
- What is hacking?
- What is the Role of Hacking in Cybersecurity?
- Tools & Technology Hacking in Cybersecurity
- Cybersecurity Hacking and Its Legal Landscape
- Legal Framework Governing Cybersecurity Hacking
- Ethical Hacking and Legal Protection
- Challenges in the Ethical Hacking
- Future of Ethical Hacking in Cybersecurity
- Conclusion
As the digital world expands, so does the need for effective cybersecurity measures. Hacking is a vital discipline that helps to secure a large network of computers. While hacking has traditionally been viewed with suspicion and associated with evil intent, ethical hacking, an essential component of contemporary security systems, is a growing issue in cybersecurity. However, hacking ethics are intricate and often blur the line between good and evil, which seems so distinct. This paper explores aspects of hacking in Cyber Security Training Courses, namely the ethical aspect of hacking, many hacking techniques, and the problematic nature of ethical hackers. We will discuss how ethical hacking may make society better and what this could imply from the broader cybersecurity hacking perspective.
Are you curious to know more about ethical hacking? Take advantage of our comprehensive online Cyber Security Course!
What is hacking?
Computer hackers are unauthorized users who obtain access to computers to steal, change, or erase data, typically by installing malicious software without your knowledge or consent. Thanks to their cunning ways and extensive technological understanding, they can obtain information you don’t want them to have. Computer hackers and online predators can target any device linked to the Internet. These Cyber Media typically employ spam messages, phishing emails, instant messaging, and webpages to spread harmful malware to your computer and compromise your network security.
What is the Role of Hacking in Cybersecurity?
- Vulnerability Assessment: Ethical hackers assess systems, networks, and applications to determine which have vulnerabilities. The assessment just represents the weak points, like outdated software, poor configurations, and susceptibility to malware attacks.
- Penetration Testing: Vulnerability scanning determines the actual security weaknesses, whereas penetration testing exploits the vulnerabilities of potential active intrusions to determine their feasibility. This will help enterprises test whether their current security technologies work in a real-world scenario.
- Security Auditing: Ethical hackers thoroughly review the present security policies and procedures. This will ensure that safety procedures are updated by checking whether they follow the proper standards and laws.
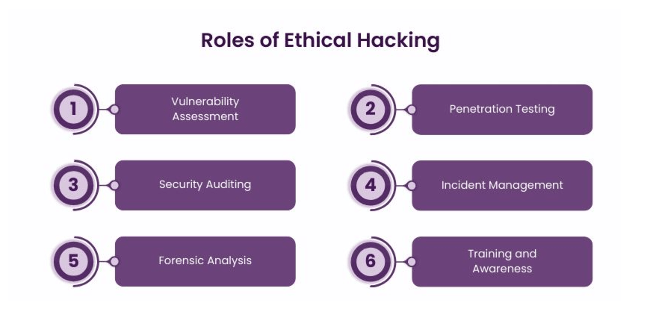
- Incident Management: If a security breach occurs, ethical hackers investigate the situation and prevent it from happening again.
- Forensic Analysis: Following the breach, ethical hackers typically do forensic analysis, which includes determining the reason and technique of the attack. This study is crucial for understanding the reasons for breaches and how to prevent them in the future.
- Training and Awareness: Ethical hackers not only ensure the company’s survival but also educate personnel on the best E-mail Security procedures.They also inform customers about the most recent cybersecurity threats and how to avoid them.
- Network scanners
Network scanners are essential in gathering information about networks and their weak points through ethical hacking. They scan a network’s devices, ports, and services, giving the ethical hacker information regarding network topology and weak points within the network that can be attacked.
- Vulnerability Assessment Software
It scans for system and application vulnerabilities, notably known vulnerabilities, misconfiguration, and bad security practices, to advise ethical hackers to improve such weaknesses, thus enhancing the security posture of targeted systems.
- Password Crackers
A password cracker is a tool that tests the readability of passwords or bypasses mechanisms used to authenticate user identity. Ethical hackers use such tools to test the strength of their passwords and identify weak or easily guessable passwords. This enables them to assess the overall Database Security of systems and advise for more robust password practices.
- Forensic Analysis Tools
Forensic analysis tools are designed to support ethical hackers in exploring security breach incidents or conducting digital forensics. These pieces of equipment help collect evidence, analyze log systems, and retrieve deleted files. A forensic analysis tool is necessary for tracking where an attack is coming from and to what extent a security breach has been accomplished.
- Network Sniffers
Network sniffers, often referred to as packet analyzers, let ethical hackers capture and analyze network traffic. They facilitate understanding of data flow within a network, spot security risks, and detect unauthorized or suspicious activities. Network sniffers are useful in monitoring network communication and identifying possible vulnerabilities or weaknesses.
- Exploitation Frameworks
Exploitation frameworks are a collection of tools and resources used to identify and exploit vulnerabilities. These frameworks provide many exploits, payloads, and post-exploitation modules, which can be quite useful for ethical hackers during the assessment and exploitation process of vulnerabilities. Such tools are founded upon knowledge of ethical hacking principles and should be used responsibly and ethically.
Cybersecurity Hacking and Its Legal Landscape
As advanced as cybersecurity threats are getting and on the increase, so is the legal framework for Hacking in Cyber Security Training Courses. Hackings of any kind can be seriously penalized in court; illegal access to computer systems adds to this serious severity for the hacker. Though ethical hacking is highly important in these processes of security reinforcement, unauthorized hacking-whether with malicious intent is illegal, and more stringent laws may apply to it. Therefore, it is a complex landscape of national laws, international agreements, and industry-specific regulations that defines the legal boundary of cybersecurity hacking.
Legal Framework Governing Cybersecurity Hacking
The legal challenge that cybersecurity hacking faces is that unauthorized access to systems is illegal in many jurisdictions, even if the hacker intends to identify vulnerabilities for the greater good. Similarly, the United States renders the act of accessing a computer system without permission and the use of deceptive means for accessing or damaging data through the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act. The European Union, through the Directive on Attacks Against Information Systems, brings into existence legal obligations regarding protection against Cyber Awareness, along with penalties for unauthorized access, modification, or damage to computer systems and data. These laws do not stop at restricting malicious hackers but also restrict ethical hackers if that hacker operates beyond legal jurisdictions. These hackers should be given explicit permission to try to find flaws in the systems owned, usually through penetration-testing contracts or bug bounty programs. Without that explicit permission, even a good-intentioned hacker would end up in jail. This implies, therefore, that maintaining operations within the law helps prevent any legal consequences.
Leverage Cyber Security to Unlock the Future! Enroll in the Master of Cyber Security Program at ACTE Right Away.
Ethical Hacking and Legal Protection
Ethical hacking is better defined in terms of cyber security, and some are even restricted by the law from hacking. Most organizations openly hire ethical hackers who test the systems for them, which creates an essential basis through which these individuals operate legally because most penetration testing contracts establish the legitimacy of these activities. Such is reduced legal risk on the part of ethical hackers because they operate under contracts that describe their legitimate actions. Some governments and organizations have also put in place incentives like bug bounty programs in which companies reward an individual for the discovery and responsible disclosure of Web Security vulnerabilities. Both the legal and regulatory frameworks, therefore, support this type of program because it provides a legitimate means by which hackers can input into cybersecurity.
Challenges in the Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking is the backbone of cyber security, but with its challenges. Here are some of the major challenges that ethical hackers face
- Legal and Ethical Dilemmas: Ethical hackers operate in the middle of a space where legality and ethical considerations come into play. Sometimes, they have to ensure they have proper authorization and are not breaching legal boundaries to avoid lawsuits.
- Scope Limitations: Most engagements have predefined scopes, that is, areas not to be tested. This leads to some vulnerabilities needing to be noticed during the testing.
- False Positives and Negatives: Identified risks may sometimes create false positives, that is, non-issues identified as issues, or false negatives, that is, real issues not identified at all. This, too, may further influence the validity of the assessment.
- Evolving Technology: Fast-changing technology changes the scenario altogether; ethical hackers must keep learning and updating themselves constantly about new threats and Vulnerability Management.
- Human Factor: Humans continue to be a crucial cyber Web Application Security weakness. Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology, hence making it hard to secure systems.
- Resource Constraints: Ethical hacking highly consumes resources in terms of time, tools, and expertise. The fact that resources constrain ethical hacking makes it less effective.
- Complexity of Systems: It is interconnected that the systems and Security themselves are. Therefore, it is difficult to point out all the possible vulnerabilities and deal with them.
Hacking In Cybersecurity Sample Resumes! Download & Edit, Get Noticed by Top Employers! DownloadFuture of Ethical Hacking in Cybersecurity
Against the growing sophistication of cyber threats, it is increasingly crucial to look ahead toward the future of ethical hacking. It is because AI-powered Malware Attack, IoT proliferation, and continuous assaults against critical infrastructure will now finally have a way to be internally defended against ethical hackers. They will, therefore, be required to ensure safety for next-generation technologies such as blockchain, autonomous vehicles, and quantum computing.However, the role of an ethical hacker would change as the differences between hackers start to be thin and unpronounceable. With this, ethical hackers would have to face even more complex legal and moral boundaries. More importantly, they would have to learn and adapt new technologies to combat new threats in innovative ways.
Preparing for a job interview in ethical hacking? Examine our blog post about Cyber Security Interview to get the most of your employment experience!
Conclusion
In summary, hacking is very important in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. Even though the word “hacking” in itself is derogatory, ethical Cyber Security Training Courses hacking is the good guy’s stuff; indeed, it forms part of protecting digital infrastructures as well as sensitive information. White-hat hackers have made tremendous strides over the last few decades by plugging holes, averting cyber attacks, and securing systems against the nature of threats that change daily. The ethical side of hacking in cybersecurity is multifaceted considering all hackers, be they white, grey-hat, or black and encompasses the factors of consent, a balance between security and privacy, and overall society. It is in the interest of the ethical hacker to deal with these dilemmas constantly to ensure that their actions serve the greater good without causing harm or breaching trust. This is relevant because the security versus privacy dilemma, particularly where confidential information is at stake, only complicates ethical choices.
Enroll in ACTE’S Cyber Security Course if you want to become an expert in Ethical Hacking field and have a prosperous career.
Tools & Technology Hacking in Cybersecurity
Ethical hacking and cybersecurity use a host of tools and technologies that can be used to assess the strength of systems, identify vulnerabilities, and propose security measures if needed. Here are some of the most commonly used essential tools for ethical hacking






