
- Introduction
- Definition and Purpose of Data Loss Prevention
- Types of DLP (Network DLP, Endpoint DLP)
- Technologies and Techniques Used in DLP
- Key Components of DLP Systems
- Policies and Procedures in DLP
- Challenges in Implementing DLP
- Best Practices for Data Loss Prevention
- Conclusion
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) refers to a set of strategies, tools, and processes used to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, sharing, or loss. The primary approaches of DLP involve identifying and classifying sensitive information, monitoring its movement across networks, and enforcing policies to prevent data breaches. These policies may include blocking, encrypting, or alerting administrators about suspicious activities. Cyber Security Training Courses often cover DLP techniques, teaching professionals how to implement these policies effectively to safeguard sensitive data within organizations. Best practices for implementing DLP include defining clear data protection policies, regularly updating classification methods, leveraging advanced monitoring tools, training employees on data security, and maintaining continuous monitoring and reporting to ensure compliance and mitigate risks.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Introduction
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, focusing on safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access, misuse, or loss. In today’s digital age, organizations face numerous threats ranging from insider breaches to external cyberattacks, making DLP solutions essential for protecting data. This content provides a comprehensive overview of DLP, including its definition, purpose, and types Network DLP and Endpoint DLP. Understanding DLP is especially important when managing security in a Demilitarized Zone, where sensitive data needs to be protected from external threats while still being accessible to authorized users. It delves into the technologies and techniques used in DLP, key components of DLP systems, and best practices for ensuring effective data protection. Furthermore, it highlights the challenges organizations face when implementing DLP and offers strategies to overcome them. By following the guidance provided, businesses can enhance their data protection efforts, reduce the risks of data leaks, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Definition and Purpose of Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) refers to a set of strategies, technologies, and policies to prevent unauthorized access, misuse, or loss of sensitive data within an organization. DLP solutions are designed to monitor and control the movement of sensitive data within and outside the corporate network, ensuring that it is not leaked, stolen, or inadvertently exposed. The primary purpose of DLP is to protect confidential information from being lost, accessed by unauthorized users, or unintentionally exposed, which could lead to security breaches, regulatory non-compliance, or financial losses. DLP is an essential part of an organization’s cybersecurity framework. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding intellectual property, personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, and trade secrets. By implementing DLP solutions, businesses can mitigate the risks associated with data breaches, data leakage, and insider threats, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical information.
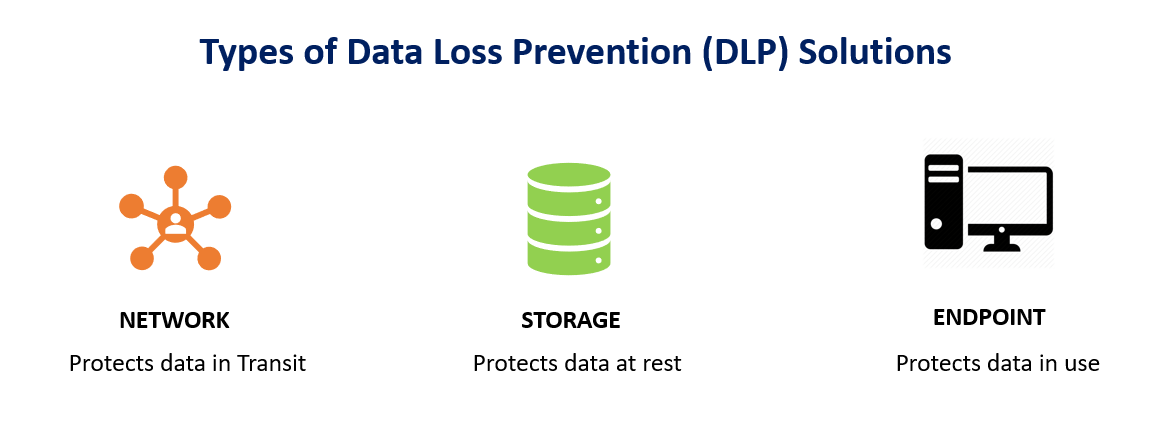
Types of DLP (Network DLP, Endpoint DLP)
- Network DLP: Network DLP focuses on monitoring and controlling the flow of sensitive data across the organization’s network. It inspects network traffic, including emails, file transfers, and web traffic, to detect and prevent unauthorized access or transmission of sensitive information.
- Use Cases: Preventing data leaks via email, social media, cloud storage services, or unauthorized file transfers. Network DLP solutions are typically deployed at network boundaries (firewalls, proxies) to intercept outgoing communications. These measures are especially important in defending against tactics like a Watering Hole Attack, where attackers target specific websites to compromise users and gain access to sensitive information.
- Advantages: Offers centralized monitoring and controls data at the network level, providing real-time protection against data leaks.
- Endpoint DLP: Endpoint DLP focuses on securing sensitive data at the endpoints, such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices. It involves monitoring and restricting data access and transfer operations on these devices, such as copying data to USB drives, printing, or emailing.
- Use Cases: Prevent employees from transferring sensitive data to personal devices, USB drives, or unauthorized applications. Endpoint DLP is critical in controlling data movement across endpoints and enforcing security policies on these devices.
- Advantages: Provides granular control over sensitive data on individual devices, allowing organizations to apply specific policies on a per-user or per-application basis.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Technologies and Techniques Used in DLP
- Content Inspection often uses deep content inspection, where the system scans the content of files, emails, or web traffic to identify sensitive information based on predefined patterns (e.g., credit card numbers, Social Security numbers, or proprietary business data).
- This technique includes keyword matching, regular expression matching, and fingerprinting (identifying patterns unique to specific documents).
- Contextual Analysis to inspect the content, DLP systems also perform contextual analysis, which involves understanding the context in which the data is being used.
- This can help determine whether the transmission of sensitive information is legitimate (e.g., a finance team sending a budget report) or potentially malicious (e.g., an employee emailing sensitive data outside the organization).
- Contextual analysis can involve user behavior analysis, location-based restrictions, and network traffic patterns. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), user identity verification, and auditing of access logs are common techniques.
- Data Encryption is commonly used as part of DLP solutions to ensure that sensitive data remains protected, even if it is transmitted outside the organization’s network.
- Encryption can be applied to both data at rest (stored data) and data in transit. Cyber Security Training Courses teach students the importance of securing both types of data and how to implement encryption protocols to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of information.
- Secure protocols like TLS/SSL and encryption algorithms (AES, RSA) are used to protect data during transmission and storage.
- Access Control uses access control mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users can access or modify sensitive data. This includes role-based access control (RBAC) and mandatory access control (MAC).
- Policy Enforcement policies by defining actions based on the sensitivity of the data and the context in which it is being accessed. For example, if a user tries to upload a sensitive document to a public cloud storage service, the DLP system might block the action or encrypt the document before allowing the upload.
- Predefined policies, real-time alerts, and automated responses (block, quarantine, notify) are used to enforce security measures.
Key Components of DLP Systems
DLP (Data Loss Prevention) systems play a crucial role in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, sharing, or leaks. These systems begin by identifying and classifying sensitive data, such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII) or financial records, using automated tools like content discovery and classification tools. Once the sensitive data is identified, DLP systems continuously monitor its usage and movement across the network, observing network traffic, user activities, and device interactions with tools such as network sensors and endpoint agents. This monitoring is closely tied to Malware Analysis, where suspicious activities and potential threats are identified, analyzed, and mitigated to prevent data leaks or security breaches. This monitoring ensures that sensitive data is handled appropriately.
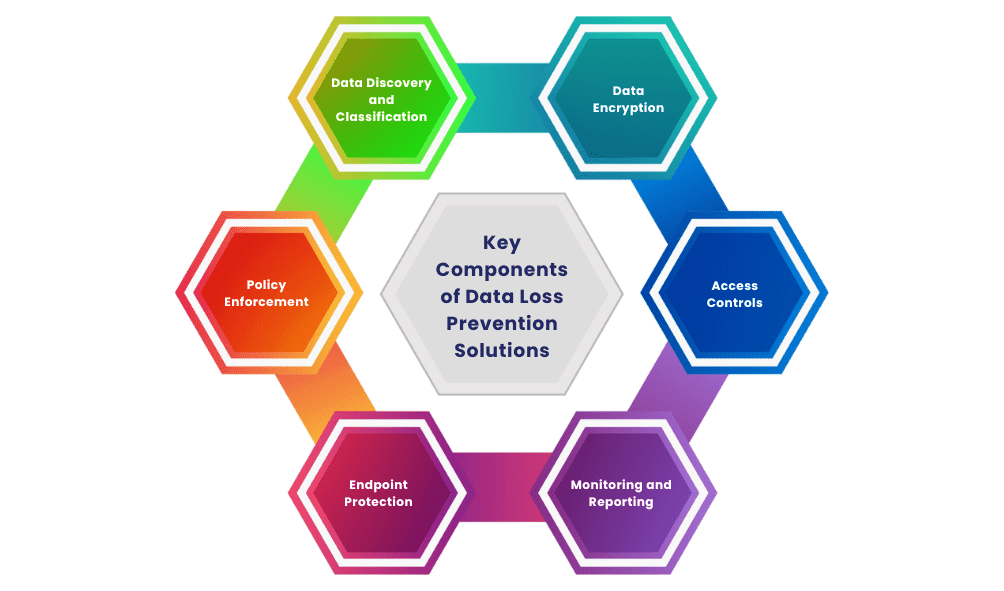
Based on predefined policies, DLP systems can take automated actions to protect data. These actions may include blocking unauthorized attempts to access or transfer sensitive data, encrypting the data to prevent exposure, or notifying administrators of potential security breaches. Furthermore, DLP solutions generate comprehensive reports and logs, which provide valuable insights into the organization’s data protection efforts. These reporting dashboards and audit trails assist organizations in maintaining compliance with regulations and improving overall security posture by enabling visibility into data activities and facilitating prompt responses to potential threats.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cybersecurity by Enrolling in Our Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course.
Policies and Procedures in DLP
Data Classification Policy:- This policy helps classify data into different sensitivity levels, such as public, internal, confidential, and restricted. Once classified, appropriate DLP policies can be applied based on the sensitivity of the data. Access Control Policy:
- Establishes rules on who can access sensitive data and how it can be shared. This policy should define role-based access and enforce the principle of least privilege. Incident Response and Reporting:
- Procedures should be in place to respond to data loss incidents. This includes reporting mechanisms, investigation processes, and corrective actions. Data Retention and Disposal Policy:
- Establishes rules for the retention of sensitive data and its secure disposal once it is no longer needed. This ensures that data is not unnecessarily retained, reducing the risk of exposure. User Awareness and Training:
- Regular training for employees on data handling, security policies, and the risks of data loss is crucial. Employees must be aware of the procedures for handling sensitive information.
Challenges in Implementing DLP
Implementing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions comes with several challenges. DLP systems often produce false positives, blocking legitimate data transfers, or false negatives, failing to detect actual data leaks. Fine-tuning these systems is complex and time-consuming. Additionally, accurately classifying sensitive data across various systems and applications is difficult, and manual classification can lead to errors, while automated methods may not always be reliable. Integrating Threat Intelligence into data classification processes can enhance accuracy by providing real-time insights into emerging threats and potential vulnerabilities, helping to improve the overall reliability of data protection measures. Employee resistance is another hurdle, as users may find DLP controls restrictive, requiring a balance between security and user convenience. Scaling DLP solutions to handle growing data volumes and more complex environments can also be challenging, and integrating DLP with other security systems like SIEM and endpoint protection can be resource-intensive and complex.
Best Practices for Data Loss Prevention
- Develop clear, actionable DLP policies that address data classification, access control, and permissible actions for each type of data.
- Monitor both network and endpoint activities to ensure comprehensive coverage. Use DLP tools to protect data in transit, at rest, and during use.
- Provide regular training to employees about the importance of data protection, common security threats, and how to follow DLP policies.
- Ensure that sensitive data is encrypted both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access during storage and transfer.
- Regularly review and update DLP policies to adapt to changes in the organization, emerging security threats, and new regulatory requirements.
- Automate DLP policy enforcement to ensure consistent protection of sensitive data. Using encryption methods like the RSA Algorithm enhances security by safeguarding information during transmission.
Preparing for a Cyber Security Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers
Conclusion
In conclusion, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a critical component of modern cybersecurity strategies aimed at safeguarding sensitive information within organizations. By implementing a comprehensive DLP solution, businesses can prevent unauthorized access, data leaks, and misuse of confidential information, whether it’s transmitted via network channels or stored on endpoints. The combination of technologies, such as content inspection, contextual analysis, and encryption, along with well-defined policies, plays a vital role in ensuring that sensitive data is protected. Cyber Security Training Courses provide in-depth knowledge of these technologies, equipping students with the skills needed to implement and manage data protection strategies effectively in real-world scenarios. While implementing DLP can come with challenges such as false positives, scalability, and integration issues, following best practices like clear policy definitions, employee education, and regular updates can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to prevent data loss. Overall, DLP solutions help mitigate risks, ensure compliance, and protect an organization’s intellectual property, reputation, and financial well-being.





