
- Introduction
- What is Spoofing?
- Types of Spoofing
- How Does Spoofing Work?
- Risks and Consequences of Spoofing
- How to Protect Yourself from Spoofing
- Conclusion
Spoofing is a deceptive tactic used to impersonate legitimate entities in order to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive information, or manipulate systems. It involves altering or falsifying data such as IP addresses, email headers, or website content to deceive the target into believing the communication is from a trusted source. To prevent such attacks, it is essential to enroll in Cyber Security Training Courses that teach how to identify and protect against these threats. In this blog, we will explore spoofing, its various types, and how it poses significant security risks. We will also discuss effective prevention techniques, common spoofing methods, and how organizations can protect themselves from falling victim to these attacks. Additionally, we will cover tools and strategies for detecting and mitigating spoofing threats.
Interested in Obtaining Your Spoofing Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Introduction
Spoofing is the type of cyberattack where the malicious actor tries to pretend as someone or something else to obtain access to confidential data, cause service disruptions, or mislead people. It can be perpetrated in several ways, targeting systems, networks, and communications in different forms. Spoofing is commonly known as one of the easiest methods a cyber-criminal can employ against his or her victim. It can take many forms, whether it be an email, website, or even an IP address. Understanding techniques such as Decryption in Cybersecurity is essential for protecting against spoofing and other similar threats. Spoofing exploits trust by masquerading as a legitimate entity, tricking victims into revealing sensitive information, downloading malware, or disrupting services, making it a highly effective yet deceptive tactic used by cybercriminals across various platforms such as emails, websites, and network communications. Spoofing types, processes, and safety precautions against attacks, all covered in this post.
What is Spoofing?
Spoofing can be defined as an act to impersonate or simulate a legitimate identity to mislead someone. In cyber security, spoofing may relate to the manipulation of the communication source or cover the actual source identity of the sender in the course of malicious action. Spoofing techniques create false legitimacy over malicious actions which result in many vulnerabilities and breaches in security. Spoofing can come in various forms, either through emails, websites, network addresses, or even satellite navigation systems. Implementing strategies like Whitelisting can help mitigate these threats by allowing only trusted sources to access critical systems and information. Since spoofing is based on deception, it is hard to distinguish between the threat and naught. Sometimes individuals and organizations might realize it is too late.
In satellite navigation systems, GPS spoofing misleads navigation systems by providing false location data, which can result in significant disruptions, especially in sectors like transportation or defense. Since spoofing relies heavily on deception, it can be difficult to detect, and often, the threat goes unnoticed until it’s too late. Organizations and individuals may realize they have been compromised after sensitive data has been exposed or systems have been breached. To mitigate the risks of spoofing, it’s important to adopt comprehensive security practices such as using encryption, multi-factor authentication, and anti-spoofing technologies, as well as educating users about identifying suspicious activity. Keeping systems updated and staying informed about emerging spoofing techniques is essential to stay ahead of cybercriminals.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Spoofing? Sign Up For Our Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Types of Spoofing
Spoofing attacks come in various types that target specific aspects of communication and technology. Here are some of the main types of spoofing:
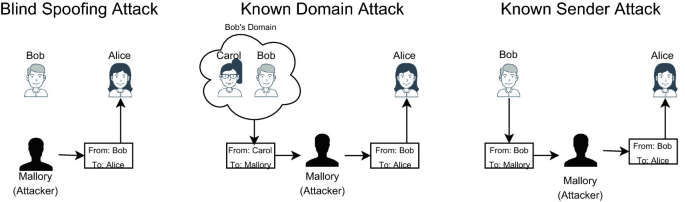
- Email Spoofing: Email spoofing is a kind of attack whereby an attacker sends an email that looks like it originates from a trusted source, be it a colleague, a company, or even an official organization like a bank. The attacker forges the “From” address of the email to make it look legitimate.This includes gaining access to confidential information, passwords, credit card details, and usernames, or by making the victim click on malicious links or downloading attachments containing malware. Most phishing attacks involve spoofing an email to trick users into giving up personal or confidential information.
- IP Spoofing: IP spoofing is when an attacker spoofs the source IP address of a packet so that the data appears to be coming from a trusted IP address. Here, the goal is to conceal one’s identity so that it can be possible to bypass the network security mechanisms or cause the victim to respond to the falsified address. Ensuring strong E-mail Security measures can help protect against such tactics by verifying the authenticity of the sender and preventing malicious impersonation.
- DNS Spoofing: DNS spoofing, also known as cache poisoning, is an attack whereby an attacker inserts corrupt data into the DNS resolver cache. Because DNS queries are often redirected to a malicious site without the knowledge of the user who is trying to access the website, this malicious site could be a spoofed login page that steals the username and password or tries to install some form of malware.DNS spoofing can weaken the integrity of web traffic and can be used during phishing campaigns or session hijacking an online session with a user.
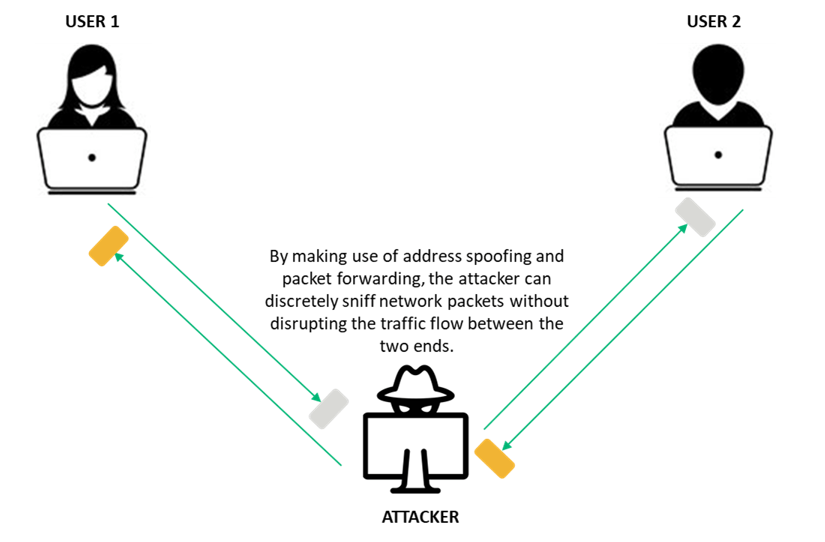
- ARP Spoofing: ARP spoofing is an attack on a local network where the attacker sends fake ARP messages to bind his MAC address with the IP address of some other device like a gateway. This way, the attacker can steal the network traffic, and conduct man-in-the-middle attacks, or even DoS attacks.ARP spoofing is particularly dangerous in a local area network (LAN) as it can be used to snoop into communications between devices or manipulate data being transferred.
- GPS Spoofing: GPS spoofing is a technique of faking GPS signals to make the GPS receiver think it is in a different location when it isn’t. This is widely used to deceive navigation systems, redirect vehicles or drones, and disturb tracking systems.Spoofing has been used against the transportation system, drones, and even military operations with misleading GPS data causing great havoc.
How does Spoofing Work?
Typically network spoofing attacks are pattern-based deceptions: impersonation or changing data in a form that is likely to mislead the target. In most cases, here is how spoofing works.Source Obfuscation, In this, the source of the message or data is hidden by the attacker such that it may seem to emanate from a trusted source. In Data Manipulation, certain attacks involve hackers changing the content of messages, packets, or requests to seem legitimate. To better understand and defend against these types of attacks, it’s important to participate in Cyber Security Training Courses that teach how to detect and prevent such malicious activities. For instance, through DNS poisoning, they forward users to forged sites.Exploiting Trust Spoofing Trust is exploited by the victim whether it’s an email, a website, or an IP address. Trust is exploited so that attackers manipulate people into taking actions such as clicking on links, downloading files, or providing sensitive information.Spoofing works well because most systems and people rely solely on the integrity of the communication, which is hard to verify in real time. Attackers mask their identity to bypass the security measures put in place and gain unauthorized access to data or systems.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cybersecurity? Enroll in the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
Risks and Consequences of Spoofing
Spoofing can result in severe consequences both on an individual and organizational level. Implementing effective Vulnerability Management practices can help identify and address weaknesses that could be exploited by spoofing attacks, reducing the risk of such consequences. Some of the risks associated with spoofing include:
- Identity Theft: Impersonating trusted entities, the attackers can access personal information, such as usernames, passwords, and bank account details, thereby causing identity theft and financial fraud.
- Data Breaches: Spoofing attacks can be used to steal sensitive corporate data, intellectual property, or trade secrets, which may lead to serious financial losses and reputational damage.
- Malware Infections: Attackers often use spoofing as a method to spread malware, such as ransomware that can encrypt files or cause some other form of damage to the system.
- Financial Loss: The most common use of spoofing attacks is to deceive victims into transferring money or giving up their payment details, thus losing a lot of money.
- Service Disruption: In IP or ARP spoofing, an attacker may disrupt your network services or engage in DDoS attacks that render systems or websites unavailable to legitimate users.
How to Protect Yourself from Spoofing
Spoofing can be difficult to detect, but there are several things to do to protect yourself and your organization:Use Strong Authentication Methods. Utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) that adds a layer of protection to accounts and systems.Educate Users: Educate your employees and users about the threat of spoofing and how they can identify suspicious emails, messages, or links. Deploy Anti-Spoofing Technologies. Employ tools such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) to safeguard against email spoofing. Always verify suspicious requests for sensitive information via phone or other means, especially when received via email or other untrusted channels. Use Secure Networks. Ensure that your network is secure by using firewalls, VPNs, and encryption to protect against IP spoofing and ARP spoofing. Additionally, enable Two-Factor Authentication to add an extra layer of security and help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. Monitor DNS Records.Use DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) to protect against DNS spoofing attacks and ensure the authenticity of your DNS records. This adds an extra layer of security, safeguarding your network from potential man-in-the-middle attacks and unauthorized data manipulation.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Spoofing is a deceitful technique that cybercriminals use to pretend to be legitimate entities and exploit trust to perform malicious activities. There are various forms of spoofing, including email spoofing, IP spoofing, DNS spoofing, ARP spoofing, and GPS spoofing, by which attackers can deceive victims into revealing sensitive information, spreading malware, or disrupting services. IP spoofing involves altering the source IP address in data packets to make it appear as though they come from a trusted network, while DNS spoofing redirects users to fraudulent websites without their knowledge. To effectively defend against these threats, it’s crucial to take Cyber Security Training Courses that provide in-depth knowledge and strategies for safeguarding against such attacks. ARP spoofing manipulates the Address Resolution Protocol to intercept communication between devices on a network, enabling attackers to steal sensitive data. Understanding how spoofing works, being aware of the risks it poses, and practicing strong security measures will help reduce the vulnerability of individuals and organizations to such attacks. Stay alert, take preventive measures, and ensure that your cybersecurity strategies are up-to-date to protect yourself from the growing threat of spoofing.





