- Introduction to Apache Pig
- Pig Latin Language Basics
- Data Flow Model
- Use Cases and Advantages
- Installation and Setup
- Pig vs Hive
- Running Pig Scripts
- Pig Execution Modes
- Built-In Functions
- Summary
Introduction to Apache Pig
Apache Pig is a high-level platform developed to simplify the processing and analysis of large datasets in the Hadoop ecosystem. It is especially useful for handling unstructured and semi-structured data. Pig enables users to create complex data transformations using a scripting language called Pig Latin, which is designed to be intuitive and easy to learn for developers and data analysts. Data Analytics Training introduces learners to Pig Latin and other essential tools building the skills needed to design modular workflows and perform scalable data preprocessing in Hadoop environments. Apache Pig was developed at Yahoo! to enable better productivity and efficiency in analyzing huge datasets. Pig scripts are executed over the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and are converted into MapReduce jobs under the hood. This abstraction saves developers from writing extensive MapReduce code, offering a quicker and more manageable approach to processing data.
Pig Latin Language Basics
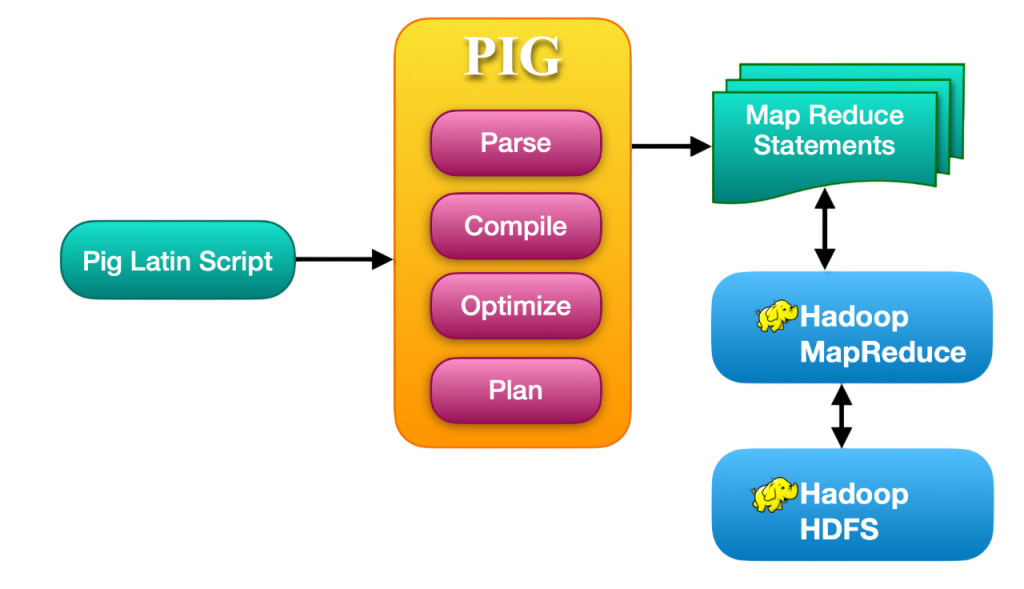
Pig Latin is the scripting language used in Apache Pig. It is designed to provide a simple interface for programmers to perform data manipulation tasks. Pig Latin commands follow a procedural data flow style and can include operations like LOAD, FILTER, JOIN, FOREACH, and GROUP. These operations are foundational in distributed data environments. Big Data & Hadoop explains how platforms like Hadoop empower such workflows enabling scalable storage, parallel processing, and seamless integration with scripting languages like Pig. These commands allow for the transformation and manipulation of large data sets in a concise and readable manner. Pig Latin abstracts the complexity of underlying MapReduce programming, allowing developers to focus more on the logic of data transformation.
Example:
- data = LOAD ‘input.txt’ USING PigStorage(‘,’) AS (name:chararray, age:int);
- filtered_data = FILTER data BY age > 25;
- DUMP filtered_data;
In this example, the data is loaded from a CSV file, filtered based on age, and the resulting data is printed. Pig Latin’s syntax is flexible and designed to resemble SQL, making it relatively easy to adopt for those familiar with database languages.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Analyst Certificate? View The Data Analytics Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Data Flow Model
The data flow model in Pig consists of a series of transformations applied to input data. Each transformation step produces a new relation (dataset), which is passed onto the next step. This approach is modular and supports logical and physical planning stages before translating the operations into MapReduce jobs.
To maximize business impact from such architectures, How Big Data Can Help You explores how data-driven strategies unlock insights, optimize workflows, and drive smarter decisions across industries. The logical plan includes a list of operators applied to the data, while the physical plan determines how these operators are executed using MapReduce. This two-tiered planning enables optimization and efficient execution of data flow model workflows.
To Explore Data Analyst in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Data Analytics Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Use Cases and Advantages
Use Cases:
- Log data processing.
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines.
- Ad-hoc data analysis.
- Data preparation for machine learning.
- Clickstream analysis.
- Web crawling and indexing.
Advantages:
- Simplifies complex data operations.
- Handles both structured and unstructured data.
- Faster development and iteration.
- Supports parallel execution on Hadoop.
- Easily integrates with other Hadoop components.
- Reduces lines of code compared to traditional MapReduce.
Pig is especially useful when dealing with large volumes of raw data that require heavy preprocessing. Its ability to process data in a step-by-step manner allows for better debugging and modular design. Data Analytics Training introduces learners to tools like Pig highlighting their role in scalable data workflows and preparing professionals to build efficient, fault-tolerant pipelines in big data environments.
Installation and Setup
To install Apache Pig:
- Download the Pig binary from the official Apache website.
- Extract the files to a directory.
- Set environment variables like PIG_HOME and update the PATH.
- Run Pig using the command: pig for Grunt shell or pig -x local for local mode.
Pig can be run in local mode for small datasets and in MapReduce mode for large-scale processing. For distributed processing, Pig should be configured with a working Hadoop environment.
System Requirements:
- Java installed (Java 1.8 or higher)
- Hadoop installed and running (for MapReduce mode)
- 2 GB RAM minimum for small scale usage
Once configured, developers can begin writing and testing scripts directly in the Grunt shell, which provides an interactive interface.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Analyst Training by Enrolling in Our Data Analyst Master Program Training Course Now!
Pig vs Hive
| Feature | Apache Pig | Apache Hive |
|---|---|---|
| Language | Pig Latin | HiveQL (SQL-like) |
| Paradigm | Procedural | Declarative |
| Flexibility | High (programmatic) | Moderate (SQL-style) |
| Learning Curve | Easy for programmers | Easy for SQL users |
| Use Case | ETL, scripting tasks | Data querying/reporting |
| Custom Functions | Easily supported | Limited |
While both tools serve similar purposes, they cater to different user groups. Hive is ideal for analysts familiar with SQL, while Pig is preferred by engineers who are comfortable with scripting.
Are You Preparing for Data Analyst Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Analyst Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Running Pig Scripts
Pig scripts are written in .pig files and can be executed in two main ways: through the Grunt shell for interactive processing or via batch execution for automated workflows. To turn these scripting skills into a career advantage, How to Become a Big Data Analyst outlines the essential tools, learning paths, and industry expectations that help professionals transition from hands-on coding to strategic data analysis roles.
- Grunt Shell: Interactive shell for line-by-line execution.
- Batch Mode: Run complete scripts using the command pig script.pig.
Example Pig Script:
- A = LOAD ‘data.txt’ USING PigStorage(‘,’) AS (id:int, name:chararray);
- B = FILTER A BY id > 10;
- C = FOREACH B GENERATE name;
- DUMP C;
This script loads data, filters based on a condition, and generates a result set with selected fields. Scripts can include UDFs (User Defined Functions), which extend Pig’s capabilities using Java, Python, or other languages.
Pig Execution Modes
- Local Mode: Runs on a single JVM and uses the local file system. Best for testing and small data.
- MapReduce Mode: Default mode that translates Pig scripts into MapReduce jobs executed on Hadoop clusters.
In local mode, no Hadoop installation is required, whereas MapReduce mode requires a working Hadoop cluster. Developers can switch between modes using command-line options or script headers. To understand how such architectures scale in real-world applications, How Facebook is Using Big Data reveals how the platform leverages distributed processing to personalize content, optimize ad delivery, and analyze user behavior at massive scale.
Built-In Functions
Pig provides a wide range of built-in functions (BIFs) for string manipulation, mathematical operations, date handling, and more. To effectively use these capabilities in distributed environments, Skills Needed to Learn Hadoop outlines the foundational knowledge required covering scripting proficiency, data flow logic, and familiarity with ecosystem tools like Pig, Hive, and HDFS.
- UPPER(): Converts strings to uppercase
- SUBSTRING(): Extracts substring from strings
- AVG(), MAX(), MIN(): Aggregate functions
- TOKENIZE(): Tokenizes strings into words
- CONCAT(), TRIM(), REPLACE(): String functions
- IS_EMPTY(): Checks if a value is null or empty
Developers can also define their own functions using Java, Python (Jython), or other languages compatible with Pig.
Summary
Apache Pig provides a simplified scripting interface for analyzing large datasets using Hadoop. With its procedural language, Pig Latin, and support for parallel execution, it accelerates the development of data workflows and simplifies big data processing. Despite some limitations, it remains a powerful tool for ETL operations, log analysis, and data preprocessing tasks. Pig is an excellent entry point for developers seeking to work with large-scale data and understand the Hadoop ecosystem. As part of a modern big data architecture, it continues to play a role in batch processing pipelines, especially in legacy systems where it is already entrenched. Data Analytics Training introduces these foundational tools helping learners grasp their role in scalable architectures and legacy workflows while preparing for more advanced platforms. As technology evolves, understanding Pig offers foundational insight into the development of more advanced and interactive frameworks like Apache Spark, Flink, and Beam.


