
- Introduction to Cassandra Training
- Benefits of Virtual Learning
- Overview of Apache Cassandra
- Understanding NoSQL and Distributed Databases
- Cassandra Architecture and Components
- Data Modeling and CQL Basics
- Replication and Partitioning
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cassandra Training
Apache Cassandra has emerged as a leading NoSQL distributed database designed for managing vast amounts of data across multiple servers with no single point of failure. It is used by enterprises needing scalability, high availability, and fault tolerance. With the exponential growth of real-time data, Cassandra’s demand has skyrocketed. To address the growing need for professionals skilled in managing and leveraging Cassandra, virtual training classrooms have become an essential mode of delivery Data Science Training. These online environments offer flexibility, interactivity, Data Modeling and CQL and immersive learning experiences for both beginners and experienced professionals looking to master Cassandra. Cassandra training provides a solid foundation in managing large-scale, distributed NoSQL databases. Learn core concepts such as data modeling, CQL querying, replication, and performance optimization. This training equips you with the skills to build high-availability, fault-tolerant applications using Apache Cassandra for real-world, data-intensive environments.
Benefits of Virtual Learning
Virtual learning has redefined the way technical education is delivered. Learners no longer need to travel or adhere to fixed classroom hours. With virtual Cassandra training, participants can join from anywhere in the world, learn at their own pace, What is Data Pipelining and interact with instructors and peers through collaborative tools. Training sessions are often recorded for later review, and learners gain access to discussion forums, documentation, and virtual labs.
These features make it convenient for working professionals to upskill without compromising their job commitments. Moreover, many training platforms provide 24/7 access to learning materials, further enhancing the flexibility and depth of learning. Virtual learning offers flexibility, allowing learners to access content anytime, anywhere. It supports self-paced study, reduces travel costs, and enables access to global instructors. Interactive tools, recorded sessions, and real-time feedback enhance engagement, making virtual learning an efficient and convenient option for modern education and training.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Overview of Apache Cassandra
- Distributed NoSQL database designed for handling large amounts of data across many servers.
- Highly scalable with the ability to add nodes without downtime.
- Fault-tolerant architecture with no single point of failure.
- Supports replication for data redundancy and high availability.
- Uses CQL (Cassandra Query Language), similar to SQL for easy querying.
- Designed for high write and read throughput in real-time applications Kafka vs RabbitMQ .
- Follows a peer-to-peer decentralized model.
- Ideal for big data and IoT applications requiring continuous uptime.
- Supports eventual consistency but configurable for strong consistency.
- Open-source with a strong community and wide adoption across industries.
- NoSQL databases store and manage data differently from traditional relational databases.
- Designed to handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data.
- Support various data models: document, key-value, column-family, and graph.
- Offer horizontal scalability by distributing data across multiple servers (nodes) Data Science Training.
- Distributed databases ensure data is spread over a cluster to enhance availability and fault tolerance.
- Use replication and partitioning (sharding) to manage data distribution and redundancy.
- Prioritize performance and scalability over strict consistency (often eventual consistency).
- Ideal for big data, real-time analytics, IoT, and web-scale applications.
- Allow flexible schema designs, adapting easily to evolving data needs.
- Examples include Cassandra, MongoDB, Redis, and HBase.
- Replication creates copies of data across multiple nodes to ensure high availability and fault tolerance.
- Cassandra allows configuring the replication factor to specify how many copies of data exist.
- Partitioning distributes data across nodes using a partition key and a consistent hashing algorithm.
- Data is stored in partitions, Cassandra Keyspace enabling efficient read/write operations based on the partition key.
- Partitioning and replication together ensure scalability, load balancing, and data durability.
- Data is stored in partitions, enabling efficient read/write operations based on the partition key.
- Replication strategies include SimpleStrategy (for single data center) and NetworkTopologyStrategy (for multiple data centers).
- Partitioning and replication together ensure scalability, load balancing, and data durability.
To Explore Data Science in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Data Science Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Understanding NoSQL and Distributed Databases
Cassandra Architecture and Components
Cassandra’s architecture is based on a peer-to-peer model where all nodes are equal, and there is no master-slave relationship. Data is partitioned across nodes using a consistent hashing mechanism. The main components of Cassandra include the Node (a single machine running Cassandra), the Cluster (a collection of nodes), the Partitioner (which determines how data is distributed), the Commit Log (for durability), BFSI Reasons for Moving Into Big Data Career Memtable (an in-memory data store), and SSTables (Sorted String Tables stored on disk). Cassandra ensures high availability through replication and handles node failures seamlessly. Understanding this architecture is vital for configuring and scaling a Cassandra environment effectively. Cassandra’s architecture is decentralized and peer-to-peer, ensuring no single point of failure. Key components include nodes, data centers, and clusters. It uses a partitioner for data distribution, a commit log for durability, and SSTables for storage, enabling high availability, scalability, and fault tolerance in distributed environments.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science Training by Enrolling in Our Data Science Master Program Training Course Now!
Hands-On Data Management
Cassandra’s architecture is based on a peer-to-peer model where all nodes are equal, and there is no master-slave relationship. Data is partitioned across nodes using a consistent hashing mechanism. The main components of Cassandra include the Node (a single machine running Cassandra), the Cluster (a collection of nodes), the Partitioner (which determines how data is distributed), the Commit Log (for durability), Memtable (an in-memory data store) An ETL Audit Process , and SSTables (Sorted String Tables stored on disk). Cassandra ensures high availability through replication and handles node failures seamlessly. Understanding this architecture is vital for configuring and scaling a Cassandra environment effectively. Cassandra’s architecture is decentralized and peer-to-peer, ensuring no single point of failure. Key components include nodes, data centers, and clusters. It uses a partitioner for data distribution, a commit log for durability, and SSTables for storage, enabling high availability, scalability, and fault tolerance in distributed environments.
Data Modeling and CQL Basics
Data modeling in Cassandra is different from traditional relational databases. Rather than focusing on normalization, Cassandra models data based on queries and access patterns. The basic unit of data storage is the table, but within tables, developers must consider how partitions and clustering Apache Spark Certification columns impact performance. Cassandra Query Language (CQL) is used to interact with the database. It resembles SQL syntactically but functions differently. For instance, joins and subqueries are not supported in CQL Querying, pushing developers to design denormalized data models.
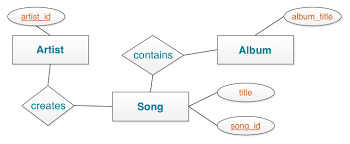
Training modules guide learners through creating tables, inserting, updating, and deleting data using CQL while ensuring optimal performance. Data modeling in Cassandra focuses on designing tables based on query patterns for efficient reads. CQL (Cassandra Query Language) resembles SQL, enabling users to create, update, and query data. Understanding primary keys, partitions, and clustering columns is essential for effective data organization and retrieval.
Are You Preparing for Data Science Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Data Science Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Replication and Partitioning
Conclusion
Apache Cassandra has proven itself as a game-changing technology in the realm of big data and real-time analytics. As more organizations shift toward scalable, fault-tolerant systems, the need for skilled Cassandra professionals will only grow. Virtual classrooms make it easier than ever for learners to gain in-demand skills without the constraints of location or rigid schedules Data Science Training. Through interactive sessions, hands-on labs, Data Modeling and CQL and expert mentorship, these training programs equip learners with both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Whether you’re a student aiming for a career in data or a professional looking to upskill, Cassandra online training can be your gateway to a rewarding and future-ready career.


