- Introduction to Business Analytics
- Applications Across Industries
- Market Growth and Demand
- Job Roles and Titles
- Skills in Demand
- Tools and Technologies
- Real-Time Decision Making
- Integration with AI/ML
- Impact on Business Performance
- Career Growth Path
- Educational Pathways
- Global Opportunities
- Conclusion
Introduction to Business Analytics
Scope of Business Analytics (BA) is the practice of iterative, methodical exploration of an organization’s data, with an emphasis on statistical analysis. It is used by companies committed to data-driven decision-making. Business analytics is a subset of business intelligence (BI) and uses data mining, predictive analytics, applied analytics, and statistics to create insights that drive business planning. Today, business analytics has become essential to remaining competitive in virtually every industry, making Business Analyst Training a critical pathway for professionals seeking to master these skills. With the explosion of big data, organizations have more information than ever before, and they need robust analytical techniques to make sense of it. Scope of Business Analytics helps transform raw data into meaningful patterns and insights that aid in improving business performance and strategic planning.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer Certification? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Certification Courses Today!
Applications Across Industries
Scope of business analyst in future is not confined to a specific sector. It plays a transformative role across a wide range of industries, especially when comparing the opportunities highlighted in Business Analysis Careers vs Business Analytics.
- Retail: Forecasting demand, optimizing pricing, and understanding customer behavior.
- Healthcare: Predicting patient outcomes, managing hospital resources, and improving patient care.
- Banking and Finance: Fraud detection, credit scoring, risk analysis.
- Manufacturing: Inventory management, quality control, and supply chain optimization.
- Telecommunications: Customer churn prediction, network optimization.
- E-commerce: Personalization, product recommendation, conversion rate optimization.
- Transportation and Logistics: Route optimization, delivery efficiency, and cost reduction.
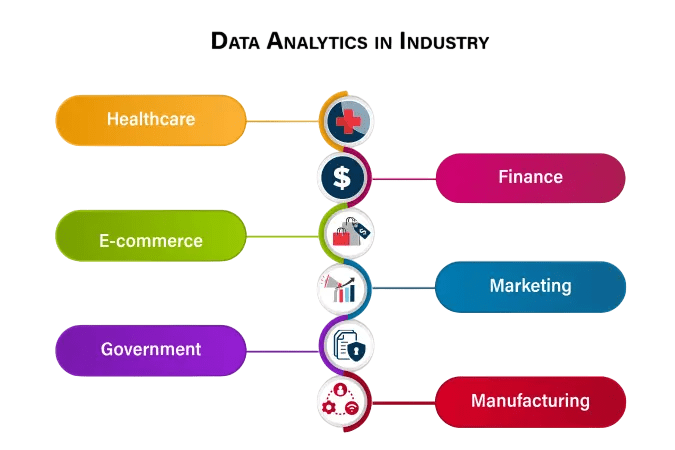
These applications demonstrate that analytics is crucial not only for profit but also for operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Market Growth and Demand
The global scope of business analyst in future market has experienced exponential growth in recent years and is projected to grow significantly in the future. According to industry reports, the market is expected to reach over USD 100 billion by 2026. Factors fueling this growth include the increasing adoption of data-driven decision-making, advancements in AI and ML technologies, and the proliferation of digital data. Organizations are actively investing in business analytics tools to stay ahead in the competitive landscape. As a result, there’s a substantial demand for skilled business analytics professionals who can analyze data and translate it into actionable insights.
Excited to Obtaining Your web developer Certificate? View The web developer course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Job Roles and Titles
The field of business analytics offers a variety of roles for professionals with diverse skill sets. Some of the most in-demand roles include:
- Business Analyst: Gathers and interprets data to help decision-making.
- Data Analyst: Focuses on processing and performing statistical analysis on datasets.
- Data Scientist: Applies advanced analytics techniques and machine learning models.
- Business Intelligence Analyst: Designs and develops BI solutions.
- Analytics Manager: Oversees analytics teams and projects.
- Quantitative Analyst (Quant): Applies mathematical models to financial and risk data.
- Operations Analyst: Focuses on improving internal operations using data.
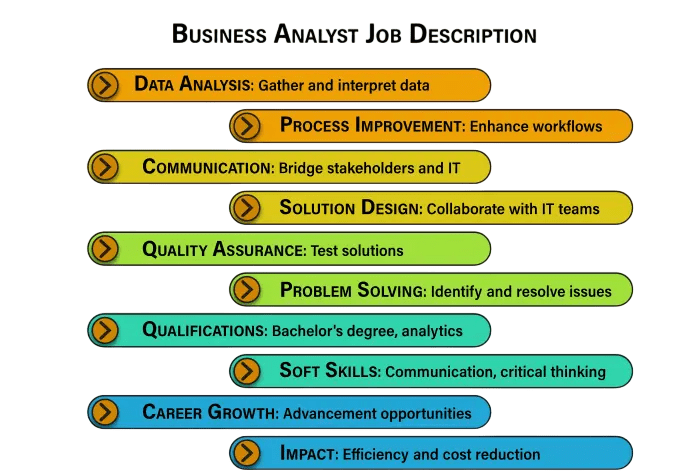
Each of these roles requires a blend of technical skills, analytical thinking, and business acumen.
Skills in Demand
A successful scope of business analyst in future requires a mix of technical skills and soft skills that help professionals turn data into actionable insights. One key skill is statistical analysis, which helps understand patterns and make predictions based on data. Data visualization is also important, as it communicates insights clearly using charts, graphs, and dashboards. Being skilled in SQL is crucial for retrieving and managing data from databases. Excel is also a powerful tool for data modeling, advanced functions, and automation using VBA. Knowing programming languages like Python or R enables scripting and performing more advanced analytics tasks. On the soft skills side, critical thinking is essential for interpreting data meaningfully and guiding business decisions. Strong communication skills are also important. Analysts need to translate complex findings into simple messages that non-technical stakeholders can understand. Professionals who develop and master these skills are in high demand in the fast-changing analytics job market.
Interested in Pursuing web developer certification Program? Enroll For Web developer course Today!
Tools and Technologies
Several tools and platforms are commonly used in the business analytics domain:
- Data Analysis and Visualization: Excel, Tableau, Power BI, QlikView
- Statistical Computing: R, SAS, SPSS
- Programming Languages: Python, SQL, Java
- Data Management: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB
- Machine Learning Platforms: Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, RapidMiner
- Big Data Technologies: Hadoop, Apache Spark, Hive
- Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud (for data storage and analytics)
Selecting the right tool depends on the complexity of the analysis, scalability needs, and team expertise.
Real-Time Decision Making
In today’s fast-paced business world, real-time analytics has become crucial for making quick, informed decisions. It allows organizations to react to changes as they happen, instead of waiting for delayed reports or past data, a capability that is further strengthened through Business Analyst Training. For example, retailers use real-time analytics to change prices based on current demand and inventory levels. Banks use it to spot fraudulent transactions right away, helping to prevent financial losses. Logistics companies apply real-time data to adjust delivery routes in response to traffic jams or weather changes. In healthcare, monitoring patient vitals in real-time can alert providers to emergencies before they worsen. These abilities come from the combination of streaming data processing, cloud computing, and interactive dashboards. Together, they let businesses gain immediate insights, improve operational efficiency, and respond better to customers, making real-time analytics an essential tool for staying competitive.
Integration with AI/ML
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are redefining the business analytics landscape. By integrating AI and ML with analytics:
- Predictive models: Anticipate future events (e.g., sales forecasts, risk probabilities).
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Allows systems to understand and generate human language.
- Automated analytics: Generate reports and insights without human intervention.
- Reinforcement learning: Helps in making sequential business decisions.
This integration leads to more sophisticated, scalable, and self-improving analytics systems that enhance business agility.
Impact on Business Performance
Business analytics drives performance in multiple ways:
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-backed decisions minimize risks and enhance outcomes.
- Increased Efficiency: Automation of routine analysis and operations.
- Customer Satisfaction: Personalized services based on data insights.
- Revenue Growth: Optimized pricing, cross-selling, and up-selling strategies.
- Risk Management: Better forecasting and mitigation strategies.
The cumulative effect of these benefits translates to a competitive advantage and long-term growth.
Career Growth Path
Scope in business analytics offers a clear and promising career path with many chances for advancement as professionals gain experience and improve their skills. Typically, one starts as a junior analyst, focusing on data collection, cleaning, and basic reporting. With time and experience, this role can progress to a senior analyst, who is responsible for deeper insights, predictive modeling, and strategic recommendations. After that, professionals may move up to become an analytics manager, leading teams and overseeing project execution. The next step is the Director of Analytics, who connects analytics initiatives with business goals and manages collaboration across teams. At the top of this path is the chief data officer (CDO), a leader who drives data-driven change across the organization. Growth in this field is further supported by certifications, ongoing learning, and specialization in areas like finance, healthcare, or marketing. These not only improve technical skills but also create industry-specific knowledge that helps professionals stand out in a competitive job market.
Educational Pathways
Scope in business analytics typically requires a strong educational foundation in quantitative disciplines. Common educational paths include:
- Bachelor’s Degree: In fields like Business, Economics, Statistics, and Computer Science.
- Master’s Degree: MBA in Business Analytics, MS in Data Science, Applied Statistics.
- Professional Certifications: Google Data Analytics Certificate, Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate, SAS Certified Advanced Analytics Professional, IIBA Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP).
These qualifications, combined with internships and practical experience, help candidates stand out.
Global Opportunities
As digital transformation spreads globally, business analytics roles are in demand across continents:
- North America: Headquarters of major analytics-driven tech companies.
- Europe: Strong demand in financial services, manufacturing, and logistics.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid digital adoption, especially in India, China, and Singapore.
- Middle East: Smart city projects and financial institutions hiring data professionals.
Remote work has also expanded access to international scope in business analytics, enabling analysts to work across time zones and borders.
Conclusion
Scope of Business Analytics is a dynamic and high-growth field that sits at the intersection of data, technology, and strategic decision-making. It transforms data into actionable intelligence, providing immense value to businesses across all sectors. From entry-level analysts to C-level roles, the career possibilities are vast and impactful, with many professionals advancing through the skills gained in Business Analyst Training. With strong demand for skilled professionals, continuous technological advancements, and expanding global applications, business analytics stands out as one of the most rewarding and future-proof career domains today. Embracing this field can lead to substantial personal and professional growth, while simultaneously helping organizations navigate the data-driven age with confidence and precision.

