
- What is Reverse Engineering?
- Why is it done this way?
- Why Do We Need?
- The role it plays in cybersecurity
- Is it Unlawful to Reverse Engineer?
- What Procedures Are Included in this Engineering?
- Kinds of rivers technologies
- Tools for this Engineering
- Conclusion
This technique is powerful for dissecting and analyzing products, systems, or software to understand the design, functionality, and underlying principles. This takes something apart into its various constituent parts, allowing security engineer and researchers to know how it works and identify short comings, sometimes inspiring innovation in new solutions. In the context of Whitelisting, this process can help security professionals understand which applications, processes, or files are deemed safe and trusted. Most notable is this common practice in software development, hardware design, and product manufacturing, where a professional develops established technologies, debugs problems, and stimulates idea generation for solutions to problems.
To Earn Your Cyber Security Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
What is reverse engineering?
Analyzing a product, system, or component to comprehend its construction, functionality, and operation is known as reverse engineering. It entails going backward from the finished product to learn how it was often created, assembled, or designed to duplicate or enhance it. In the field of Cyber Security Training Courses, reverse engineering plays a critical role in identifying vulnerabilities, discovering hidden threats, and understanding the inner workings of malicious software. By deconstructing malware or insecure systems, cyber network security professionals can develop countermeasures, patch vulnerabilities, and improve overall security defenses.
Why is it done this way?
It is a method used to comprehend a product or technology’s operation completely. When knowledge of the original structure or design is difficult to obtain or requires detailed examination, it is done. The key objective is to get a thorough grasp of how things work. This procedure entails inspecting and decoding technology to uncover its core concepts, parts, and functionality. It accomplishes several goals, including discovering possible computer security flaws, improving or optimizing technology, developing suitable substitutes, and learning from previous solutions.
Why Do We Need?
One method for completely comprehending the operation of a technology or product is the reverse. When the original design or construction knowledge is difficult to obtain or requires detailed examination, it is done. In the context of Web Application Security, reverse engineering plays a critical role in identifying vulnerabilities in web applications. The fundamental objective is to obtain a thorough understanding of how things work. This procedure entails dissecting and deconstructing the technology to expose its basic ideas, elements, and workings. It accomplishes several goals, including finding potential security flaws, improving or optimizing technology, developing appropriate substitutes, guaranteeing the longevity of products, and learning from previous solutions.
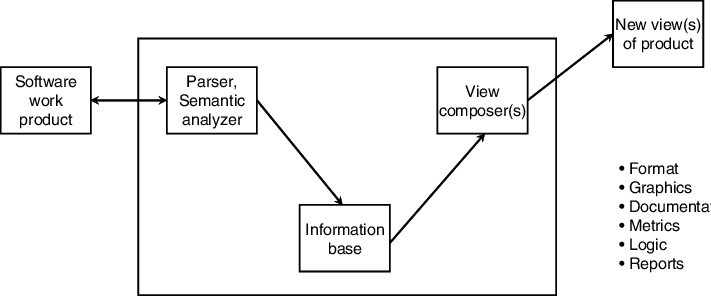
The role it plays in cybersecurity
- Understanding: Even if the original design or documentation for a technology or product is unavailable, it can help people understand how it operates. They can learn more about the inner workings, systems, and procedures involved.
- Learning from Pre-Existing Solutions:Using reverse, researchers, engineers, and developers can examine and absorb knowledge from pre-existing solutions. They can learn from successful designs and technology, recognize best practices, and incorporate those insights into their work.
- Reproduction or reconstruction:It can occasionally replicate a product or technology. In the context of the Internet of Things, reverse engineering is often used to replicate or understand how IoT devices work. By breaking down the technology behind these connected devices, researchers and developers can identify vulnerabilities.
- Enhancements and Improvements:This allows engineers to determine the advantages and disadvantages of current technologies. By identifying and comprehending a system or product’s shortcomings, engineers can improve and enhance its design, functionality, and security.
- Security Analysis:By examining the underlying code or structure, security professionals can find vulnerabilities, potential exploits, or weaknesses that could be dangerous. This data can then be used to strengthen security protocols and guard against threats.
- Software Development:
A corporation could reverse engineer a legacy software system, for example, to guarantee compatibility with modern technology or to make changes.Reverse engineering becomes a feasible measure to ensure that legacy systems may be continued in operation within a company-wide technology policy.
- Hardware engineering:
Hardware components can be reverse-engineered to better comprehend, troubleshoot, or understand how microchips or circuit boards work. This is typical in the electronics business.
- Automotive Industry:
In the realm of cybersecurity, Keylogger can be used by attackers to “dissect” a victim’s keystrokes, recording sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or personal messages.
- Security analysis:
Security experts use engineering to analyze malware or other potentially dangerous software. This aids in comprehending threats and creating defenses against them.
- Consumer electronics:
Users and technicians may reverse engineer smartphones and other devices to unlock new features, alter software, or fix hardware faults.
- Aerospace Industry:
To increase performance, safety, and efficiency, engineers may reverse engineer aircraft components. Through reverse engineering the aircraft components, one becomes able to see even better into the design faults or inefficiencies and therefore improves effectiveness in optimizations. It contributes towards a better material, aerodynamics, and performance in all other aspects, thus a more secure and fuel-economic airplane.
- Fashion & Apparel:
To comprehend the construction of clothing products and replicate similar styles, clothes designers may employ the reverse.Reverse engineering allows designers to learn the patterns, materials, and stitch of a successful product. They can reproduce the same kind of style or invent something new but with good quality and craftsmanship.
- Medical Devices:
Prosthetics and orthopedic implants are two examples of medical devices used to research and improve.Reverse engineering of prosthetics and orthopedic implants in medical devices allows the carrying out of research on key features of the design for improvement to support the needs of patients better.
- Ghidra: The National Security Agency (NSA) created Ghidra, a free and open-source engineering tool that supports the analysis of harmful code and the detection of software flaws.
- OllyDbg: This debugger was created especially for Microsoft Windows. It is employed in analyzing and comprehending 32-bit software’s assembly-level code.
- Radare2: An open-source framework for binary file analysis and reverse, Radare2 offers some network security tools. It provides features like debugging and disassembly.
- AutoIt: This Windows app is one of its frequent uses. In the context of Google Dorking, scripting languages can be leveraged to automate the search for vulnerable or misconfigured systems online.
- IDA Python: Users may create Python scripts to automate various engineering activities. IDA Pro is a programming tool.
- JD-GUI: A Java decompiler that can reverse engineer Java programs to produce code that is understandable by humans.
- IDA Decompiler: An IDA Pro addon that simplifies the process of decomposing binaries into a higher-level programming language so that the logic of the code may be understood more easily.
- PEiD: A software development tool for locating and identifying compilers, packers, and cryptors. To find out if a file has been obfuscated, use this tool.
- ReClassEx: A reverse and memory analysis tool that allows you to examine C++ and C code in software applications.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cybersecurity? Sign Up For Our Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Is it Unlawful to Reverse Engineer?
Intellectual Property Rights If the object of reverse is covered by trade secrets, copyrights, or patents, then doing so without authorization may violate these rights. Ethical hacker can raise ethical concerns even when it isn’t specifically prohibited, particularly when privacy or security are compromised. Security Research To find weaknesses and strengthen Cyber Security Training Courses, engineering is frequently accepted as legitimate and even encouraged. Competition and Fair Use Reverse may be permitted for fair competition and interoperability.
What Procedures Are Included in This Engineering?
First analysis entails a cursory analysis of the technology to comprehend its function, architecture, and constituent parts fully. Record keeping Document as much information as possible about the technology, including its features, behavior, and physical attributes. Decomposition Dissect the technology into its most basic element. In the case of software, this could entail reviewing the code and breaking it into digestible chunks. This process is crucial for identifying Risk Threat and Vulnerability in software systems. This process is especially useful in identifying potential cyber threats within the software. By analyzing the code, cybersecurity experts can pinpoint vulnerabilities, malicious functions, or hidden exploits that could be used by attackers. Understanding these risks allows for the development of effective countermeasures to protect systems and users from emerging cyber threats. Reconstruction In this step, the technology’s functionality is attempted to be recreated, frequently through the creation of a similar physical component or the replication of the source code. It’s similar to piecing together a puzzle.
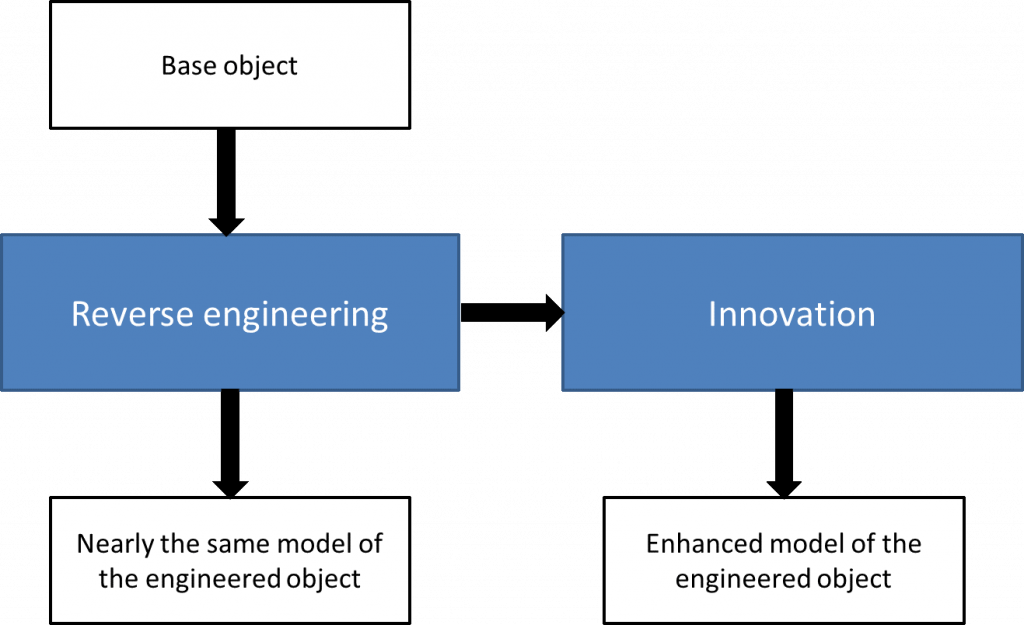
Testing Verify that your rebuilt version does the same tasks as the original technology. This is a crucial step in ensuring that the solution you reverse-engineered is accurate. Enhancement It occasionally seeks to improve the original technology. This step entails determining what needs to be changed and implementing those changes. Record-keeping (again) The reverse engineered technique should also have thorough documentation, just as the original analysis did. This documentation helps to understand and maintain the technology. Report Write a thorough report explaining your results, the procedure, and any adjustments you made.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Kinds of reverse technologies
Tools for this Engineering
IDA Pro is a well-known and effective tool that aids professionals in deciphering and analyzing the inner workings of malware and software. Users can use it to debug and disassemble binary code.
Go Through These Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering is similar to figuring out a technological riddle. It aids in our comprehension of how devices, software, and even entire Cyber Security Training Courses systems operate. The primary objectives are gaining knowledge, advancing current technology, and producing innovative and entertaining work. It’s an adaptable approach utilized in a variety of industries, including software development and aerospace, and it has advantages like improving security, encouraging creativity, and resolving compatibility problems.





