocity, and variety of big data. Issues such as storage limitations, slow processing, lack of scalability, and high costs plague conventional systems. To overcome these challenges and build scalable solutions, explore Data Science Training a hands-on program that teaches learners how to work with distributed frameworks, optimize performance, and unlock insights from complex datasets. As data complexity increases, so does the demand for a robust, scalable, and fault-tolerant framework. Enter Apache Hadoop, a game-changer in how businesses store, process, and derive insights from data.
Introduction to Apache Hadoop
Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework developed to support the processing of large data sets in a distributed computing environment. Originally inspired by Google’s MapReduce and Google File System (GFS) papers, Hadoop was created by Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella and later adopted by the Apache Software Foundation. To understand the hurdles faced in deploying such large-scale systems—and how to overcome them—explore Big Data Challenges With Solutions a practical guide that outlines common pain points in big data environments and offers proven strategies for scalability, security, and performance optimization. It enables organizations to store massive amounts of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data and process it efficiently across clusters of computers. Its distributed architecture, fault tolerance, and scalability make it the go-to solution for big data processing.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
How Hadoop Transforms Data Handling
Decentralized Data Management: Hadoop transforms away from traditional centralized systems to a decentralized model for data storage and processing. To understand how different processing engines operate within this framework, explore Spark vs MapReduce a side-by-side comparison that highlights their execution models, speed, fault tolerance, and suitability for batch versus real-time analytics.
- Horizontal Scalability: Unlike relational databases that need larger machines, Hadoop scales horizontally by adding more nodes to the cluster. This approach improves cost-effectiveness.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Using commodity hardware for scaling makes Hadoop a budget-friendly option for managing large amounts of data.
- Data Locality Principle: Hadoop processes data where it is stored, which reduces network congestion and boosts overall performance.
- Versatile Data Handling: It can manage vast amounts of data, including petabytes of clickstream data and unstructured text files.
- Transformative Data Utilization: Hadoop changes how we manage, store, and use data, making it an important part of modern data strategies.
- HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System): This is the storage layer of Hadoop. It stores data in blocks across multiple nodes and maintains replication to ensure fault tolerance.
- MapReduce: The original processing engine of Hadoop, MapReduce allows for parallel processing of large data sets. It divides tasks into smaller sub-tasks (Map) and then aggregates results (Reduce).
- YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): This is Hadoop’s cluster management system. It manages resources and schedules tasks across the cluster, enhancing Hadoop’s flexibility.
- Common Utilities: These include Java libraries and APIs that support the other modules and facilitate seamless operation within the Hadoop ecosystem.
- Facebook: Uses Hadoop to process petabytes of user data to improve advertising algorithms and user experience.
- Yahoo!: One of the earliest adopters of Hadoop, Yahoo! uses it for search indexing and advertising analytics.
- Spotify: Leverages Hadoop to process streaming data and provide personalized music recommendations.
- Bank of America: Uses Hadoop to analyze customer transactions and detect fraud in real time.
- NASA: Utilizes Hadoop for satellite data analysis and large-scale image processing.
- Live Instructor-Led Classes: Interactive sessions with industry experts.
- Self-Paced Modules: Pre-recorded lectures and hands-on labs.
- Cloud Lab Access: Practice Hadoop commands and tools in a simulated real-world environment.
- Capstone Projects: Real-life projects to build practical skills.
- Assignments and Quizzes: Reinforce learning through exercises.
- Community Support: Discussion forums and peer-to-peer learning.
- Understanding of big data architecture and Hadoop ecosystem.
- Proficiency in HDFS, MapReduce, and YARN.
- Knowledge of data ingestion tools like Flume and Sqoop.
- Ability to analyze data using Hive, Pig, and Spark.
- Skills in job scheduling and workflow orchestration (Oozie).
- Familiarity with Hadoop security and performance tuning.
- Experience with real-world data sets and analytics use cases.
To Explore Data Science in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Data Science Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Key Components of Hadoop
Hadoop’s architecture is composed of several key modules, each serving a specific function: HDFS for storage, YARN for resource management, MapReduce for processing, and Hadoop Common for shared utilities. To understand how these components work together in a distributed environment, explore What Is a Hadoop Cluster a foundational guide that explains the structure, setup, and operational dynamics of Hadoop clusters powering big data solutions.
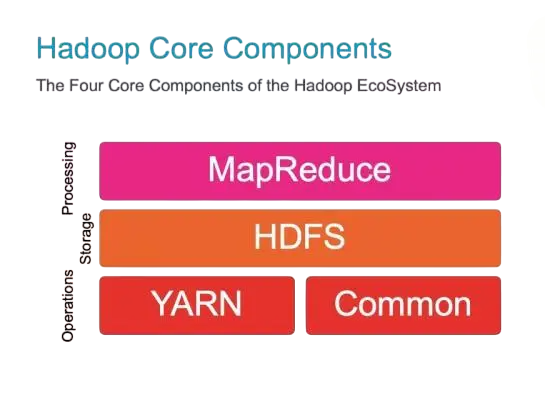
Together, these components make Hadoop a comprehensive platform for big data analytics.
Big Data Analytics with Hadoop
Hadoop empowers organizations to perform complex analytics on massive data sets that were previously impossible to manage. By distributing both data and computation, Hadoop ensures that analytics jobs are completed faster and more efficiently. Businesses use Hadoop for data mining, machine learning, predictive analytics, and statistical modeling. For instance, a retail company can use Hadoop to analyze customer purchasing patterns to optimize inventory. To gain practical experience with these techniques and tools, explore Data Science Training a hands-on course that empowers learners to build intelligent models, uncover patterns, and drive data-informed decisions across industries. A telecom company may analyze call data records to detect fraudulent activity. The power of Hadoop in big data analytics lies in its speed, flexibility, and scalability.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science Training by Enrolling in Our Data Science Master Program Training Course Now!
Integration with Other Technologies
One of Hadoop’s greatest strengths is its ability to integrate with a wide range of technologies. It seamlessly connects with data ingestion tools like Apache Flume and Sqoop, query engines like Apache Hive and Impala, and workflow management tools like Apache Oozie. Hadoop also integrates with modern data platforms such as Apache Spark, which provides in-memory processing for faster analytics. Business intelligence tools like Tableau and Power BI can be used on top of Hadoop for visualizations. To understand how data deduplication enhances accuracy in such environments, explore Dedup : Splunk Documentation a technical guide that explains how Splunk’s dedup command filters duplicate events, streamlines log analysis, and improves data clarity across enterprise systems. With cloud integration (AWS EMR, Azure HDInsight, Google Dataproc), Hadoop becomes even more powerful and accessible.
Are You Preparing for Data Science Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Science Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Real-Life Enterprise Case Studies
Hadoop has been successfully adopted by major enterprises across various industries:
These case studies reflect the transformative impact of Hadoop on business performance, customer engagement, and operational efficiency.
Hadoop for Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence (BI) involves converting raw data into actionable insights. Hadoop’s ability to handle diverse and large-scale datasets makes it a powerful backend for BI. Traditional BI systems rely on structured data, but modern BI needs access to semi-structured and unstructured sources like emails, web logs, and social media. To understand how these diverse data types are efficiently moved and transformed across systems, explore What is Data Pipelining a foundational guide that explains the architecture, tools, and best practices behind building scalable, automated data workflows. Hadoop fills this gap by enabling comprehensive data ingestion and processing. Through integration with Hive or Impala, users can run SQL-like queries on massive datasets. BI dashboards built on Hadoop enable data-driven decisions in marketing, operations, HR, and finance departments.
Virtual Training Features
Learning Hadoop has become easier thanks to the availability of high-quality online training platforms. Virtual Hadoop training includes hands-on labs, real-time data ingestion, and log analysis exercises. To deepen your understanding of log parsing and field extraction, explore What is Splunk Rex a focused guide that explains how the Rex command uses regular expressions to extract fields from event data, enabling more precise and actionable insights.
These features make it possible to become proficient in Hadoop from the comfort of your home.
Skills Gained
Completing a Hadoop training program equips learners with the following skills: building distributed systems, managing large-scale data ingestion, and performing advanced analytics using tools like Hive, Pig, and Spark. To extend these capabilities into cloud-native environments, explore What is Azure Data Lake a comprehensive guide that explains how Microsoft’s scalable storage and analytics service supports big data workloads with enterprise-grade security and performance.
These competencies are highly valued across industries that depend on data analytics and big data platforms.
Summary
Apache Hadoop has revolutionized the world of data management. By enabling distributed storage and parallel processing, it overcomes the limitations of traditional systems. Its robust architecture, integration capabilities, and ability to handle all types of data make it a top choice for enterprises seeking to unlock the full potential of big data. To gain hands-on experience with these technologies and build a future-proof career, explore Data Science Training a comprehensive program that covers Hadoop, Spark, machine learning, and real-world analytics workflows. With rising global demand for data professionals, mastering Hadoop is not only a strategic career move but a future-proof investment. Whether you are an aspiring data engineer, a seasoned analyst, or a decision-maker, Hadoop empowers you to harness data in ways never imagined before.


