
- What is Hadoop?
- Why Use Hadoop Instead of Traditional Databases?
- What is the Hadoop Ecosystem?
- What is HDFS?
- What is MapReduce?
- What is YARN and How Does it Work?
- What Languages Are Used in Hadoop?
- How is Data Stored and Processed?
- What Are the Career Opportunities in Hadoop?
- How to Learn Hadoop Effectively?
- Future Scope of Hadoop
- Conclusion
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop FAQs are essential for anyone looking to understand how this powerful framework works. Hadoop is an open-source framework developed by the Apache Software Foundation designed to handle large volumes of structured and unstructured data. It offers distributed storage (via HDFS) and distributed processing (via MapReduce). Unlike traditional databases that struggle with scalability and unstructured formats, Hadoop thrives on commodity hardware and can manage data at the petabyte scale. To master these technologies and build scalable data solutions, visit Data Science Training a hands-on course that teaches the architecture, tools, and techniques behind modern Big Data platforms. It enables organizations to store, process, and analyze data efficiently in parallel, making it an essential tool in the era of Big Data. For beginners and professionals alike, Hadoop FAQs provide clarity on core concepts, best practices, and common challenges, helping users maximize the benefits of this transformative technology.
Why Use Hadoop Instead of Traditional Databases?
Traditional databases, especially RDBMS, are optimized for transactional workloads and limited in their capacity to scale horizontally. Hadoop, on the other hand, provides the ability to process vast datasets by distributing the workload across multiple nodes. It supports semi-structured and unstructured data like logs, images, and videos, making it more versatile. To gain hands-on experience with real-time processing and in-memory computation, dive into Practice Apache Spark a project-based resource designed to help learners build scalable applications using Spark’s core components and libraries. Moreover, Hadoop’s cost-efficiency, fault tolerance, and parallel processing capabilities give it a clear advantage when managing Big Data environments.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Analyst Certificate? View The Data Analytics Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
What is the Hadoop Ecosystem?
The Hadoop ecosystem comprises multiple components and tools that extend Hadoop’s functionality: from distributed storage and parallel processing to real-time querying and data warehousing. To compare two of its most pivotal technologies, explore Apache Hive vs HBase a side-by-side breakdown of Hive’s SQL-like querying strengths versus HBase’s low-latency, NoSQL capabilities for real-time access.
- HDFS: Hadoop Distributed File System for scalable storage.
- MapReduce: Distributed processing engine.
- YARN: Resource management system.
- Hive: SQL-like querying.
- Pig: Scripting for data flow.
- HBase: NoSQL database.
- Sqoop: Data transfer between Hadoop and relational databases.
- Flume: Data ingestion from logs.
- Oozie: Workflow scheduling.
- Zookeeper: Coordination service for distributed applications.
- Spark: In-memory data processing.
These tools work together to form a robust platform for data engineering, analysis, and machine learning.
To Explore Data Analyst in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Data Analytics Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
What is HDFS?
HDFS stands for Hadoop Distributed File System. It stores large files across a cluster by splitting them into blocks (default 128MB or 256MB) and replicating each block (default 3 times) for fault tolerance. To understand how distributed databases manage logical data containers, explore Cassandra Keyspace a foundational guide that explains how keyspaces define replication strategies, organize column families, and structure data across nodes in Apache Cassandra. HDFS is optimized for high-throughput data access and designed to be fault-tolerant. Data is written once and read many times, which is ideal for analytical applications.
What is MapReduce?
MapReduce is Hadoop’s original programming model for batch data processing. It splits the job into two phases: the map phase, which filters and sorts data, and the reduce phase, which aggregates results. To master these foundational concepts and build production-grade solutions, explore Spark and Hadoop Developer a certification-focused guide that equips professionals with the skills needed to design, optimize, and deploy big data applications using Spark and Hadoop.
- Map phase: Transforms input data into intermediate key-value pairs.
- Reduce phase: Aggregates these pairs to produce final results.
MapReduce jobs can be written in Java or supported via streaming for other languages. Though slower than Spark for some tasks, MapReduce is reliable for massive batch operations.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Analyst Training by Enrolling in Our Data Analyst Master Program Training Course Now!
What is YARN and How Does it Work?
YARN, or Yet Another Resource Negotiator, changes Hadoop’s architecture by separating job scheduling and resource management from data processing components. YARN has three key parts: the ResourceManager, which allocates system resources; the NodeManager, which manages execution on individual nodes; and the ApplicationMaster, which coordinates resources and job execution for each application. To understand how these components work together in distributed computing environments, visit Data Science Training a hands-on course that explores cluster architecture, resource scheduling, and scalable data processing frameworks. This framework allows Hadoop to run multiple processing engines at once, including Spark, Tez, and MapReduce. It improves computational flexibility and performance in distributed computing environments.
Are You Preparing for Data Analyst Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Analyst Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
What Languages Are Used in Hadoop?
Hadoop’s versatility shows in its strong support for multiple programming languages. This allows developers with different backgrounds to use its powerful data processing features. Although it is primarily written in Java, Hadoop also supports Python through Hadoop streaming and PySpark, Scala for Apache Spark development, and R via Hadoop and SparkR. To understand how these diverse tools converge to extract value from massive datasets, explore Big Data Analytics a comprehensive guide that explains the principles, platforms, and techniques driving data-driven decision-making across industries. Additionally, SQL-like languages such as HiveQL, Impala, and Presto improve its flexibility. This means teams can use their preferred programming environments. This range of languages not only expands Hadoop’s use but also helps organizations fully utilize their data processing capabilities by bringing together developers with different technical skills.
How is Data Stored and Processed?
HDFS stores data in block form across distributed nodes. When a processing job (MapReduce or Spark) is submitted, Hadoop applies the principle of data locality: bringing computation to the data node. This reduces network congestion. To turn these technical foundations into professional opportunities, explore Career in Big Data Analytics a practical guide to building expertise, earning certifications, and navigating the evolving landscape of data-driven roles. The processing framework reads data blocks, performs transformation or analysis, and writes the result back to HDFS or another destination.
What Are the Career Opportunities in Hadoop?
Hadoop opens the door to various data-centric careers, including data engineering, analytics, and architecture. These roles demand proficiency in distributed processing, scripting, and data transformation. To build a strong foundation in these areas, explore Apache Pig Explained a beginner-friendly guide that demystifies Pig’s data flow language, its role in the Hadoop ecosystem, and how it simplifies complex ETL operations.
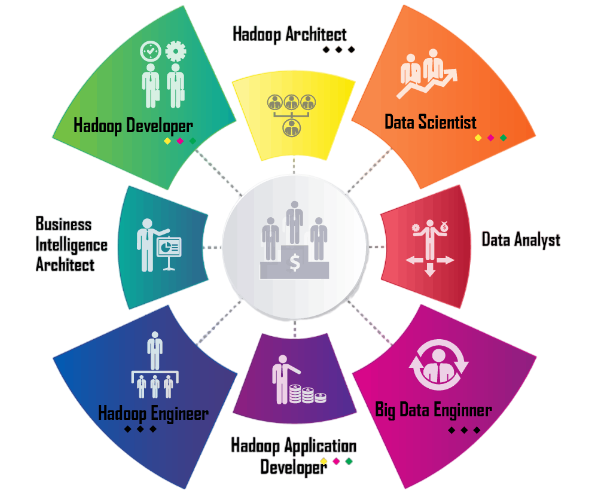
- Hadoop Developer: Develops applications using Hadoop tools.
- Big Data Engineer: Designs data pipelines and systems.
- Data Analyst: Extracts insights using Hive, Pig, or Spark.
- Hadoop Administrator: Manages cluster setup, performance, and security.
- ETL Developer: Handles data ingestion and transformations.
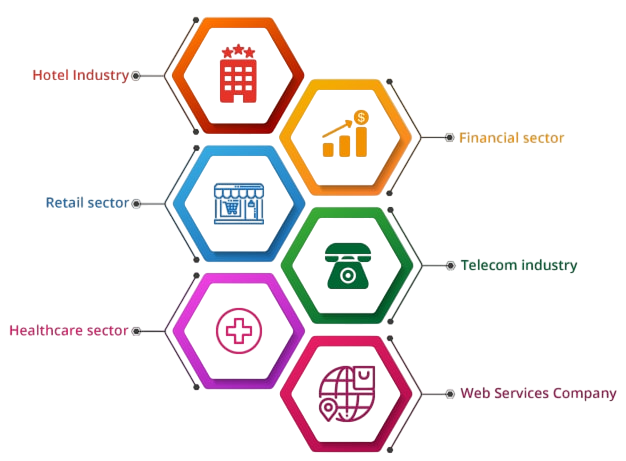
These roles exist in IT services, telecom, healthcare, banking, and retail industries, among others.
How to Learn Hadoop Effectively?
A structured learning plan is essential: it helps learners progress from foundational concepts to advanced implementations with clarity and confidence. To master query execution, schema inference, and distributed data manipulation, explore Spark SQL and the DataFrame API a hands-on guide that explains how Spark bridges relational processing with scalable, in-memory computation for big data analytics.
- Start with basics: HDFS, MapReduce, and YARN.
- Understand ecosystem tools: Hive, Pig, HBase, Spark.
- Install a local cluster or use platforms like Cloudera Quickstart.
- Practice data ingestion using Flume and Sqoop.
- Work on real-time projects: sentiment analysis, clickstream analytics.
- Get certified via Cloudera, Hortonworks, or Udacity.
- Join communities like StackOverflow, GitHub, and Reddit for support.
Future Scope of Hadoop
Despite the emergence of cloud-native platforms and modern frameworks, Hadoop still plays a foundational role in many enterprise data stacks. Its modular architecture makes it highly extensible. To see how search and indexing capabilities integrate with distributed storage, explore Solr and Hadoop a technical overview of how Apache Solr enhances Hadoop by enabling fast, scalable search across massive datasets.
Organizations continue to rely on HDFS for storage, and Hadoop can integrate with cloud services and modern tools like Kafka and Kubernetes. The rise of hybrid cloud environments ensures Hadoop skills will stay relevant.
Conclusion
Hadoop FAQs are a helpful starting point for anyone looking to understand why Hadoop is a vital part of the Big Data revolution. From its storage system (HDFS) to its processing engines (MapReduce, Spark), Hadoop empowers organizations to extract value from their massive data stores. Its open-source nature, broad ecosystem, and flexibility make it a desirable skill for data engineers and analysts. For those exploring the field, Hadoop FAQs provide answers to common questions about setup, architecture, and best practices, helping users get up to speed quickly. To build practical expertise and move beyond the basics, visit Data Science Training a hands-on course that equips learners with the tools and techniques needed to master Hadoop and other Big Data technologies. As data continues to grow, so does the demand for professionals who can manage and analyze it effectively using Hadoop. Whether you’re an aspiring developer, a system administrator, or a data scientist, Hadoop FAQs can guide your learning and career path, unlocking exciting opportunities and impactful projects in the data-driven world.


