
- What is Big Data?
- Origins and Evolution
- 5 V’s of Big Data
- Milestones in Big Data Development
- From RDBMS to Distributed Systems
- Key Technologies (Hadoop, Spark, etc.)
- Industry Adoption
- Success Stories
- Future Outlook
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to extremely large datasets that are difficult to manage, process, and analyze using traditional data processing tools. These datasets are generated from various sources such as social media platforms, sensors, business transactions, mobile devices, and the internet of things (IoT). The key attributes of Big Data include its volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value. With advanced analytics and powerful computing capabilities, Big Data enables organizations to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and insights that lead to more informed decisions Big Data Training and strategic advantages. Big Data refers to extremely large and complex datasets that are difficult to manage, process, or analyze using traditional data processing tools. It is characterized by the 5 V’s: Volume (vast amounts of data), Velocity (fast data generation), Variety (different data types), Veracity (data accuracy), and Value (insights derived). Big Data comes from sources like social media, sensors, devices, and online transactions. Businesses and organizations use Big Data analytics to uncover patterns, trends, and associations, enabling better decision-making, innovation, and competitive advantage. Technologies like Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases are commonly used to handle and analyze Big Data.
Origins and Evolution
The origins of Big Data can be traced back to the early 2000s when the digital revolution began generating data at unprecedented rates. Before that, data was mostly structured and could be stored and queried using relational database management systems (RDBMS). As data grew in complexity and volume, traditional systems became inadequate. In 2001, Doug Laney introduced the three V’s Volume, Velocity, and Variety to describe data growth challenges. This led to the Big Data Analysis development of new tools like Apache Hadoop in 2005, which allowed distributed storage and processing. Over time, technologies like Spark, Kafka, and NoSQL databases emerged, shaping the current Big Data landscape. Big Data originated from the growing need to handle massive volumes of data generated by digital technologies. Initially used in scientific research and business intelligence, it evolved with advancements in storage, processing power, and tools like Hadoop and Spark. Today, it drives decision-making across industries, transforming how data is utilized.
Do You Want to Learn More About Big Data Analytics? Get Info From Our Big Data Course Training Today!
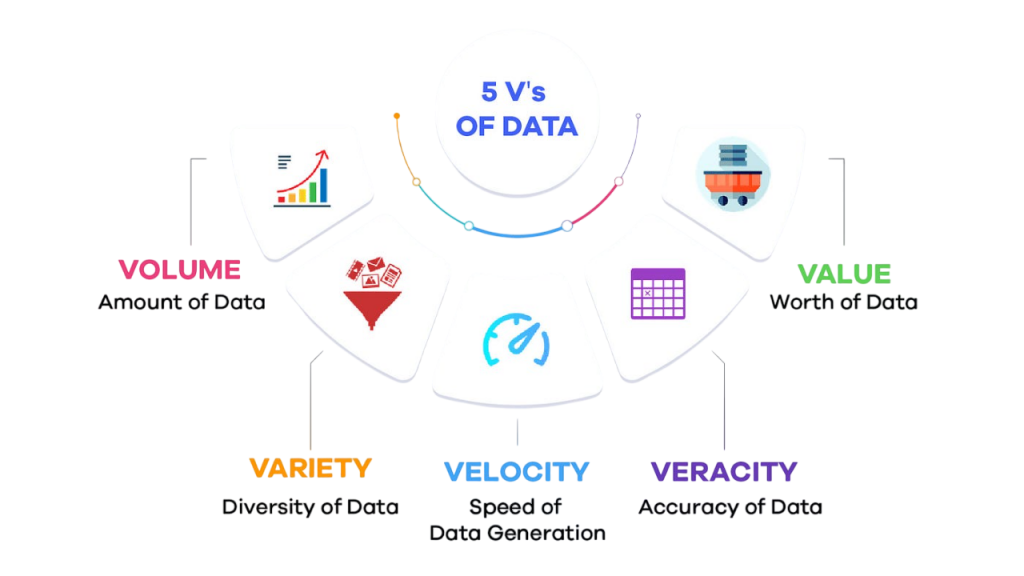
5 V’s of Big Data
- Volume – Refers to the sheer amount of data generated daily from various sources such as transactions, emails, videos, sensors, and more.
- Velocity – The speed at which data is generated, transmitted, and processed. Real-time analytics have become a necessity Big Data Career Path .
- Variety – Includes different forms of data: structured (databases), semi-structured (XML, JSON), and unstructured (images, text, video).
- Veracity – Indicates the reliability and accuracy of data. Inconsistent or low-quality data can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Value – The insights derived from Big Data that help organizations make better decisions, create new products, and improve services.
Milestones in Big Data Development
- 2001: Doug Laney introduces the 3 V’s model.
- 2004: Google publishes the MapReduce paper, laying the foundation for distributed computing.
- 2005: Launch of Hadoop, an open-source project inspired by Google’s work.
- 2008: Apache Hive and Pig are introduced to simplify Hadoop querying Career in Big Data Analytics .
- 2010: Spark is released to enable in-memory processing and faster data analytics.
- 2014: Kafka becomes the go-to platform for streaming data.
- 2020 and beyond: Real-time analytics, AI integration, and cloud-native solutions dominate the Big Data space.
- Apache Hadoop: Offers distributed storage (HDFS) and batch processing (MapReduce).
- Apache Spark: Performs in-memory data processing for faster analytics, machine learning, and streaming.
- Apache Kafka: A robust platform for handling real-time data feeds.
- NoSQL Databases: Such as MongoDB, Big Data Can Help You Do Wonders Cassandra, and HBase for scalable data storage.
- Apache Hive and Pig: High-level languages for querying large datasets.
- Elasticsearch: Used for full-text search and log analytics.
- Flume and Sqoop: For data ingestion from different sources.
- Healthcare: For genomics, disease prediction, and personalized treatment.
- Retail: Personalized recommendations, dynamic pricing, and inventory management.
- Banking & Finance: Fraud detection, credit scoring, and algorithmic trading.
- Telecommunications: Customer churn prediction and network optimization BFSI Sector Big Data Insights .
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization.
- Government: Crime analytics, smart city planning, and policy formulation.
- Netflix: Leverages viewing history and behavioral data to make personalized recommendations and decide on new content.
- Amazon: Uses Big Data for inventory forecasting, pricing, customer service, and product recommendations Data Analytics Tools for Big Data Analysis .
- Facebook: Analyzes user behavior and interactions to improve engagement and target ads.
- UPS: Optimized delivery routes using sensor data and analytics, saving millions in fuel costs.
Would You Like to Know More About Big Data? Sign Up For Our Big Data Analytics Course Training Now!
From RDBMS to Distributed Systems
Traditional relational databases were built for structured data and lacked the scalability to handle the diverse and voluminous datasets generated today. This limitation led to the rise of distributed systems like Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and Apache Cassandra, which enabled horizontal scaling and fault tolerance. Instead of relying on a single machine, data is stored and processed across multiple nodes Big Data Training, increasing reliability and speed. This shift not only solved storage issues but also allowed for real-time analytics and large-scale machine learning. The shift from Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) to distributed systems marks a significant evolution in data management. Traditional RDBMS excel at handling structured data with fixed schemas but struggle with the scale and variety of modern data. Distributed systems, like Hadoop and NoSQL databases, address these challenges by spreading data across multiple nodes, enabling scalable storage and parallel processing.
Key Technologies in the Big Data Ecosystem
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Big Data Analytics Training by Enrolling in Our Big Data Analytics Master Program Training Course Now!
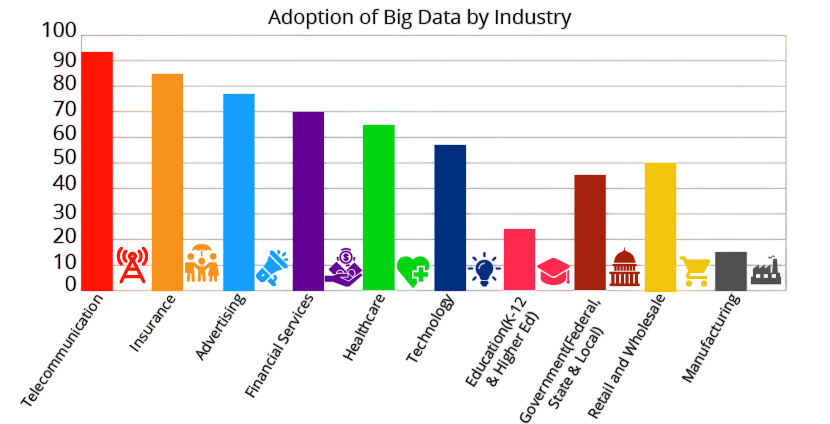
Industry Adoption
Big Data is being used across nearly every sector:
Preparing for Big Data Analytics Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Big Data Analytics Interview Questions & Answer To Ace Your Interview!
Success Stories and Case Studies
Future Outlook
In today’s data-driven world, understanding the evolution from traditional RDBMS to distributed systems is crucial. Distributed architectures like Hadoop have revolutionized how we store, process, Database and analyze massive datasets, enabling faster insights and better decision-making. Embracing these technologies allows organizations to handle diverse data types at scale, driving innovation and competitive advantage Big Data Training. As data continues to grow, mastering distributed systems will be key to unlocking its full potential and shaping the future of technology and business. As Big Data matures, so will the need for ethical considerations, transparency, Big Data Development and responsible AI. Organizations that align their data strategies with innovation and governance will lead in their respective industries.


