
- What is Cybersecurity?
- What is Data Science?
- Key Differences Between Cybersecurity and Data Science
- Areas Where Cybersecurity and Data Science Overlap
- Future of Cybersecurity and Data Science
- Transition Between Cybersecurity and Data Science
- Conclusion
Two stand out as crucial in the digital world for business operations and technological development Cybersecurity Training Courses. Both deal with protecting the data and driving business decisions but are oriented to different foci. Cybersecurity deals with the protection against cyber threats. In contrast, data science is concerned with concluding data. In contrast, scientific data is concerned with concluding data. This blog will explore the differences and the overlap between Cybersecurity and data science analyst, including their definitions, objectives, skill sets, and how these disciplines increasingly intersect in today’s tech landscape.
What is Cybersecurity?
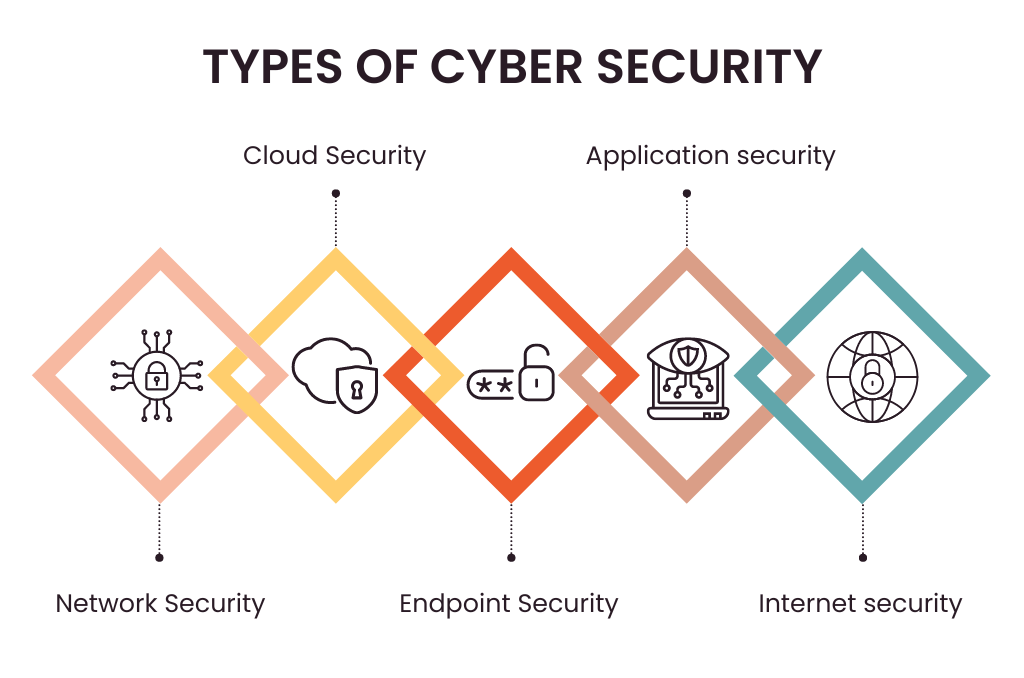
Cybersecurity is the practice that protects computer systems, networks, and data from various forms of cyber threats, including hacking, malware, ransomware, and other malicious activities. The cybersecurity experts preserve information/data and systems as confidential, integral, and available, AI in Cybersecurity called the CIA triad. Some main areas of cybersecurity:
- Network Security: Computer network security protection against unauthorised access, attacks, and data breaches.
- Application Security: Software applications protection against vulnerabilities and exploits.
- Information Security: Data is protected from theft and misuse to ensure confidentiality and integrity, whether it’s in motion or at rest.
- Endpoint Security: Protecting hardware, including laptops and mobile phones, from a cyber attack.
- Incident Response and Recovery: The plan for handling incident responses and recovery in place to recover normal operations within minutes of a security breach occurs.
Are you curious to know more about Cybersecurity ? Take advantage of our comprehensive online Cyber Security Online Training .
Cybersecurity professionals protect themselves through firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and multi-factor authentication, with technologies transforming to combat the ever-changing nature of cyber threats. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, cybersecurity professionals are also applying artificial intelligence and machine learning more to predict, detect, and respond to attacks in real-time and enhance their defence strategies.
What is Data Science?
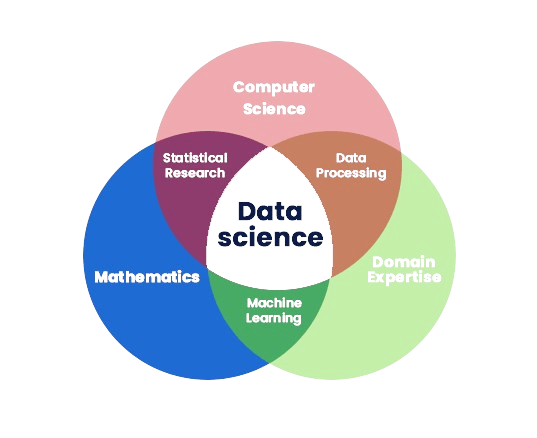
Data Science Domain Data Science is that area or domain of getting insights from big data through which machine learning techniques are combined with statistics and data mining. A data scientist is charged with understanding trends, predicting potential events, and drawing actionable insights to guide business decisions. Data scientists use tools such as Python, R, SQL, TensorFlow, and Tableau to draw insights from data sets that help them make decisions. The first step involves gathering raw data from various sources and ensuring the data is cleaned, clean, and ready for analysis. Find patterns, correlations, and trends in data using statistical methods. Create algorithms that let systems learn from their data and come to conclusions or predictions. Utilise tools like Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases to manage and analyse very large datasets. In addition to the core skills of data collection, cleaning, and analysis, data scientists often work closely with business leaders to ensure that their insights align with organisational goals. They transform raw data into actionable strategies by applying advanced techniques such as predictive modelling, Network Segmentation natural language processing (NLP), and deep learning. data science analyst also extends to real-time data processing, allowing businesses to make more informed decisions based on immediate trends or changes. By leveraging large-scale data analytics, data scientists help companies optimise operations, improve customer experiences, and uncover new market opportunities, ultimately driving growth and innovation.
To Sign up for ACTE Cyber Security Online Training and get a head start in your career cyber security.
Key Differences Between Cybersecurity and Data Science
- Cybersecurity and data science are critical disciplines in today’s digital landscape, but they serve different purposes. Cybersecurity is focused on protecting digital systems, networks, and data and analytics from cyber threats, including hacking, malware, and unauthorised access.
- It involves implementing defensive measures, identifying vulnerabilities, and responding to incidents to maintain data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. In contrast, data science analyst is centred around extracting insights from vast datasets using statistical analysis, machine learning, and data mining techniques.
- The goal is to uncover trends, make predictions, and provide actionable insights to drive strategic business decisions. The main distinctions between these fields are found in their goals, approaches, and results. While cybersecurity professionals work to secure data and defend against cyber risks, data scientists focus on analysing data to inform decision-making, optimise processes, and predict future outcomes.
- Cybersecurity requires knowledge of encryption, firewalls, and threat detection tools, while data science analyst demands expertise in programming, machine learning, and statistical modelling. Although the fields differ in their core functions, they intersect in areas like data protection and privacy, where data scientists must ensure that sensitive information is handled securely while extracting meaningful insights.
- Cybersecurity Training Courses are increasingly converging in the face of evolving technology. As organisations collect and process more data, the need for data protection has grown significantly. Data scientists, who often work with sensitive information, must integrate cybersecurity principles to ensure that data is secure and compliant with privacy regulations.
- Similarly, cybersecurity experts leverage scientific data techniques like machine learning and predictive analytics to detect and mitigate security threats more effectively. By combining the strengths of both fields, businesses can protect their digital infrastructure and gain deeper insights into security risks, ensuring a more proactive and data-driven approach to cybersecurity.
Areas Where Cybersecurity and Data Science Overlap
Protecting Sensitive Information
Data scientists typically handle highly confidential information, such as customer and financial scientific data. iot cybersecurity professionals ensure such information is adequately protected through encryption data and analytics Threat Intelligence masking and proper controls over access. Both fields, therefore, collaborate to prevent such intrusions or unauthorised access.
Machine Learning for Threat Detection
Now, it has become one of the major streams of data science that will play a significant role in detection processes in cybersecurity. Machine learning algorithms will be able to find deviations in scientific data patterns that usually occur as signs of cyber attacks, such as DDoS attacks or ransomware. Data scientists team up with cybersecurity specialists in building predictive models to predict safety risks and detect those well ahead of time to minimise loss from the threat.
Data-Driven Cybersecurity Strategies
Cybersecurity teams now rely on data science to enhance their threat detection and defence. Data science enables the analysis of historical attack data to understand emerging threats and optimise security measures. Data analytics help iot cybersecurity teams design more effective security policies, anticipate vulnerabilities, and improve response times.
Transform Your Career with Cyber Security Knowledge Enroll in ACTE’s Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
Future of Cybersecurity and Data Science
This will continue to grow in the years to come as data increases and threats in the cyber world grow in sophistication, requiring that data science be infused more deeply into cybersecurity. Indeed, we already see systems of AI and ML being used to predict and even detect cyberattacks before they happen. The future will be dominated by the continued use of data science for driving predictive iot cybersecurity measures, enabling organisations to move from reactionary stances to proactive ones. Additionally, since more value will be given todata and analytics, Comptia Certification Path data protection and privacy regulations will be more intricate, and security professionals will have to adapt to the changes in partnership with data scientists to ensure effective, robust data protection strategies.
This is because data science will become an imperative component in solving existing problems while preparing new ones; it will have to go beyond the cyber-security requirements of dealing with the new challenges created by IoT devices, cloud computing, and the rise of big data analytics. This will be an even more critical role for machine learning and artificial intelligence, especially in self-threat detection, real-time responses, and detailed anomaly detection. The data-driven models help organisations better predict potential security breaches, identify emerging threats, and adjust their security protocols appropriately. As these technologies intertwine more and more, the partnership between data scientists and cybersecurity professionals becomes the key to protecting assets for business while using data to foster innovation and growth.
Transition Between Cybersecurity and Data Science
- Build Foundational Knowledge: If you come from a cybersecurity background, basic familiarity with one of the other two Python or R will serve as a foundation for the other one. If you come from data science to cybersecurity, network security protocols, cryptography, and aspects of threat detection-based techniques will be necessary.
- Leverage existing expertise: Both employ problem-solving expertise. Cybersecurity experts can leverage their security protocol knowledge to devise more effective data privacy solutions while applying advanced analytical skills by data scientists to improve monitoring cyber and cybersecurity.
- Online Course or Certification: Many online learning centres provide teaching courses in select fields of study. Look for cybersecurity courses that include data analytics or programs under Data Classification science with security applications. Cross-Functional Approach: By interacting and collaborating with professionals from both fields, you will learn more about each domain so that you can combine the best practices of both.
- Stay Updated with Industry Trends: Both cybersecurity and data science are fast-evolving fields, and staying up-to-date with the latest trends, tools, and technologies is essential. network security with professionals from both domains at these events can foster collaboration and inspire new ones.
- Hands-On Projects: One of the most effective ways to bridge the gap between cybersecurity and data science is through practical, hands-on experience. Working on real-world projects that combine both disciplines, such as building a machine learning model for threat detection or developing a data privacy algorithm.
Preparing for a job interview in cybersecurity ? Examine our blog post about Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers to get the most of your employment experience!
Conclusion
Though different and distinct, these realms are crucial to the digital world today. iot cybersecurity is concerned with protecting sensitive data and analytics digital assets, while data science is about extracting insights from organisations so that such decisions would rather be based on data than intuition. Thus, by increasing overlap between these two fields, there is a chance for the professional who can achieve that ‘bridging use of the ‘power of and analytics techniques in the service of cybersecurity and vice versa’. As both fields advance, organisations incorporating data science into iot cybersecurity will be better poised to encounter and respond to emerging threats while making proactive decisions regarding protecting their digital infrastructure. In the future, that’s going to require a crop of professionals who can play in one arena but know how to use the strength of both Cybersecurity Training to create a secure, data-driven world.





