
- Introduction to Role
- Educational Background
- Core Responsibilities
- Required Skills
- Tools and Technologies Used
- Day-to-Day Activities
- Learning and Development
- Career Path
- Tips for Success
- Resume and Portfolio Tips
- Conclusion
Introduction to Role
Every profession or job role has a unique purpose, scope, and set of expectations. Understanding a role thoroughly is essential for anyone considering entering that career path, whether a student, job seeker, or professional looking to transition or grow. This guide will walk you through the critical aspects of a professional role from educational background and core responsibilities to the Resume and Portfolio Tips, tools used, and future career prospects.By the end of this article, Junior Business Analyst you will have a deep insight into what it takes to succeed in a Problem Solving particular job, how to prepare yourself, and what the career outlook looks like.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer Certification? Sign Up For Our Business Analyst Online Training Today!
Educational Background
Most professional roles require a specific educational foundation, though the level and type of education can vary widely depending on the field.
- Formal Education: Many roles demand at least a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field. For example, a software developer typically needs a degree in computer science, software engineering, or related areas. Roles in finance may require degrees in accounting, economics, or business administration.
- Advanced Degrees: Some specialized positions might require a master’s degree, MBA, or PhD. For instance, research-oriented roles, senior management positions, or specialized engineering jobs often prefer or require advanced education.
- Certifications and Diplomas: Beyond formal degrees, professional certifications validate expertise and skills. Examples include PMP for project managers, CPA for accountants, CISSP for cybersecurity professionals, or AWS certifications for cloud specialists. These certifications often enhance employability and career advancement.
- Non-traditional Education: Online courses, boot camps, and self-study have become increasingly valuable, Problem Solving especially in tech roles. Many employers now recognize Tools and Technologies Used demonstrated through projects or certifications over formal education alone.
- Key Deliverables: What are the main outputs or products you must deliver? For example, a marketing analyst’s deliverables might include market research reports, campaign performance analysis, and recommendations.
- Scope of Work: Does the role require individual Scope of Work, collaboration, or managing teams? Are you responsible for specific projects, client relations, or internal processes?
- Decision Making: Will you be expected to make autonomous decisions, or will your role be more supportive? Some roles require strategic thinking and leadership, while others focus on execution.
- Compliance and Standards: Many roles require adherence to industry standards, legal regulations, or company policies. For example, finance roles must comply with tax laws and auditing standards.
- Job-Specific Skills: These are the core competencies needed to perform the tasks. For example, a data analyst needs skills in SQL, Excel, and data visualization tools. A civil engineer needs proficiency in CAD software and structural analysis.
- Analytical Skills: Most roles require the ability to analytical Skills critically, whether it’s interpreting data, solving problems, or assessing risks.
- Digital Literacy: Competency in using relevant software and digital tools is essential. Even non-technical roles now expect familiarity with visualization tools, communication platforms, and basic software.
- Communication: Clear verbal and written communication is crucial, especially in roles involving teamwork, client interaction, or reporting.
- Time Management: Managing deadlines and prioritizing tasks ensures productivity and reliability.
- Adaptability: The ability to learn new skills, adjust to changing conditions, and stay updated with industry trends is invaluable.
- Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with colleagues, stakeholders, and clients is often required.
- Problem Solving and Creativity: Innovative thinking and troubleshooting are highly valued across all roles.
- Industry-Specific Software: For example, graphic designers use Adobe Creative Suite, while accountants use QuickBooks or SAP.
- Project Management Tools: Jira, Trello, Asana, or Microsoft Project are commonly used for task tracking and collaboration.
- Communication Platforms: Slack, Microsoft Teams, Zoom, or email are essential for daily communication.
- Data Tools: Excel, Tableau, Power BI, Python, or R may be used for data analysis roles.
- Development Environments: Software developers use IDEs like Visual Studio, Eclipse, or PyCharm.
- Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud skills are increasingly important.
- Routine Tasks: What regular activities will you perform? This could be attending meetings, reporting progress, coding, conducting tests, or client follow-ups.
- Interaction Levels: Will you spend time collaborating with teams, communicating with clients, or working independently?
- Pace and Environment: Is the Scope of work fast-paced and deadline-driven or steady and research-focused?
- Flexibility: Some roles require fieldwork, travel, or remote work flexibility.
- Professional Development: Many organizations offer courses, workshops, and certifications to upskill employees.
- Self-Learning: Employees are encouraged to stay updated on industry trends, new technologies, and best practices.
- Mentorship: Guidance from experienced colleagues or leaders can accelerate learning.
- Cross-Functional Exposure: Some roles offer opportunities to work across departments, broadening skillsets.
- Technical Complexity: Some roles require mastering complex systems or handling ambiguous problems.
- High Responsibility: Roles that impact business outcomes may involve pressure and accountability.
- Workload and Deadlines: Managing multiple priorities and meeting tight deadlines can be stressful.
- Communication Barriers: Miscommunication within teams or with clients can hamper progress.
- Keeping Skills Updated: Rapid technological change demands constant learning.
- Work-Life Balance: Depending on the role, maintaining balance may be difficult.
- Entry-Level Positions: Most roles have entry points requiring foundational skills and supervision.
- Mid-Level Roles: With experience, professionals take on more responsibility, complex tasks, and possibly team leadership.
- Senior and Leadership Roles: These include management, strategy, and decision-making responsibilities.
- Specializations: Professionals may choose to specialize in niche areas or broaden their scope.
- Lateral Moves: Switching to related roles or industries for growth or interest.
- Entrepreneurship: Experienced professionals may start consulting or own businesses.
- Build Strong Fundamentals: Master the core skills and knowledge your role demands.
- Be Proactive: Take initiative in learning, problem-solving, and contributing beyond assigned tasks.
- Develop Soft Skills: Communication, teamwork, and adaptability often distinguish top performers.
- Network: Build relationships inside and outside your organization.
- Seek Feedback: Constructive criticism helps improve performance.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of industry changes, tools, and technologies.
- Balance Workload: Manage time efficiently to avoid burnout.
- Document Achievements: Keep a record of your contributions for performance reviews and resumes.
- Tailor to the Role: Highlight skills and experiences relevant to the specific job.
- Use Action Words: Emphasize accomplishments with words like “developed,” “managed,” “implemented,” or “led.”
- Quantify Achievements: Use metrics to demonstrate impact, e.g., “Increased sales by 20%.”
- Showcase Tools and Technologies: Mention software and methodologies you are proficient in.
- Include Certifications: List relevant courses and certifications.
- Keep it Concise and Organized: Use clear headings and bullet points.
- Build an Online Portfolio: For creative or technical roles, showcase projects, code repositories, or case studies.
- Include Keywords: Many recruiters use ATS (Applicant Tracking Systems); use keywords from the job description.
Core Responsibilities
Every role has a defined set of core responsibilities: the primary tasks and duties you will be expected to perform daily, weekly, or monthly. Understanding these helps you prepare for what the job entails.
Required Skills
Skills required for a role can be broadly categorized into technical skills and soft skills.
Technical Skills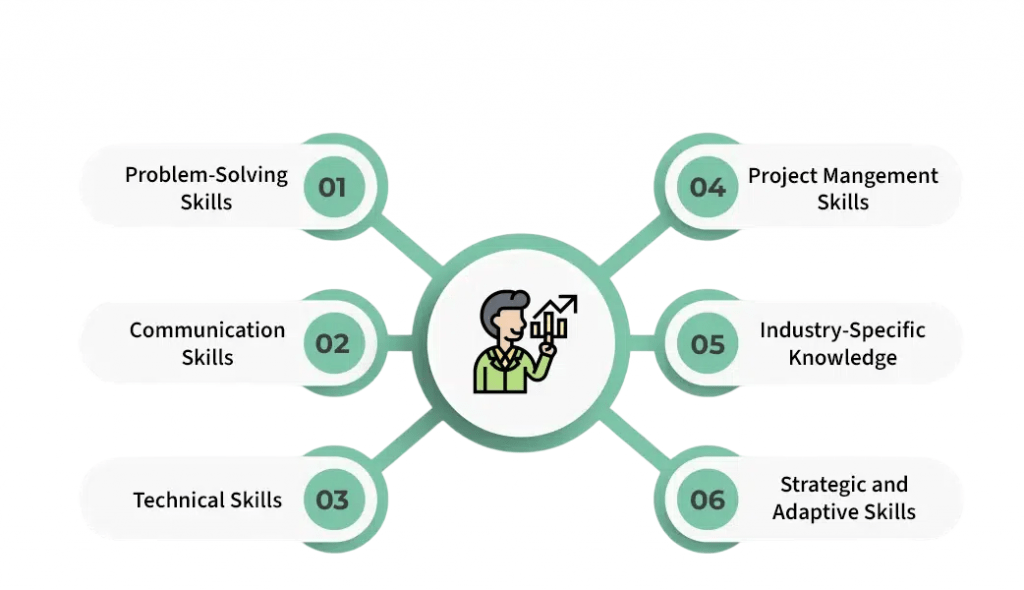
Are You Preparing for Business Analyst Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Business Analyst Interview Questions & Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Tools and Technologies Used
Modern workplaces leverage a variety of tools and technologies used to enhance efficiency and productivity. Familiarity with these can be a decisive factor in hiring and career growth.
Day-to-Day Activities
Understanding the daily workflow helps candidates visualize what their typical workday will look like.
Learning and Development
Continuous learning is key to career growth and job satisfaction. Onboarding and Training: New hires usually undergo induction training to understand company culture, visualization tools, and processes.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Business Analyst? Enroll For Business Analyst Masters Program Training course Today!
Challenges Faced
Every job has its challenges. Knowing them prepares you mentally and strategically.
Career Path
A well-defined career path motivates professionals and helps with long-term planning.
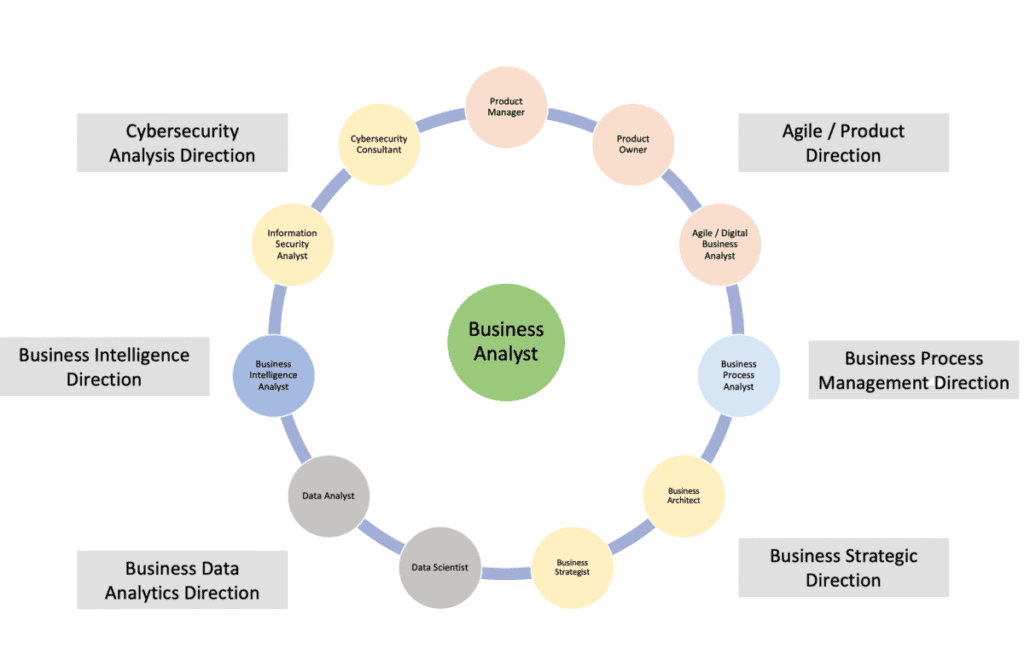
Are You Interested in Learning More About Business Analyst? Sign Up For Our Business Analyst Online Training Today!
Tips for Success
To excel in any role, consider the following:
Resume and Portfolio Tips
Your resume and portfolio tips are your professional brand. They must reflect your capabilities effectively.
Conclusion
A clear understanding of a professional role Junior Business Analyst from education and responsibilities to career prospects enables informed decisions and better preparation. Whether you are entering the Scope of Work, switching careers, or planning growth, this guide provides a foundational blueprint to navigate your journey.Success in any role requires a blend of skills, Analytical Skills Tools and Technologies Used knowledge, continuous learning, and strategic career management. By leveraging the Resume and Portfolio Tips and insights shared here, you can position yourself for a fulfilling and rewarding career.




