
- Cloudera Hadoop Admin
- Role of a Hadoop Administrator
- Setting Up and Managing Hadoop Clusters
- YARN Resource Management
- Hadoop Security Configuration
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting Clusters
- Backup and Recovery in Hadoop
- Hands-On Admin Exercises
- Cloudera Certification Guide
- Summary
Cloudera Hadoop Admin
With the explosion of data across industries, the need for scalable, distributed data processing frameworks has become more crucial than ever. Hadoop, an open-source framework developed by the Apache Software Foundation, has emerged as a key solution to handle Big Data. Cloudera, one of the leading commercial providers of Hadoop, offers an enterprise ready distribution of Hadoop, along with management tools, support, and training as part of its broader Data Science course offerings. The Cloudera Hadoop Administrator course is specifically designed for professionals responsible for the operation and maintenance of Hadoop clusters. It covers a range of administrative tasks, including installation, configuration, monitoring, tuning, and security. This training equips learners with the practical skills required to manage large-scale data processing systems and ensure their stability, security, and performance.
Role of a Hadoop Administrator
A Hadoop Administrator plays a vital role in managing and maintaining a Hadoop infrastructure. Their responsibilities include deploying new Hadoop clusters, maintaining existing systems, ensuring high availability, and overseeing the day-to-day operations of the cluster.
- Hadoop Admins must handle user access, manage file permissions, schedule data processing jobs, and coordinate with developers and data engineers.
- They also play a key part in security implementation, performance tuning, resource allocation, backup management, and troubleshooting.
- As organizations increasingly adopt data-driven strategies, the demand for skilled Hadoop Administrators continues to grow, especially in sectors like finance, telecom, healthcare, and e-commerce.
- Managing a Hadoop cluster includes adding or removing nodes, balancing data distribution, scheduling jobs, and ensuring that all services are running efficiently.
- Cluster health checks, regular maintenance, and resource monitoring are integral to keeping the cluster operational, and these skills are emphasized in comprehensive Hadoop Training programs.
- Ensuring optimal hardware resource utilization (CPU, memory, and disk) across nodes is critical for consistent performance.
- The ResourceManager handles global resource scheduling, while NodeManagers manage resources on individual nodes.
- ApplicationMasters negotiate resource containers from the ResourceManager and work with NodeManagers to execute tasks.
- Hadoop Administrators configure YARN parameters to control memory allocation, CPU usage, and application queues, a key topic in Understanding Big Data.
- They also set up capacity schedulers or fair schedulers based on organizational policies to ensure efficient multi-tenant usage and workload balancing.
- It enables admins to monitor disk usage, memory consumption, CPU load, HDFS status, YARN job statistics, and more.
- Monitoring tools help detect issues like under-replicated blocks, high latency jobs, failed services, and data node failures.
- Troubleshooting involves analyzing log files, identifying root causes of errors, and applying appropriate fixes skills essential for professionals preparing for the Future of Big Data.
- Common issues may include out-of-memory errors, node unreachability, misconfigured parameters, or job failures. Proactive monitoring and log analysis ensure minimal downtime and help maintain a healthy cluster.
- Learners also practice creating and restoring HDFS snapshots, replicating data with DistCp, and interpreting logs to resolve job errors.
- Realistic scenarios help reinforce theoretical knowledge and prepare candidates for job responsibilities.
- Hands-on labs also simulate common challenges faced in production environments, helping admins build confidence and efficiency in dealing with complex tasks.
- The certification requires hands-on expertise and focuses on practical tasks rather than theoretical questions.
- Key topics covered in the exam include installation, configuration, high availability, HDFS and YARN management, security implementation, and performance tuning.
With an emphasis on the fundamental abilities needed to install, maintain, and safeguard Cloudera Hadoop clusters, the article offers a thorough review of Hadoop Administrator Training as part of a comprehensive Guide To Big Data . The Hadoop Administrator Training gives professionals practical experience to debug and optimise Hadoop settings via hands-on activities and real-world scenarios. In addition to preparing applicants for Cloudera’s CCA-131 certification, completing Hadoop Administrator Training opens up lucrative employment options in Big Data administration.
Do You Want to Learn More About Data Science? Get Info From Our Data Science Course Training Today!
Setting Up and Managing Hadoop Clusters
Setting up a Hadoop cluster involves installing and configuring various components such as HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System), YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator), and MapReduce. Cloudera Manager, a powerful administration console, simplifies the deployment and configuration of Hadoop clusters. Administrators use it to install software across nodes, manage services, and automate operational tasks.
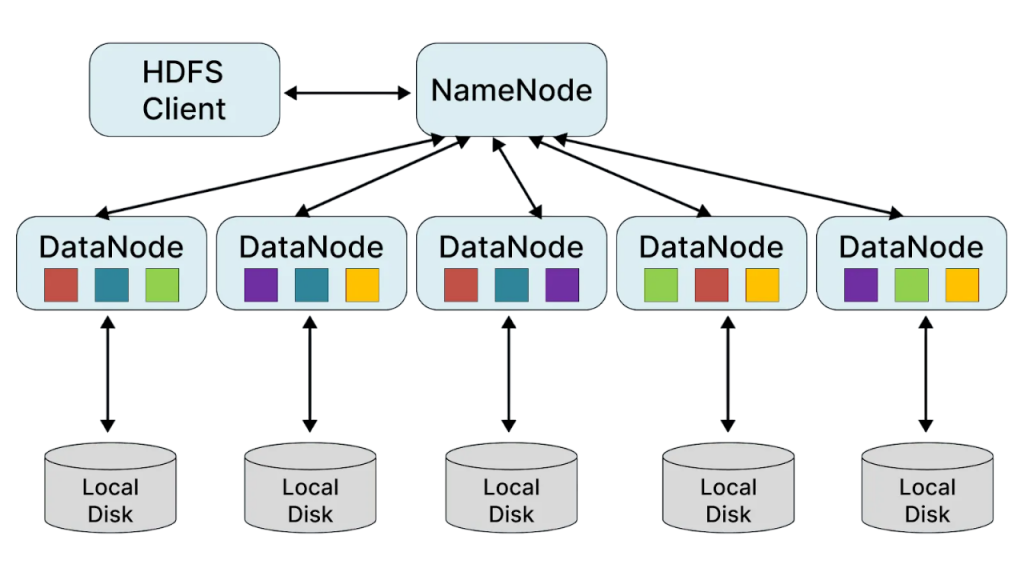
This article offers a detailed guide for professionals looking to manage Hadoop cluster environments using Cloudera’s enterprise tools. It covers key administrative tasks such as installation, configuration, security, and monitoring to efficiently manage Hadoop cluster operations. With hands-on training and certification insights, learners gain the practical knowledge required to manage Hadoop cluster infrastructure effectively, ensuring performance, scalability, and high availability in Big Data ecosystems.
Would You Like to Know More About Data Science? Sign Up For Our Data Science Course Training Now!
YARN Resource Management
YARN serves as the resource management layer of Hadoop and is responsible for job scheduling and resource allocation. It separates the resource management and job scheduling functions, enabling multiple data processing engines such as MapReduce, Spark, and Hive to run on a single Hadoop cluster. YARN consists of the ResourceManager, NodeManagers, and ApplicationMasters.
The essay explores the responsibilities of a Hadoop administrator, emphasising the use of the YARN Scheduler for resource management. It describes how workload balance, resource allocation, and job prioritisation are managed by the YARN Scheduler throughout a Hadoop cluster. Learners get practical skills to configure and optimise the YARN Scheduler for effective cluster performance and multi-tenant usage through practical training in real-world scenarios.
Hadoop Security Configuration
Securing a Hadoop cluster is crucial to protect sensitive enterprise data and comply with data governance regulations. Hadoop security configuration involves multiple layers: authentication, authorization, encryption, and auditing. Administrators implement Kerberos-based authentication to verify user identities. Apache Ranger or Sentry can be used to manage access control and permissions, topics often covered in Trending Analytics Courses. Role-based access, user groups, and fine-grained policies ensure only authorized users can perform specific actions on HDFS, Hive, or other services. Encrypting data in transit using SSL and at rest using HDFS encryption zones adds another layer of security. Auditing tools generate logs for all user and admin activities, helping organizations detect anomalies and maintain compliance. Security in Hadoop is not a one-time setup; it requires regular monitoring, patch updates, and policy reviews.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science Training by Enrolling in Our Big Data Analytics Master Program Training Course Now!
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Clusters
Monitoring a Hadoop cluster ensures that administrators are promptly alerted about performance degradation, node failures, or resource bottlenecks. Cloudera Manager offers a comprehensive dashboard that provides real-time metrics, logs, heatmaps, and alerts.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to Cloudera Hadoop Admin training, focusing heavily on effective Cluster Management. It covers critical topics like installation, configuration, monitoring, and security to help professionals master Cluster Management in real-world Big Data environments. Through hands-on labs and certification preparation, learners gain the skills required for seamless Cluster Management and long-term success in Hadoop administration roles.
Preparing for Data Science Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer To Acte Your Interview!
Backup and Recovery in Hadoop
Data integrity and availability are critical in any Big Data environment. Hadoop does not provide native backup tools, but administrators implement backup strategies using tools like DistCp (Distributed Copy), HDFS snapshots, and third-party solutions.Snapshots allow for point in time recovery of HDFS directories, making them useful during accidental deletions or corruption, a concept often covered in a Data Science course focused on Big Data management. Administrators schedule regular snapshots and ensure they are stored in secure, redundant locations. DistCp is used to replicate data between clusters, which helps in disaster recovery.
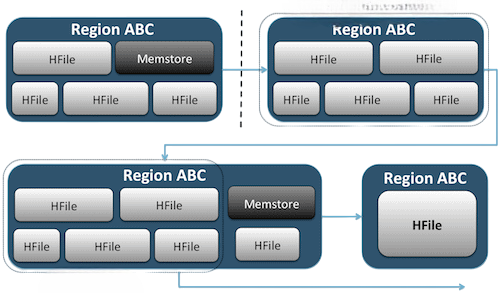
Additionally, creating metadata backups for NameNode directories and storing configuration files off-cluster ensures faster recovery. Backup and disaster recovery plans are tested periodically to ensure that data restoration processes are efficient and reliable in real scenarios.
Hands-On Admin Exercises
Hands-on practice is a crucial part of the Cloudera Hadoop Admin curriculum. Practical exercises help administrators develop real-world skills in cluster deployment, service configuration, and troubleshooting. Exercises may include installing Cloudera Manager, setting up a multi-node cluster, configuring HDFS, managing users and groups, implementing Kerberos authentication, tuning YARN settings, and simulating data failures and recoveries practical skills that pave the way for successful Big Data Careers .
The article explores the key responsibilities of a Hadoop Administrator, emphasizing the importance of performance, reliability, and data security in managing Cloudera Hadoop clusters. It highlights how administrators implement authentication, encryption, and access control measures to maintain strong data security practices. With real-world exercises and certification guidance, this training ensures professionals are well-equipped to handle complex Big Data systems while prioritizing data security at every layer.
Cloudera Certification Guide
Cloudera offers a globally recognized certification for Hadoop Administrators known as the CCA-131: Cloudera Certified Administrator for Apache Hadoop. This exam validates the candidate’s knowledge in managing and securing a Hadoop cluster using Cloudera Manager.
The exam is performance-based and conducted on a live cluster environment, covering technologies such as Solr and Hadoop. Preparation involves completing Cloudera’s official training, practicing lab exercises, and reviewing use-case-based scenarios. Achieving this certification boosts credibility, enhances career opportunities, and validates the administrator’s ability to handle real-world Hadoop operations.
Summary
The career path for Hadoop Administrators is both lucrative and evolving. Entry-level professionals typically start as Junior Hadoop Administrators or Support Engineers. With experience, they progress to roles like Senior Hadoop Administrator, Big Data Engineer, or Cloud Data Platform Engineer. Professionals may also specialize in DevOps for Big Data, Security Administration, or Data Infrastructure Architecture as part of an advanced Data Science course curriculum. The transition to cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or GCP opens further career paths, as enterprises move their Hadoop workloads to cloud-native ecosystems. Skills in Spark, Kafka, Kubernetes, and cloud storage services enhance an admin’s profile. Industries such as banking, telecom, healthcare, retail, and government sectors actively seek Hadoop Admins to manage petabyte-scale data workloads.


