
- Introduction: The Real-Time Data Imperative
- What is Apache Storm?
- The Origins and Evolution of Storm
- How Apache Storm Works
- Apache Storm Architecture
- Core Concepts: Spouts, Bolts, and Topologies
- Key Features of Apache Storm
- Use Cases of Storm in the Real World
- Conclusion
Introduction: The Real-Time Data Imperative
In today’s fast-moving digital landscape, the value of data lies not just in its volume but in the speed at which it can be processed and acted upon. Traditional batch processing systems are effective for retrospective analytics, but they fall short when businesses require real-time decision-making such as fraud detection, system monitoring, live dashboards, or user personalization. This growing demand for low-latency, high-throughput streaming systems has given rise to technologies that specialize Data Science Training in real-time data stream processing. Among the pioneers of this movement is Apache Storm, a distributed framework that allows for real-time computation over unbounded streams of data. It paved the way for building scalable, fault-tolerant stream processing applications capable of handling billions of events daily. In today’s fast-paced digital world, real-time data has become essential for timely decision-making and operational efficiency. Organizations rely on instant insights to stay competitive, respond to market changes, and enhance customer experiences. Embracing real-time data is no longer optional; it’s a strategic imperative for success across industries.
What is Apache Storm?
Apache Storm is a free and open-source distributed real-time computation system. It is designed to process unbounded streams of data—those that continuously flow in, like website clickstreams, sensor outputs, or social media feeds—rather than static datasets. Storm enables users to define topologies made up of data sources and processing steps, which are executed continuously Scala Certification and concurrently across a cluster of machines. The system supports parallel processing, guaranteed message processing, and horizontal scalability, making it suitable for building real-time analytics applications.
Written primarily in Clojure and Java, Storm integrates well with other big data systems like Apache Kafka, Hadoop, and databases, and it is known for being lightweight, resilient, and simple to deploy. Apache Storm is a distributed, real-time computation system designed for processing large streams of data with low latency. It enables developers to build applications that can process unbounded data in real time Spark SQL , making it ideal for use cases like fraud detection, real-time analytics, and monitoring systems. Storm uses a topology-based architecture, where data flows through spouts (data sources) and bolts (processing units). It is scalable, fault-tolerant, and integrates well with big data ecosystems like Apache Kafka and Hadoop. With its high throughput and reliability, Apache Storm is a powerful tool for real-time stream processing in modern data-driven applications.
Do You Want to Learn More About Data Science? Get Info From Our Data Science Course Training Today!
The Origins and Evolution of Storm
- Created by Nathan Marz: Originally developed at BackType, a social media analytics company.
- Twitter Acquisition: Twitter acquired BackType in 2011 and open-sourced Storm to the community.
- Apache Incubation: Entered the Apache Incubator in 2013 to foster community development and governance.
- Top-Level Apache Project: Graduated to a top-level Apache project in 2014 due to its growing popularity and stability Apache Pig.
- Active Development: Over time, Storm added features like improved fault tolerance, multi-language support, and better resource management.
- Integration: Evolved to integrate smoothly with technologies like Apache Kafka, Hadoop, and various NoSQL databases.
- Used Across Industries: Adopted widely for real-time analytics, log processing, monitoring, and more.
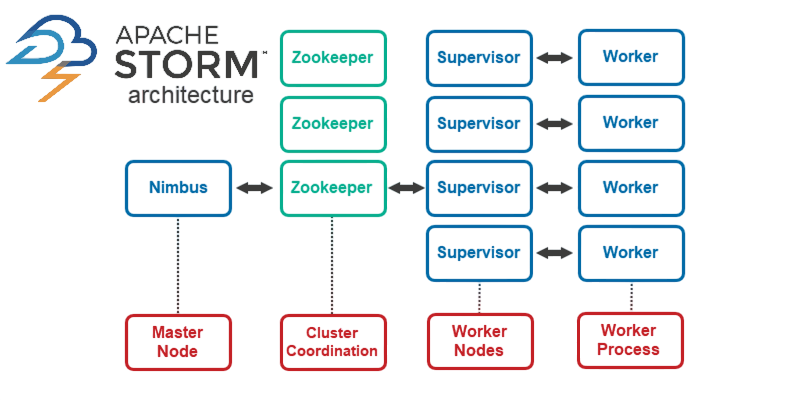
- Nimbus: This is the master node responsible for distributing code, assigning tasks to worker nodes, and monitoring task execution. It is analogous to Hadoop’s JobTracker.
- Supervisor: These run on worker nodes and manage the execution of assigned tasks. They listen to Nimbus for work assignments and start/stop processes accordingly.
- Worker Processes: Each worker process executes a subset of a topology’s tasks. Big Data Career Path It can run one or more executors.
- Executors: These are threads within a worker process that run tasks associated with bolts or spouts.
- Tasks: The actual units of execution—each bolt or spout is broken down into tasks, allowing fine-grained parallelism.
- ZooKeeper: Storm uses Apache ZooKeeper to manage coordination between Nimbus and Supervisors and to track the state of topologies.
- Spouts: These are sources of streams in a Storm topology. A spout reads data from external systems like Apache Kafka, Redis, RabbitMQ, or sockets. It emits streams of tuples into the system.
- Bolts: These are the processing units. Bolts can perform operations such as filtering, joining, Big Data Analytics aggregating, or writing to databases. They can also emit new tuples to other bolts.
- Tuple: The basic data unit in Storm. A tuple is an ordered list of elements that a spout emits and a bolt processes.
- Stream: An unbounded sequence of tuples.
- Topology: The overall graph of computation. It defines how spouts and bolts are connected and how data flows between them. Topologies run indefinitely (unlike Hadoop jobs, which terminate).
- Real-Time Processing: Storm processes data as it arrives, ensuring minimal latency and enabling real-time insights.
- Scalability: Easily scales horizontally by adding more worker nodes and increasing parallelism.
- Fault Tolerance: Storm reassigns failed tasks to other workers and ensures that no tuple is lost.
- Reliable Message Processing: Career in Big Data Analytics Guarantees at-least-once processing. You can achieve exactly-once semantics with external coordination.
- Multi-Language Support: Developers can write spouts and bolts in Java, Python, Ruby, or any language using Storm’s multi-language protocol.
- Flexible Topologies: Allows the construction of complex, custom processing pipelines tailored to specific workflows.
- Easy Integration: Works well with Kafka, HDFS, NoSQL databases, RDBMSs, and cloud storage solutions.
- Backpressure Support: Controls flow by slowing down producers when consumers can’t keep up.
- Pluggable Messaging: You can configure custom message serializers and transport mechanisms.
- Real-Time Analytics: Data Architect Salary Online retailers use Storm to generate live dashboards showing user behavior, sales, and inventory status.
- Fraud Detection: Financial institutions analyze transaction streams in real time to identify fraudulent activity as it happens.
- Monitoring Systems: IT departments use Storm to process logs and metrics for real-time alerting and anomaly detection.
- Recommendation Engines: Media platforms and e-commerce websites use Storm to generate dynamic content or product recommendations based on user behavior.
- Ad-Click Stream Analysis: Digital advertising firms monitor and analyze user clicks to optimize bidding and ad placement.
- IoT Data Processing: Storm can handle real-time sensor data from connected devices to power smart home or industrial applications.
- Social Media Sentiment Analysis: Companies monitor brand mentions in real time Cassandra Keyspace to gauge public opinion and respond quickly.
Would You Like to Know More About Data Science? Sign Up For Our Data Science Course Training Now!
How Apache Storm Works
Apache Storm processes streams of data in a distributed, parallel fashion. When data enters the system, it is broken into tuples, essentially records of data which then flow through a user-defined topology. A topology defines how the data should be processed, transformed, aggregated, and routed. The processing pipeline consists of two main components: spouts and bolts. Spouts are responsible for reading or receiving the input data streams (such as Kafka topics or HTTP feeds), and bolts perform computation on that data like filtering, enriching, counting, or storing. The topology runs continuously, with each tuple traversing the path defined Data Science Training by the topology graph. Storm executes these operations across multiple worker nodes in a cluster, enabling parallelism and scalability. Messages are acknowledged at each stage, big data and if a failure is detected, Storm will replay the tuple to ensure data integrity and processing reliability. This ability to guarantee at-least-once processing is one of Storm’s core strengths. Apache Storm processes real-time data streams using a topology composed of spouts and bolts. Spouts act as data sources, while bolts perform processing tasks like filtering, aggregation, or transformation. The system distributes tasks across a cluster, enabling scalable, fault-tolerant, and low-latency stream processing for continuous, real-time data analytics.
Apache Storm Architecture
Apache Storm’s architecture is composed of various components that work together to enable scalable and fault-tolerant stream processing:
This architecture is highly modular, enabling fault tolerance, scalability, and real-time processing of high-throughput data.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science Training by Enrolling in Our Big Data Analytics Master Program Training Course Now!
Core Concepts: Spouts, Bolts, and Topologies
Understanding Storm’s basic processing model is crucial for building effective topologies:
Each of these components can be scaled independently by defining the level of parallelism at which they operate.
Preparing for Data Science Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer To Acte Your Interview!
Key Features of Apache Storm
Key Features of Apache Storm offers a number of features that make it suitable for production-grade real-time processing:
These features help organizations implement robust and reliable real-time data processing solutions with Storm.
Use Cases of Storm in the Real World
Apache Storm has been widely adopted across industries due to its ability to process data in real time.
Common use cases include:
These applications demonstrate Storm’s versatility and reliability in mission-critical environments. Storm is best when immediate processing is needed, while batch systems are better suited for offline data aggregation and reporting.
Conclusion
Apache Storm remains a powerful, scalable, and reliable platform for real-time data stream processing. Its ability to process data at low latency, scale horizontally, and recover gracefully from failures makes it a strong candidate for mission-critical applications in any industry. Although newer systems like Apache Flink and Kafka Streams offer more integrated processing models or richer APIs,Data Science Training Storm continues to be favored in production environments where performance, flexibility, and reliability are paramount. As the demand for streaming analytics grows in sectors like fintech, telecom, IoT, and AI, Apache Storm,Apache Storm Architecture will likely retain its place as a foundational tool for real-time computation, especially in architectures that value modularity and robustness.


