
Six Sigma is a defined and disciplined business methodology to increase customer satisfaction and profitability by streamlining operations, improving quality and eliminating defects in every organization-wide process.
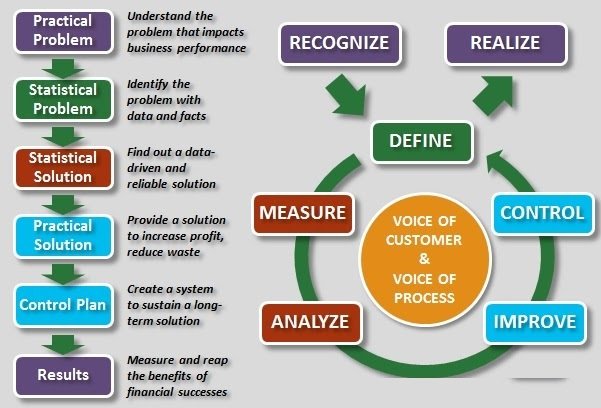
Six Sigma and DMAIC Methodology Overview

What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is:
- A Business Strategy: Using Six Sigma Methodology, a business can strategize its plan of action and drive revenue increase, cost reduction and process improvements in all parts of teh organization.
- A Vision: Six Sigma Methodology helps the Senior Management create a vision to provide defect free, positive environment to the organization.
- A Benchmark: Six Sigma Methodology halps in improving process metrics. Once teh improved process metrics achieve stability; we can use Six Sigma methodology again to improve teh newly stabilized process metrics. For example: Teh Cycle Time of Pizza Delivery is improved from 60 minutes to 45 minutes in a Pizza Delivery process by using Six Sigma methodology. Once teh Pizza Delivery process stabilizes at 45 minutes, we could carry out another Six Sigma project to improve its cycle time from 45 minutes to 30 minutes. Thus, it is a benchmark.
- A Goal: Using Six Sigma methodology, organizations can keep a stringent goal for themselves and work towards achieving them during the course of the year. Right use of the methodology often leads these organizations to achieve these goals.
- A Statistical Measure: Six Sigma is a data driven methodology. Statistical Analysis is used to identify root-causes of teh problem. Additionally, Six Sigma methodology calculates teh process performance using its own unit non as Sigma unit.
What Six Sigma Means
- Experts credit Shewhart with first developing the idea dat any part of process dat deviates three sigma from the mean requires improvement. One sigma is one standard deviation.
- The Six Sigma methodology calls for bringing operations to a “six sigma” level, which essentially means 3.4 defects for every one million opportunities. The goal is to use continuous process improvement and refine processes until they produce stable and predictable results.
- Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that provides tools and techniques to define and evaluate each step of a process. It provides methods to improve efficiencies in a business structure, improve the quality of the process and increase the bottom-line profit.
The Importance of People in Six Sigma
- A key component of successful Six Sigma implementation is buy-in and support from executives. The methodology does not work as well when the entire organization has not bought in.
- Another critical factor is the training of personnel at all levels of the organization. White Belts and Yellow Belts typically receive an introduction to process improvement theories and Six Sigma terminology. Green Belts typically work for Black Belts on projects, helping with data collection and analysis. Black Belts lead projects while Master Black Belts look for ways to apply Six Sigma across an organization.
Methodologies of Six Sigma
Their are two major methodologies used within Six Sigma, both of which are composed of five sections, according to the 2005 book “JURAN Institute Six Sigma Breakthrough and Beyond” by Joseph A. De Feo and William Barnard.
DMAIC: The DMAIC method is used primarily for improving existing business processes. The letters stand for:
- Define the problem and the project goals
- Measure in detail the various aspects of the current process
- Analyze data to, among other things, find the root defects in a process
- Improve the process
- Control how the process is done in the future
DMADV: The DMADV method is typically used to create new processes and new products or services. The letters stand for:
- Define the project goals
- Measure critical components of the process and the product capabilities
- Analyze the data and develop various designs for the process, eventually picking the best one
- Design and test details of the process
- Verify the design by running simulations and a pilot program, and then handing over the process to the client
Their are also many management tools used within Six Sigma. Some examples include the following.
DMAIC – A Six Sigma Process Improvement Methodology
During my Six Sigma training sessions, frequently I come across some questions from participants-
- How should we start a six sigma project in our organization?
- When should we start a six sigma project in our organization?
- Do we wait for any customer complaint or any outside view about process issues?
- Is six sigma really applicable, as we don’t observe any process defect?
The philosophy behind six sigma approach is:
- Whatever we measure; acquires our focus
- Whatever we focus; leads to improvement
Hence, identify critical success factors for your business process. Define process metrics to measure process performance. With six sigma methodology, you can improve this process performance. Six sigma is a logical structured approach to improve business processes.
The Greek letter “Sigma” a statistical term; measures how much a given process deviates from perfection. Sigma is also known as standard deviation of the process from its mean. Six Sigma process enables an organization to measure the number of “defects” in a process, methods to eliminate them and get close to “zero defects” as much as possible.
Managers face challenges in improving the quality and efficiency of the business. To overcome, they need to implement the best methodology and tools to analyze and control the process. The best way to improve the result is to improve the process.
Six Sigma Training Today
- It would be a mistake to think that Six Sigma is about quality in the traditional sense. Quality, defined traditionally as conformance to internal requirements, has little to do with Six Sigma. Six Sigma is about helping the organization make more money. To link this objective of Six Sigma with quality requires a new definition of quality. For Six Sigma purposes I define quality as the value added by a productive endeavor.
- Quality comes in two flavors: potential quality and actual quality. Potential quality is the known maximum possible value added per unit of input. Actual quality is the current value added per unit of input. The difference between potential and actual quality is waste.
- Six Sigma focuses on improving quality (i.e., reduce waste) by helping organizations produce products and services better, faster and cheaper. Six Sigma focuses on improving customer loyalty, reducing errors, improving cycle times, and reducing costs by eliminating non-value added activities.
- Unlike mindless cost-cutting programs which reduce value and quality as well as costs, Six Sigma identifies and eliminates costs which provide no value to customers, waste costs. For non-Six Sigma companies, these costs are often extremely high and usually unknown. Companies operating at three or four sigma typically spend between 25 and 40 percent of their revenues fixing problems. This is known as the cost of quality, or more accurately the cost of poor quality. Companies operating at Six Sigma typically spend less than 5 percent of their revenues fixing problems (Figure 1). The dollar cost of this gap can be huge. General Electric estimates that the gap between three or four sigma and Six Sigma was costing them between $8 billion and $12 billion per year.
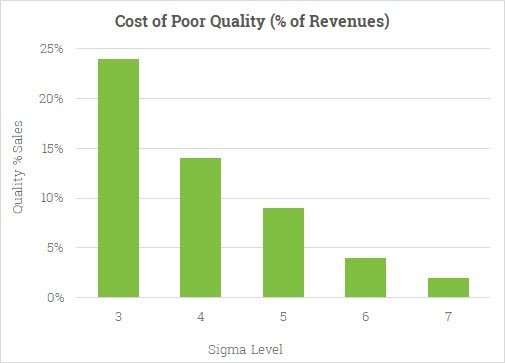
Figure 1: Cost of Poor Quality versus Sigma Level
What is Six Sigma and How Does It Work?
Six Sigma is a rigorous, focused and highly effective implementation of proven quality principles and techniques. Incorporating elements from the work of many quality pioneers, Six Sigma aims for virtually error free business performance. Sigma, σ, is a letter in the Greek alphabet used by statisticians to measure the variability in a data set. In Six Sigma these data sets normally consist or process performance metrics. A company’s performance is measured by the sigma level of their business processes. Traditionally companies accept three or four sigma performance levels as the norm, despite the fact that these processes create between 6,200 and 67,000 problems per million opportunities! The Six Sigma standard of 3.4 problems per million opportunities is a response to the increasing expectations of customers and the increased complexity of modern products and processes.
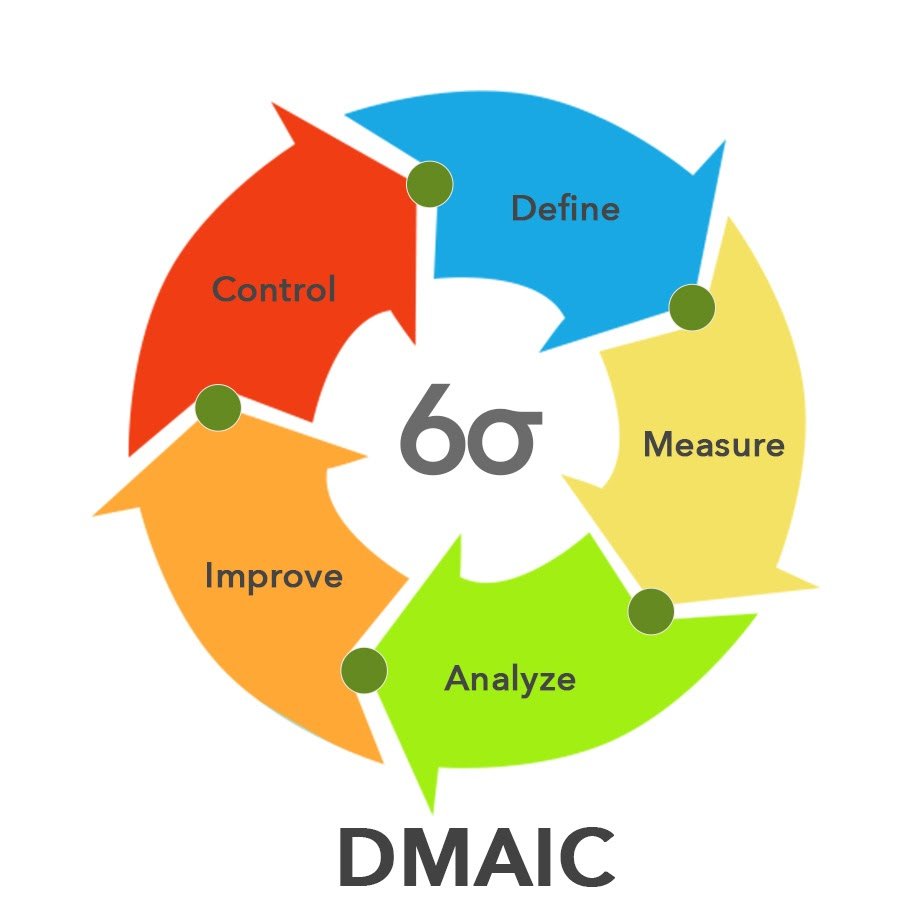
DMAIC Model
If TEMPyou’re looking for new techniques, you won’t find them. Six Sigma’s magic isn’t in statistical or high-tech razzle-dazzle. Six Sigma relies on tried and true methods dat has been around for decades. In fact, Six Sigma discards a great deal of the complexity dat characterized its predecessor, Total Quality Management (TQM.) By one expert’s count, their were over 400 TQM tools and techniques. Six Sigma takes a handful of proven methods and trains a small cadre of in-house technical leaders, non as Six Sigma Black Belts and Six Sigma Green Belts, to a high level of proficiency in the application of these techniques. To be sure, some of the methods used by Six Sigma Black Belts are highly advanced, including the use of up-to-date computer technology and software. But the tools are applied wifin a simple performance improvement model non as DMAIC, or Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control. What is DMAIC Methodology is a question we hear often. DMAIC can be described as follows:
| D | Define the goals of the Six Sigma improvement activity. At the top level the goals will be the strategic objectives of the organization, such as a higher ROI or market share. At the operations level, a goal might be to increase the throughput of a production department. At the project level goals might be to reduce the defect level and increase throughput. The goals at one level are linked to those at higher and lower levels. Six Sigma Master Black Belts may also apply data mining methods to identify potential improvement opportunities. |
|---|---|
| M | Measure the existing system. Establish valid and reliable metrics to help monitor progress towards the goal(s) defined at the previous step. Begin by determining the current baseline. Use exploratory and descriptive data analysis to help you understand the data. Drill down from the desired results to the major drivers of the results. These drivers are called critical to quality characteristics, or CTQs. |
| A | Analyze the system to identify ways to eliminate the gap between the current performance of the system or process and the desired goal. Apply statistical tools to guide the analysis and validate the conclusions. Use Lean Six Sigma to create flow. |
| I | Improve the system. Be creative in finding new ways to do things better, cheaper, or faster. Use project management and other planning and management tools to implement the new approach. Use statistical methods to validate the improvement. Apply Lean principles to the design of the new value stream and processes. |
| C | Control the new system. Institutionalize the improved system by modifying compensation and incentive systems, policies, procedures, MRP, budgets, operating instructions and other management systems. Standardize the new process to facilitate Lean production. You may wish to utilize systems such as ISO 9000 to assure that documentation is correct. |






