
- What is Cryptojacking?
- How Cryptojacking Works
- Types of Cryptojacking Attacks
- The Impact of Cryptojacking
- Cryptojacking vs. Traditional Malware
- Identifying Cryptojacking
- Protecting Against Cryptojacking
- The Future of Cryptojacking
- Conclusion
- Malicious Ads (Malvertising): Hackers embed hidden scripts in online advertisements, which, when clicked or even viewed by a user, execute the crypto-jacking code in the background with no user notification.
- Phishing Emails and Links: Phishing emails may contain links that take victims to infected websites or attach files that deliver cryptojacking malware.
- Drive-By Downloads: A vulnerability in a browser may be exploited via a drive-by download attack. Simply visiting a compromised website might cause the automatic downloading and execution of cryptojacking software.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: An attacker may exploit the vulnerabilities in a particular software or on a devices-the vulnerable version of your browser, perhaps an unsecured server-to gain access and deploy cryptojacking malware.
- The most immediate financial expense from cryptojacking software is related to the absolute power and use of computing resources.
- For instance, in the context of households, that would translate to increased power bills. In contrast, business power bill organizations will experience unforeseen bills concerning over-utilized cloud resources or large electricity consumption from infected devices.
- The business organization incurs financial expenses in terms of IT resources expended to eliminate malware and rectify the systems impacted by crypto-jacking.
- Cryptojacking malware often uses a large portion of a system’s CPU or GPU. As a result, systems slow down, become less responsive, or crash more easily.
- It would give users an uncomfortable experience. For organizations, this would mean they would lose productivity and face inefficient operations.
- Although crypto jacking does not steal sensitive data, the threat to security is real. Attackers can easily gain entry into the core systems where data breaches, ransomware, or several other forms of malicious activities can take place.
- In extreme cases, the Cybersecurity Training Courses software itself could be used to install payloads that compromise private data.
- High CPU processing: If your computer’s processor runs for an extended period at maximum levels, even when idle, this may be due to crypto-jacking.
- Lagging system performance: An attacker performing mining will slow down the system, making it react slower.
- Device overheating: In most cases, devices overheat because the processing load increases by the mining performed by an attacker.
- Higher electricity use: If energy usage has significantly risen compared to usual, this is likely related to cryptojacking.
- Install an ad blocker that prevents rogue scripts from running in a browser.
- Use antivirus software to identify and block crypto-jacking malware.
- Keep updating software and systems, as well as patch known vulnerabilities.
- Monitor CPU and network for unusual behaviors.
- Business Security Measures.
- It is necessary to ensure endpoint protection in all devices from infections of cryptojacking.
- Update the software and hardware occasionally to mend the vulnerabilities that will be exploited.
- Use, and network traffic should be under surveillance to monitor any abnormal consumption. Staff should be trained on the dangers of phishing attacks and malicious links that may lead to cryptojacking.
What is Cryptojacking?
One type of cyberattack is cryptojacking, where the hacker secretly harnesses a victim’s computing resources to mine crypto without the user’s knowledge or consent. The hacker then installs malware on the device, which can be a computer, smartphone, or server, and uses it to execute computationally expensive calculations needed for mining digital currencies such as Bitcoin, Monero, or Ethereum.
Even though crypto jacking does not steal data and does not cause immediate damage to systems, its presence can have many unforeseen adverse consequences, including inefficiency, increased operating costs, and added security risks. The more the value of cryptocurrencies hikes, the more cybercriminals are attracted to crypto-jacking.
How Cryptojacking Works
Cybersecurity Training Courses malware uses a victim’s device to solve difficult cryptographic puzzles that are part of cryptocurrency mining. Mining helps verify transactions on the blockchain and keeps the network secure. The more computational power an attacker can command, the faster they can mine cryptocurrencies and earn rewards. What is so risky about cryptojacking is that it works secretly in the background, and often, the user is not even aware that their system has been hijacked.
Why is Cryptojacking a Growing Problem?
Cryptojacking is a threat to individuals and corporations. It may not steal data but slow devices, surge energy consumption, and open such systems to other hacking threats. This can pile up heavy financial costs for businesses, especially if it hits cloud infrastructure or servers, for the cost increases whenever computational demand does.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cryptojacking Professional? View the Cybersecurity Online Training Offered by ACTE Right Now!
How Cryptojacking Works
Delivery Methods of Cryptojacking Attacks
Cryptojacking attacks can be executed in one of many different forms, including but not limited to:
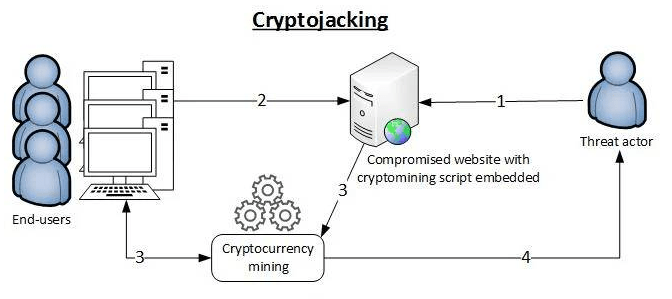
Cryptocurrency Mining through Cryptojacking
Naturally, the malware connects to a mining pool after installing itself on the victim’s system; this is a network of miners that pool their computing resources to mine cryptocurrency. Rather than purchasing expensive hardware, the CPU or GPU is used to perform the necessary calculations for mining. These processes continue running in the background, and unless there is significant performance degradation, the victim is unlikely to detect the attack. Increased Threat Intelligence can help users recognize subtle signs of cryptojacking and take preventive measures before it causes damage.
Taking Advantage of System Vulnerabilities
Cryptojackers further take advantage of any vulnerabilities in software to gain unauthorized access to devices. This may include outdated software, misconfigured devices, or unsecured servers. Once they gain entry into a system, they install their crypto-jacking malware and begin utilizing all the resources in the system to mine right away.
To Earn Your Cryptojacking Certification, Gain Insights from Leading Cryptojacking Experts and Advance Your Career with ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training .
Types of Cryptojacking Attacks
1. Browser-based cryptojacking
This type of crypto-jacking happens when cybercriminals push malicious JavaScript code onto a website or an advertisement. Once the victims surf on the affected website, they will automatically have the crypto-jacking script load within their browser. This script will then conduct cryptocurrency mining using the processing power of the victim’s computer. Because this type of attack does not involve any form of downloading, it is stealthier and much more difficult to detect.
2. Malware- and Software-Based Cryptojacking
Malware-based crypto-jacking attacks work by distributing malicious software to hijack a particular system’s resources. The malware might be spread through phishing emails and attachments or through exploited software vulnerabilities. The spyware operates silently in the background as it consumes resources on your system and secretly mines cryptocurrency on your behalf without your consent.
3. Cloud and Network Cryptojacking
Cloud infrastructure and networked devices are also targets for cryptojacking attacks. Hackers may exploit an enterprise’s cloud power for large-scale digital currency mining, leading to significant increases in cloud service bills. Effective Data Classification helps identify critical resources and better protect sensitive systems from such threats.
The Impact of Cryptojacking
Financial Impact
Poor System Performance
Organizational Security Threats
cryptojacking software is another threat in organizations, posing a more severe security threat because the compromised resources are involved in more than that. For instance, if the hackers have successfully penetrated a network, they might install different types of malware to steal data or carry out other destructive attacks, like ransomware or DoS attacks.
Looking to Master Cyber Security? Check Out the Cybersecurity Expert Masters Program Training Course Offered by ACTE Today!
Cryptojacking vs. Traditional Malware
Differences Key between Cryptojacking and Other Malware
Even though cryptojacking has similarities with traditional malware, the difference lies in what is targeted. While most forms of conventional malware aim at data exfiltration, extorting money from the victims, or disrupting the operational systems, the nature of traditional malware usually differs from cryptojacking because it primarily involves hijacking computer resources to mine for cryptocurrencies. This is another reason cryptojacking software often goes silently in the back end without clear and visible symptoms; it is harder to detect than other types of malware, which could cause obvious damage or data theft.
How Cryptojacking Evades Detection
Cryptojacking malware is designed to be stealthy, consuming system resources without triggering obvious signs like data loss or crashes. Victims may remain unaware their devices are being used for mining until performance issues arise. Because it doesn’t display overtly malicious behavior, cryptojacking software bypasses many traditional security measures. Effective Vulnerability Management is key to detecting and preventing such hidden threats by addressing system weaknesses that can be exploited.
Identifying Cryptojacking
Signs of Infection on a Device
Some signs that might reveal infection due to crypto-jacking malware in devices are as follows:
Detection Tools and Techniques
Cryptojacking may also be detected by monitoring system performance with CPU or GPU usage tracking tools. Network monitoring tools can also discover unusual traffic patterns that describe Cryptojackers behaviour. Specialized tools are also specifically designed for cryptojacking malware cryptojacking detection, and most antivirus software now includes cryptojacking detection.
Monitoring System Performance
On Windows and macOS systems, users check CPU utilization in the Activity Monitor or Task Manager. Unexplained bursts of CPU usage are common indicators of Cryptojackers. Periodic checks on system resource usage may aid in the early cryptojacking detection of infections, especially when coupled with strong Web Security practices to prevent malicious scripts from compromising your devices.
Protecting Against Cryptojacking
Best Practice for Users
How to Manage Cryptojacking Malware
If you suspect that your system has cryptojacking malware installed, scan it with a full antivirus test and use malware removal tools. You may also have to uninstall applications that suspect malicious activity, update or reinstall an operating system or application, or remove the threat.
Getting Ready for an Cyber Security Job Interview? Check Out Our Extensive List of Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers to Help You Prepare!
The Future of Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking Tactics on the Evolve
As cryptocurrency mining becomes highly lucrative, cryptojacking attacks will be far more advanced. New modes of exploitation and vulnerability discovery will continue to push attackers to the limit, making it extremely harder to identify and filter out such attacks. Cryptojacking malware will eventually be even stealthier and impossible to trace.
New Trends Expected in Cryptojacking Attacks
Cybercriminals’ focus has diversified towards new targets: connected devices and cloud infrastructures, continuing with the rapid growth of IoT devices and cloud-based computing. Interestingly, the new attack vectors necessitate newly devised security measures to combat cryptojacking at scale, as highlighted by experts in the IP Subnet industry.
Blockchain’s Potential in Combating Cryptojacking
Interestingly, blockchain technology can assist in fighting crypto-jacking attacks. New platforms and protocols have been developed to detect and prevent unauthorized mining and are offered as a countermeasure to this cybercrime. Due to its decentralized nature, blockchain may provide a means for tracing and mitigating cryptojacking in the future.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity Training is a relatively rampant cyber threat that quietly hijacks computing resources to extract cryptocurrencies through mining. Even though it does not immediately result in data thefts or system crashes, it facilitates increased operational costs, degraded system performance, and security vulnerabilities. Hence, taking robust security measures to advance Cryptojackers has become necessary for any individual or organization, with frequent monitoring of systems and updating software, including antivirus and malware cryptojacking detection tools.





