
- Introduction: The Real-Time Data Imperative
- Why Use Apache Ambari?
- Prerequisites for Deploying Ambari
- Preparing the Hadoop Cluster Environment
- Installing Ambari Server
- Installing and Configuring Ambari Agents
- Launching the Ambari Web UI
- Using Ambari to Deploy Hadoop Services
- Conclusion
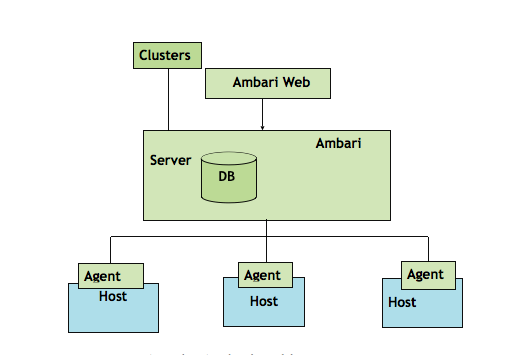
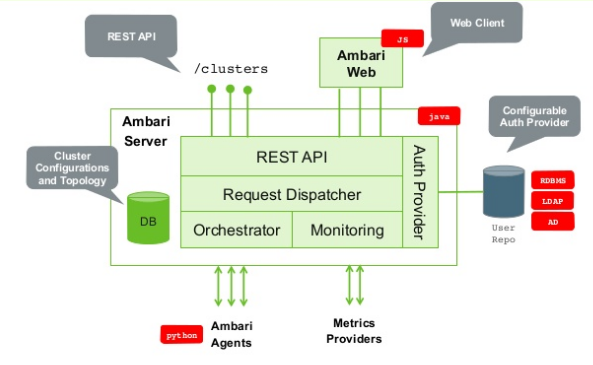
Introduction to Ambari and Its Role in Hadoop
An open-source management tool called Apache Ambari was created to make Apache Hadoop cluster provisioning, configuration, monitoring, and maintenance easier. It offers comprehensive tools, RESTful APIs, and an intuitive web interface to assist system administrators in effectively managing the whole Hadoop environment. Ambari is essential to simplifying and facilitating Hadoop cluster management, Data Science Training particularly in large-scale settings. Administrators may manage services like HDFS, YARN, Hive, and Spark, check metrics like CPU use and disk space, and carry out standard operations like starting, stopping, and restarting services all through its user-friendly dashboard. Ambari’s automation is one of its main advantages. By managing software installation and configuration across all cluster nodes, it expedites the setup procedure. Additionally, it interfaces with other tools for performance optimization and alerts, and it enables role-based access control. Ambari essentially acts as Hadoop clusters’ primary control panel, lowering the technical obstacles and operational Scala Certification overhead typically involved with large data infrastructure management. Because of this, it is a crucial tool for businesses looking to manage scalable, robust, and closely watched Hadoop deployments.
Why Use Apache Ambari?
Before diving into the deployment steps, it’s crucial to understand why Ambari is widely used.
Key Benefits of Apache Ambari:
- Simplified Cluster Setup: Easy installation of Hadoop and its ecosystem tools using a GUI.
- Centralized Monitoring: Real-time health checks, alerts, and metrics from across the cluster.
- Configuration Management: Edit and propagate configuration changes with ease.
- User Management: Spark SQL Integrates with Kerberos and LDAP for authentication and role-based access.
- RESTful APIs: Automate operations like adding nodes, starting services, or collecting metrics.
- Service Lifecycle Management: Easily start, stop, and restart Hadoop services. For administrators and DevOps professionals, Ambari streamlines tasks that would otherwise require manual SSH logins, configuration edits, and command-line tools.
Do You Want to Learn More About Data Science? Get Info From Our Data Science Course Training Today!
Prerequisites for Deploying Ambari
Before deploying Apache Ambari, certain prerequisites must be met to ensure a smooth and successful installation. First, you need a supported operating system—typically CentOS, RHEL, or Ubuntu with all nodes in the Hadoop cluster running the same OS version. Proper network configuration is essential; all hosts should have consistent DNS resolution, static IPs, and be able to communicate with each other using SSH. Ambari requires a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for each host. Additionally, passwordless SSH access must Data Science Training be enabled from the Ambari server to all cluster nodes. You’ll also need to install Java (JDK 8 or later, depending on the Ambari version) and set appropriate environment variables. A supported database (like PostgreSQL or MySQL) is required to store Ambari metadata. Finally, ensure your system has adequate memory, disk space, and CPU resources to handle the demands of Ambari and the Hadoop services it will manage.
Would You Like to Know More About Data Science? Sign Up For Our Data Science Course Training Now!
Preparing the Hadoop Cluster Environment
Before deploying Apache Ambari, certain prerequisites must be met to ensure a smooth and successful installation. First, you need a supported operating system, typically CentOS, RHEL, or Ubuntu with all nodes in the Hadoop cluster running the same OS version. Proper network configuration is essential; all hosts should have consistent DNS resolution, static IPs, and be able to communicate with each other using SSH. Ambari requires a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for each host. Additionally, passwordless SSH access must be enabled Data Architect Salary from the Ambari server to all cluster nodes. You’ll also need to install Java (JDK 8 or later, depending on the Ambari version) and set appropriate environment variables. A supported database (like PostgreSQL or MySQL) is required to store Ambari metadata. Finally, ensure your system has adequate memory, disk space, and CPU resources to handle the demands of Ambari and the Hadoop services it will manage.
Installing Ambari Server
Prepare the System
- Ensure supported OS (e.g., CentOS/RHEL/Ubuntu) is installed.
- Set hostname, FQDN, and update /etc/hosts.
- Disable SELinux and firewall (or configure ports).
- Download the Ambari repository file from the official Apache site Kafka vs RabbitMQ .
- Place it in the system’s repository directory (e.g., /etc/yum.repos.d/ for RHEL/CentOS).
- Run: sudo yum install ambari-server (or apt-get for Ubuntu).
- Run: ambari-server setup
- Choose JDK version, database type (default is PostgreSQL), and other configurations during setup.
- Run: ambari-server start
- Open browser and go to: http://
:8080 - Login with default credentials: admin / admin
- Follow the step-by-step wizard to add hosts, install Hadoop services,Apache Hive vs HBase Guide and configure the cluster.
- Ensure hostnames, FQDNs, and SSH access from Ambari Server are properly set.
- Download and configure the Ambari repository on each agent node Apache Spark Certification.
- Install Ambari Agent using yum install ambari-agent or apt-get install ambari-agent.
- Edit /etc/ambari-agent/conf/ambari-agent.ini to set the Ambari Server’s hostname.
- Start the Ambari Agent service with ambari-agent start.
- Verify agent connection in the Ambari Server Web UI during cluster setup.
- Start/Stop Services: Use Ambari to control HDFS, YARN, and other services.
- Monitor Metrics: View real-time CPU, memory, HDFS usage, job execution times.
- Alerts & Health Checks: Configure alerts for disk space, service failures, and node issues What is Azure Data Lake .
- Add Nodes or Services: Dynamically scale your cluster without manual reconfiguration.
- Configuration Management: Version control, update configs, rollback to previous states.
Install and Configure the Ambari Repository
Install Ambari Server Package
Set Up Ambari Server
Start Ambari Server
Access Ambari Web UI
Begin Cluster Installation Using the Web UI
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science Training by Enrolling in Our Big Data Analytics Master Program Training Course Now!
Installing and Configuring Ambari Agents
Preparing for Data Science Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer To Acte Your Interview!
Launching the Ambari Web UI
Once the Ambari Server is installed and running, you can access the Ambari Web User Interface (UI) through a web browser. By default, the UI is available at port 8080 on the Ambari Server host. To launch it, open your browser and enter the URL in the format: http://
Using Ambari to Deploy Hadoop Services
Ambari allows service lifecycle management directly from the UI.
After Cluster Setup:
Ambari simplifies even the most complex operations, ensuring administrators have full visibility and control.
Conclusion
Deploying Apache Ambari on a Hadoop cluster is a strategic decision that saves time, reduces complexity, and improves manageability. With its intuitive UI, powerful REST APIs, Role in Hadoop and robust monitoring, Ambari transforms Hadoop from a set of individual services into a cohesive and efficient ecosystem Data Science Training. From installation and configuration to scaling and troubleshooting, MySQL, Ambari supports every stage of the Hadoop lifecycle. Whether you’re building your first big data platform or managing a multi-node enterprise cluster, Apache Ambari is your go-to solution for managing Hadoop at scale.


