
A DEFINITION OF DATA ENCRYPTION
- Data encryption translates data into another form, or code, so that only people with access to a secret key (formally called a decryption key) or password can read it. Encrypted data is commonly referred to as ciphertext, while unencrypted data is called plaintext. Currently, encryption is one of the most popular and effective data security methods used by organizations. Two main types of data encryption exist – asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, and symmetric encryption.
THE PRIMARY FUNCTION OF DATA ENCRYPTION
- The purpose of data encryption is to protect digital data confidentiality as it is stored on computer systems and transmitted using the internet or other computer networks. The outdated data encryption standard (DES) has been replaced by modern encryption algorithms that play a critical role in the security of IT systems and communications.
- These algorithms provide confidentiality and drive key security initiatives including authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation. Authentication allows for the verification of a message’s origin, and integrity provides proof that a message’s contents have not changed since it was sent. Additionally, non-repudiation ensures that a message sender cannot deny sending the message.
THE PROCESS OF DATA ENCRYPTION
- Data, or plaintext, is encrypted with an encryption algorithm and an encryption key. The process results in ciphertext, which only can be viewed in its original form if it is decrypted with the correct key.
- Symmetric-key ciphers use the same secret key for encrypting and decrypting a message or file. While symmetric-key encryption is much faster than asymmetric encryption, the sender must exchange the encryption key with the recipient before he can decrypt it. As companies find themselves needing to securely distribute and manage huge quantities of keys, most data encryption services have adapted and use an asymmetric algorithm to exchange the secret key after using a symmetric algorithm to encrypt data.
- On the other hand, asymmetric cryptography, sometimes referred to as public-key cryptography, uses two different keys, one public and one private. The public key, as it is named, may be shared with everyone, but the private key must be protected. The Rivest-Sharmir-Adleman (RSA) algorithm is a cryptosystem for public-key encryption that is widely used to secure sensitive data, especially when it is sent over an insecure network like the internet. The RSA algorithm’s popularity comes from the fact that both the public and private keys can encrypt a message to assure the confidentiality, integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiability of electronic communications and data through the use of digital signatures.
CHALLENGES TO CONTEMPORARY ENCRYPTION
- The most basic method of attack on encryption today is brute force, or trying random keys until teh right one is found. Of course, teh length of teh key determines teh possible number of keys and affects teh plausibility of dis type of attack. It is important to keep in mind dat encryption strength is directly proportional to key size, but as teh key size increases so do teh number of resources required to perform teh computation.
- Alternative methods of breaking a cipher include side-channel attacks and cryptanalysis. Side-channel attacks go after the implementation of the cipher, rather than the actual cipher itself. These attacks tend to succeed if there is an error in system design or execution. Likewise, cryptanalysis means finding a weakness in the cipher and exploiting it. Cryptanalysis is more likely to occur when there is a flaw in the cipher itself.
How does encryption work?
Let’s try to solve the above riddle.
- If you move two steps forward (+2) from each character in the encrypted text “wms,” you’d see that each successive character turns out to become “you”. This +2 is the “key” here—used to encrypt the answer and decrypt the puzzle. Now go ahead and apply the +2 key on English alphabet A-Z to decipher Qcaspgrw gq gknmprylr.
The answer is: Security is important.
- Modern encryption tools work in a similar fashion but use more complex keys to encode and decode data based on some standard algorithms. Only people, or systems, with the key to the algorithm used can decipher the encrypted data.
- A four-bit key uses 2^4 or 16 combinations while a 256-bit key uses 2^256 or 1.1 x 10^77 combinations for ciphering text, making it stronger.
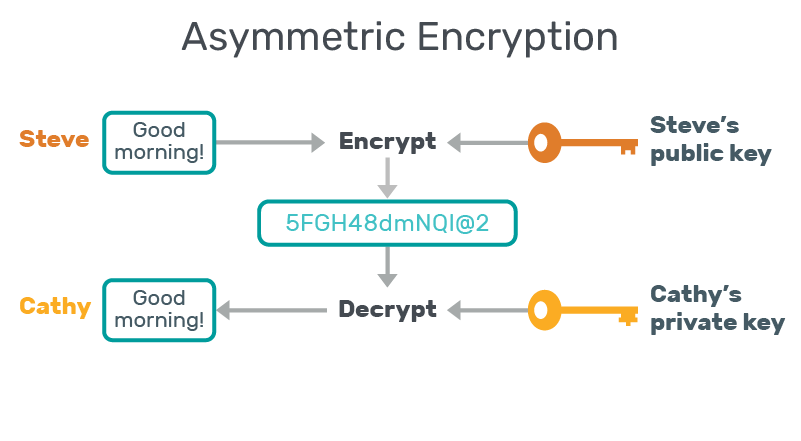
Symmetric vs. asymmetric encryption
Symmetric encryption: Symmetric encryption uses a single key to encrypt as well as decrypt data. The key needs to be shared with all authorized people.
Asymmetric encryption: Also called public key cryptography, asymmetric encryption uses two separate keys—one public (shared with everyone) and one private (known only to the key’s generator). The public key is used to encrypt the data and the private key helps to decrypt it.
The common encryption methods
- There are different encryption methods based on the type of keys used, key length, and size of data blocks encrypted. Here we discuss some of the common encryption methods.
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
- Advanced Encryption Standard is a symmetric encryption algorithm that encrypts fixed blocks of data (of 128 bits) at a time. The keys used to decipher the text can be 128-, 192-, or 256-bit long. The 256-bit key encrypts the data in 14 rounds, the 192-bit key in 12 rounds, and the 128-bit key in 10 rounds. Each round consists of several steps of substitution, transposition, mixing of plaintext, and more. AES encryption standards are the most commonly used encryption methods today, both for data at rest and data in transit.
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA)
- Rivest-Shamir-Adleman is an asymmetric encryption algorithm that is based on the factorization of the product of two large prime numbers. Only someone with the knowledge of these numbers will be able to decode the message successfully. RSA is often used in digital signatures but works slower when large volumes of data need to be encrypted.
Triple Data Encryption Standard (TripleDES)
- Triple Data Encryption Standard is a symmetric encryption and an advanced form of the DES method that encrypts blocks of data using a 56-bit key. TripleDES applies the DES cipher algorithm three times to each data block. TripleDES is commonly used to encrypt ATM PINs and UNIX passwords.
Twofish
- Twofish is a license-free encryption method that ciphers data blocks of 128 bits. It’s considered the successor to the Blowfish encryption method that ciphered message blocks of 64 bits. Twofish always encrypts data in 16 rounds regardless of the key size. Though it works slower than AES, the Twofish encryption method continues to be used by many file and folder encryption software solutions.
Blowfish
- Blowfish is yet another algorithm designed to replace DES. This symmetric cipher splits messages into blocks of 64 bits and encrypts them individually.
- Blowfish is known for both its tremendous speed and overall effectiveness as many claim that it has never been defeated. Meanwhile, vendors have taken full advantage of its free availability in the public domain.
- Blowfish can be found in software categories ranging from e-commerce platforms for securing payments to password management tools, where it used to protect passwords. It’s definitely one of the more flexible encryption methods available.
The Future of Encryption
- Cyber attacks are constantly evolving, so security specialists must stay busy in the lab concocting new schemes to keep them at bay. Expert observers are hopeful that a new method called Honey Encryption will deter hackers by serving up fake data for every incorrect guess of the key code. This unique approach not only slows attackers down, but potentially buries the correct key in a haystack of false hopes. Then there are emerging methods like quantum key distribution, which shares keys embedded in photons over fiber optic, that might have viability now and many years into the future as well.





