
- Introduction: The Need for Distributed Search
- What is Apache Solr?
- Introduction to SolrCloud
- Why Use SolrCloud?
- SolrCloud Architecture Explained
- Core Components in SolrCloud
- Key Features of SolrCloud
- Use Cases of SolrCloud in the Real World
- SolrCloud vs Standalone Solr vs Elasticsearch
- Conclusion: The Future of SolrCloud in Enterprise Search
Introduction: The Need for Distributed Search
With the explosion of data in recent years, organizations need robust systems not only to store information but also to retrieve it quickly and accurately. Traditional relational databases, while reliable for structured data, are not optimized for full-text search or complex query capabilities across massive datasets. As businesses moved toward big data architectures, the demand grew for scalable, fault-tolerant, and intelligent search engines. Apache Solr emerged as a strong solution for enterprise-grade search, built on top of Apache Lucene, and is often covered in a comprehensive Data Science course due to its importance in handling large-scale search and analytics. However, when it came to scaling out horizontally and distributing search capabilities across data centers or cloud environments, SolrCloud became the go-to architectural model. Apache SolrCloud is a powerful distributed search system designed to handle large-scale, real-time search needs in enterprise environments. As a distributed search system, it provides high availability, fault tolerance, and horizontal scalability by distributing data across multiple nodes. The architecture of this distributed search system relies on components like ZooKeeper to manage coordination and ensure seamless operation. With its robust features, SolrCloud remains a leading distributed search system for organizations requiring reliable and scalable search solutions.
What is Apache Solr?
Apache Solr is an open-source, high-performance search platform based on the Apache Lucene library. It is designed for handling full-text search, faceted search, filtering, distributed indexing, and real-time querying.Solr supports advanced features like geospatial search, hit highlighting, rich document parsing, and result ranking, complementing skills gained in courses like Understanding Apache Storm for handling real-time data processing.
- Apache SolrCloud is a leading solution for High Availability Search, ensuring that search services remain operational even during node failures.
- Its design prioritizes High Availability Search through features like replication, failover, and load balancing across multiple nodes.
It exposes a REST-like API and provides powerful query capabilities through Solr Query Language (SolrQL). Used by major companies like Netflix, Zappos, and Instagram, Solr is the backbone of many modern enterprise search engines. While Solr is powerful on its own, scaling it for massive amounts of data, user queries, and geographic distribution required a more dynamic and robust solution hence, SolrCloud was born.
Do You Want to Learn More About Data Science? Get Info From Our Data Science Course Training Today!
Introduction to SolrCloud
SolrCloud is a distributed version of Apache Solr that adds support for horizontal scalability, fault tolerance, and centralized configuration management. In SolrCloud, multiple Solr instances called nodes are connected together in a cluster. This cluster shares a common configuration and automatically handles data distribution, replication, and failover. SolrCloud allows you to split your search index into multiple shards and replicas, distributing them across the nodes of the cluster, which highlights concepts similar to those discussed in Why Learn R Programming? for efficient data management and analysis. This ensures that queries are executed in parallel and data remains available even if individual nodes fail. The system uses Apache ZooKeeper for coordination and cluster management, ensuring consistency and operational awareness across the distributed environment. In essence, SolrCloud brings cloud-native features to Solr, making it ideal for production environments where uptime, speed, and scalability are mission-critical.
Would You Like to Know More About Data Science? Sign Up For Our Data Science Course Training Now!
Why Use SolrCloud?
There are several compelling reasons to adopt SolrCloud, especially when dealing with enterprise-level data and high query volumes.
- High Availability: SolrCloud provides replication and failover support, ensuring that your search application remains online even during node failures.
- Horizontal Scalability: By distributing index shards across multiple nodes, SolrCloud can handle increased load by simply adding more servers.
- Automatic Failover: If a node goes down, SolrCloud reassigns responsibilities to other nodes without requiring manual intervention, a concept also covered in the Guide to Apache Ambari for Hadoop Administration for managing cluster reliability.
- Centralized Configuration: With ZooKeeper, configuration files can be managed centrally, reducing the risk of inconsistency between nodes.
- Load Balancing: SolrCloud distributes both read and write operations across the cluster, optimizing performance and resource usage.
- Easy Cluster Expansion: Adding new nodes or increasing capacity can be done dynamically, without downtime.
- Nodes: Individual instances of Solr running on servers. Each node can serve multiple cores or collections.
- Collections: Logical indexes made up of multiple shards, similar to a database table.
- Shards: Subsets of a collection. Each shard holds a portion of the data and can be distributed across different nodes.
- Replicas: Copies of shards for redundancy. There are different types—NRT (Near Real-Time), TLOG (Transaction Log), and PULL replicas which are often explained in a Data Science course focused on distributed search systems.
- ZooKeeper Ensemble: A ZooKeeper Ensemble is a group of ZooKeeper servers that work together to manage distributed systems reliably. For high availability, the ZooKeeper Ensemble must have a majority of servers (a quorum) running to maintain consensus and ensure fault tolerance.
- Leaders: Each shard has a leader responsible for coordinating indexing operations and keeping replicas in sync.
- Router: Determines which shard should store or query a document based on routing rules.
- Distributed Indexing: Automatically splits large datasets across shards, enabling faster indexing and searching.
- Dynamic Cluster Scaling: Easily add or remove nodes without disrupting the service.
- Fault Tolerance and High Availability: Built-in replication ensures data is not lost during hardware or node failures.
- Near Real-Time Search: Offers low latency for indexing and querying, even in large environments.
- Centralized Configuration Management: Reduces administrative overhead by syncing configurations across the cluster via ZooKeeper.
- Flexible Replica Types: Use different replica types to balance write performance, durability, and resource usage, similar to improvements highlighted in Special Features of New Hadoop 3.0
- Shard Splitting: Collections can be split dynamically to accommodate data growth without reindexing the entire dataset.
- Document Routing and Smart Partitioning: Custom routing rules help maintain even distribution and minimize query times.
- Cross-Data Center Replication: Supports geo-distributed deployments with automatic replication between data centers.
- SolrCloud vs Standalone Solr: Standalone Solr works well for smaller projects or single-node applications, but it lacks built-in support for distributed indexing, replication, and fault tolerance. SolrCloud is designed for high availability and scale, automatically handling sharding and load balancing.
- SolrCloud vs Elasticsearch: Elasticsearch is often seen as more developer-friendly and integrates easily with the Elastic Stack (Kibana, Beats, Logstash). However, SolrCloud is known for more advanced search capabilities like rich text parsing, better relevancy tuning, and complex query handling. SolrCloud uses ZooKeeper for coordination, while Elasticsearch has its own cluster management built-in.
These features make SolrCloud suitable for use in large-scale, high-availability environments such as e-commerce sites, digital libraries, news aggregators, and SaaS platforms.
SolrCloud Architecture Explained
SolrCloud is designed around a set of nodes that collectively manage and serve a distributed index. Each node in the SolrCloud cluster can host one or more cores, which are the basic units of indexing and searching. The cluster is divided into collections, which are logical groupings of documents. Each collection is subdivided into shards, and each shard can have multiple replicas for redundancy and load distribution.This article provides a comprehensive overview of SolrCloud Architecture Explained, detailing how SolrCloud enables scalable, fault-tolerant distributed search. By focusing on SolrCloud Architecture Explained, readers gain insights into key components like shards, replicas, and ZooKeeper coordination.
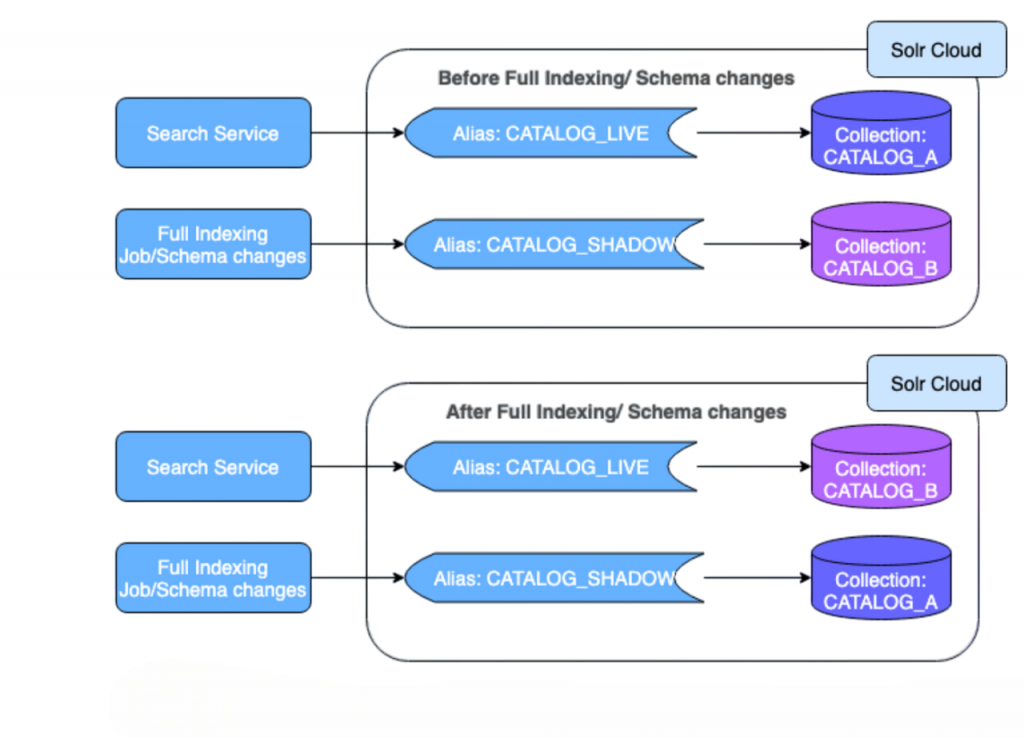
The role of Apache ZooKeeper in this architecture is vital. It maintains the state of the cluster, manages the configuration files, keeps track of live nodes, and performs leader elections. Apache SolrCloud is a leading solution for High Availability Search, ensuring that search services remain operational even during node failures. Its design prioritizes High Availability Search through features like replication, failover, and load balancing across multiple nodes. ZooKeeper enables nodes to communicate and coordinate changes without manual orchestration, a key concept often emphasized in Cloudera Certification.When a document is added to a collection, SolrCloud decides which shard and which replica should receive the data. Queries are also distributed across shards, and the results are merged and returned to the client seamlessly.This architecture ensures that data and queries are handled efficiently across the cluster, while also offering built-in fault tolerance and dynamic scaling.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science Training by Enrolling in Our Big Data Analytics Master Program Training Course Now!
Core Components in SolrCloud
Understanding the essential components of SolrCloud helps clarify how the system operates:
These components work together to provide a seamless and resilient distributed search platform that scales with your needs.
Preparing for Data Science Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer To Acte Your Interview!
Key Features of SolrCloud
SolrCloud offers a wide range of features that make it a strong choice for distributed search environments:
These features make SolrCloud an enterprise-ready solution for any organization needing scalable and reliable search functionality.
Use Cases of SolrCloud in the Real World
SolrCloud is used across various industries and applications due to its robustness and scalability. In e-commerce, companies use SolrCloud to power product search, filters, and recommendation engines that serve millions of users daily. Digital publishers leverage SolrCloud to provide fast and contextual content retrieval, even as their archives grow to millions of articles. Financial services firms use it to index and search transaction records, customer profiles, and regulatory documents. Healthcare platforms rely on SolrCloud to search through electronic medical records, lab results, and medical literature. Government portals and legal systems also employ SolrCloud to make public records and legal documentation searchable and accessible. Its combination of real-time performance, fault tolerance, and flexible deployment options make it ideal for any large-scale search application requiring reliability and speed, topics often explored in discussions like Data Science vs Data Analytics vs Big Data.
SolrCloud vs Standalone Solr vs Elasticsearch
When deciding on a search solution, it’s important to understand the differences between SolrCloud, standalone Solr, and Elasticsearch.
Ultimately, the choice depends on specific requirements. SolrCloud is preferred in enterprise contexts where customization, query precision, and scalability are essential.
Conclusion: The Future of SolrCloud in Enterprise Search
Apache SolrCloud stands as a mature, flexible, and powerful solution for distributed search needs in modern enterprises. Its design enables it to scale horizontally with ease while offering high availability, fault tolerance, and rich search features out of the box. SolrCloud is especially valuable in environments where the dataset is vast, user queries are complex, and uptime is non-negotiable, making it a key topic in many advanced Data Science course. As data continues to grow and businesses seek more intelligent and scalable search solutions, SolrCloud is poised to remain a cornerstone technology in digital transformation strategies. Whether deployed on-premises, in hybrid setups, or on the cloud, SolrCloud offers the reliability and depth needed for next-generation search applications.


