
- What is Ethical Hacking?
- Why is it important for cybersecurity?
- Tools of the Trade for Ethical Hackers
- Career Paths in Ethical Hacking & Cybersecurity
- Skills Required for Ethical Hacking
- Eligibility to Become an Ethical Hacker
- Conclusion
Ethical hacking has emerged as one of the most significant components of the broad cybersecurity career landscape. Organizations, as data breaches, hacking incidents, and security threats rise, tend to make proactive efforts to improve their defenses. Organizations seek professionals with skills who can test such systems to find vulnerabilities even before malicious hackers or black-hat hackers can access them. In this era, digital security marks business safety and personal security. As cyber threats evolve, professionals must also be vigilant against risks like Cyber Defamation, where false or damaging information is spread online to harm an individual’s or company’s reputation.
Interested in Obtaining Your Ethical Hacking Certificate? View The Ethical Hacking Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
What is Ethical Hacking?
This kind of authorized check of computer systems, networks, or applications is defined as Ethical Hacking to discover the possible weaknesses that cybercriminals can exploit. The only difference between an ethical hacker and a malicious hacker is that an ethical hacker will behave according to his intentions and legality. In contrast, an ethical hacker is hired by organizations for penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and other security tests to track and resolve vulnerabilities, often after completing Ethical Hacking Course to enhance their expertise and stay updated on the latest security practices. On the other hand, ethical hackers operate exactly like black-hat hackers, but they do so with the permission of the organization working for them. They intend to find loopholes in the system and report them to the organization while assisting them in filling in those security gaps.
Why is it important for cybersecurity?
- Identifying Vulnerabilities: Ethical hacking is believed to be the best way to identify vulnerabilities in an organization’s system and network. Simulating real-life attacks may reveal weaknesses used by malicious people.
- Penetration Testing: The vast majority of ethical hacking activities usually involve penetration testing. This process involves a hacker trying to break down the security system of any system or network, which allows organizations to understand their vulnerabilities and take appropriate measures.
- Risk Assessment: Ethical hacking would allow an organization to know how much at risk it is towards potential cyber-attacks. One valuable resource in this process is the Google Hacking Database, which contains advanced search queries used to uncover sensitive information and vulnerabilities across the internet.
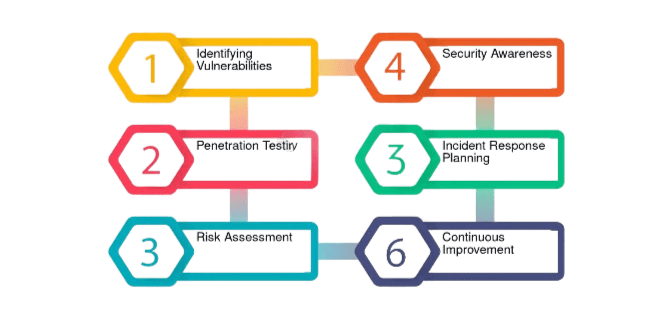
- Security Awareness: Ethical hacking increases the awareness of staff members and other stakeholders regarding the need for cybersecurity. Organizations can educate their labour force by showing them the risks and vulnerabilities that may strike an organization.
- Incident response planning: Ethical hacking can help organizations prepare and develop effective incident response plans by simulating various attack types. Organizations can then test against these attacks and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Ongoing Enhancement Ethical hacking is an activity that fosters ongoing improvement in cyber security. This will keep organizations abreast of the newest threats and best practices in security with the regular assessment and testing of their systems.
- Penetration Tester: professionals simulate Ethical Hacking on networks, systems, and applications to find vulnerabilities.
- Security Consultant: Experts advise organizations on building their overall security posture, including managing risk and ensuring compliance.
- Security Analyst: A security analyst monitors networks and systems to detect security breaches, respond to an incident, and ensure the security protocol is followed, often by completing Ethical Hacking Course to stay informed on the latest security threats and best practices.
- Vulnerability Assessor: A vulnerability assessor is an expert who specializes in finding weaknesses within software, networks, or infrastructure before they become suspicious of possible exploitation.
- Incident Responder: A responder to an incident is an expert who addresses security breaches, helping organizations contain and recover from cyberattacks.
To Earn Your Ethical Hacking Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Ethical Hacking Training Today!
Tools of the Trade for Ethical Hacker
Ethical hackers depend on a wide spread of specific tools in their search to identify and exploit the weaknesses in systems in search of security. However, one of the most important platforms is Kali Linux, being a Linux distribution, comes with more than 600 pre-installed penetration testing as well as security auditing tools; amongst them is Metasploit, Nmap, and Wireshark. Among others Metasploit is very helpful in simulating real-world attacks, automating exploits, and testing system defenses. Tools such as Wireshark capture network traffic and let hackers analyze that, while Nmap aids discovery of the network, pointing out which ports are open, what services are running, et cetera. However, while these tools are powerful, they highlight the need for strong Cyber Awareness across an organization. These other quite important tools include John the Ripper for breaking the passwords. Aircrack-ng-a suite to test the security of your wireless networks by cracking WEP as well as WPA-PSK encryption. Netcat is used for a really diverse kind of works like banner grabbing and reverse shells, Hydra however, is very common in most kinds of brute-force password attacks on many protocols. These tools form the backbone for all ethical hacking, therefore empowering professionals to find weaknesses in applications, strengthen defenses, and safeguard systems from potential threats. Mastery of them, coupled with an intrinsic grasp of cybersecurity, is necessary for anyone pursuing a career in ethical hacking.
Career Paths in Ethical Hacking & Cybersecurity
Are You Considering Pursuing a Cybersecurity Master’s Degree? Enroll For Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
Skills Required for Ethical Hacking
Technical competency is the first and most crucial skill that ethical hackers should acquire. It includes knowing different programming languages, operating systems, network protocols, and cybersecurity tools. A person should know how to use tools such as Metasploit, Nmap, and Wireshark, among others used for pen testing. Similarly, they must know deeply about attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and buffer overflows. Ethical hackers should be analytical in assessing vulnerabilities for possible computer systems and network breaches. One key aspect of this process involves understanding the use of Payloads, which are pieces of code or software designed to carry out specific actions, such as executing commands or extracting sensitive data once a vulnerability is exploited. Their analytical skills should enable them to employ critical thinking and creativity in developing ways that others will not see.
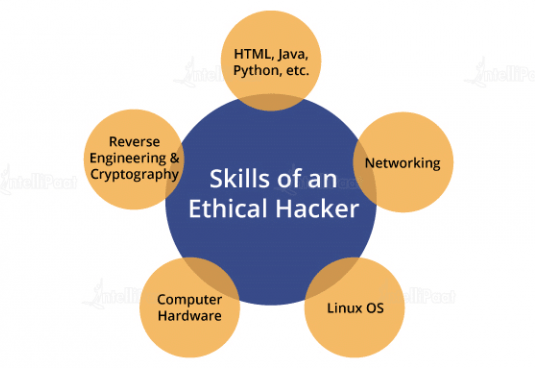
The term ethical refers to strict ethical practice from a hacker’s perspective. They have to use their skills for society’s betterment and not personal needs. Ethical hackers must maintain intense codes of conduct and are committed to observing specific ethical standards while providing services. They must learn and update their skills daily to counter what may emerge as a potential threat from attackers. Ethical hackers also need awareness of the latest threats and vulnerabilities, along with being updated with the latest security patches and updates. Becoming a good ethical hacker is a much more ideal requirement than mere technical skills. Ethical hackers must possess high analytical, communication, and ethical skills. They also need to constantly learn and enhance their skills to stay caught up with the attacker. Such skills enable ethical hackers to determine and fix loopholes before others misuse them.
Eligibility to Become an Ethical Hacker
Educational Qualification
Qualification means a university degree to enter a career in ethical hacking. Prospective ethical hackers must have academic qualifications to pursue advanced studies and certifications in cybersecurity. They need to have completed 10+2 or equivalent from a recognized board. They must have achieved a minimum aggregate percentage of 50% in their 10+2. Candidates should also appear for the relevant entrance test and clear the cut-off to get admission. Many recruiters want the candidates to have at least a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, cyber security, or anything related to that stream.
Technical Skills
To the professional in ethical hacking, technical skills will resonate since hacking may be necessary to grasp or exploit existing weaknesses in systems and networks. Hence, one’s ability to master one or more programming languages and understand different operating systems and such networking concepts is essential. The programming languages to be known must include Python, JavaScript, and C/C++. Familiarize the person with different operating systems, especially the Linux distributions, such as Kali Linux and Windows.
Cybersecurity Knowledge
Cyber security’s main principles and practical understanding form the core; ethical hackers must understand, which helps them determine, access, and mitigate security threats. A key skill for ethical hackers is understanding techniques like Google Dorking, which involves using advanced Google search queries to uncover hidden information or vulnerabilities on websites and web servers. Basic cybersecurity principles include threat landscapes, attack vectors, and protection methods.
Soft Skills
Soft skills include communication, problem-solving, and teamwork, all transitional between technical knowledge. They should be able to present complex technical facts understandably and work effectively with multiple teams. A good ethical hacker needs excellent verbal and written communication skills while presenting his findings to the members and the client. Critical thinking and complex problem-solving skills are required to determine and solve an ethical hacker’s internal weaknesses. High coordination and teamwork with other IT experts and security groups in implementing appropriate integrated security measures.
Certifications and Continuous Learning
These certifications will reflect your proper knowledge and skills that make you a desirable employee of any organization. On the other hand, however, continuous learning is required since the cybersecurity field is very dynamic and very fluid. Therefore, any ethical hacker should be current concerning the latest cybersecurity trends and technologies. Other certifications like CEH, OSCP, and CompTIA Security+ follow this. To prove that you have the capability and knowledge, you would continue with training programs, webinars, and cybersecurity conferences.
Legal and Ethical Standards
Ethical hackers hold themselves to high legal and ethical standards. Respect for confidentiality and privacy, as well as obtaining sufficient authority to hack, are some of the fundamental values. Ethical hackers need to follow strictly laid-down ethical standards and legal conditions. Respect privacy and confidentiality. Always have authorization before engaging in hacking activities. Continuous learning and experience, along with keeping up with the industry’s developments, are what will make a person a legitimate and esteemed ethical hacker.
Preparing for Ethical Hacking Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Ethical Hacking Interview Question & Answer
Conclusion
The job of an ethical hacker will depend on changing threats, but it will always be a strong cornerstone in any cybersecurity plan. To those who want to enter the industry, however, changing needs for cybersecurity professionals spell endless options. A very fulfilling and high-paying career is in store for the technically sophisticated problem solver interested in cybernetics and digital security. The more the field expands, the greater the job security, good pay, and impact potential through working in Ethical Hacking and cybersecurity employment, especially for those who have completed Ethical Hacking Course to enhance their skills and qualifications. Yet, proper training with credentials in ethical hacking and an excellent commitment to the code of ethics bode brightly for the next generation of cybersecurity professionals in this highly wanted industry. With such sophisticated cyber threats, a job undertaken by an ethical hacker will become ever so much more important as it identifies vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them. Such a profession guarantees highly paid salaries and the possibility of dealing with cutting-edge technologies and making a tangible difference in the protection of digital infrastructure. The demand for an ethical hacker will be great in sectors such as finance and healthcare, government, technology, and so on. With proper skills, certifications, and integrity, professionals can find space in this ever-growing and dynamic field, contributing to the battle against cybercrime.





