
- Introduction to Core Business Analyst Skills
- Communication and Stakeholder Skills
- Requirement Gathering Techniques
- Documentation and Modeling Tools
- Process Mapping and Use Case Creation
- Agile, Scrum, and Waterfall Methodologies
- Prototyping and Wireframing Tools
- Technical Skills (SQL, APIs, Data Flows)
- Data Analysis and Visualization
- Negotiation and Conflict Management
- Continuous Learning and Certifications
- Conclusion
Introduction to Core Business Analyst Skills
Business analyst Skills serve as a bridge between business needs and technological solutions. To be effective in their role, Business analysts must master a diverse range of core skills that allow them to understand stakeholder Requirement Gathering Techniques, analyze data, and support project teams. These skills span communication, analysis, documentation, and technology. A well-rounded Business analyst who interacts with various stakeholders contributes significantly to the success of a project by ensuring that the final product aligns with business goals. The following sections delve into the core competencies every aspiring or practicing business analyst should develop.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer Certification? Sign Up For Our Business Analyst Online Training Today!
Communication and Stakeholder Skills
Effective communication lies at the heart of business analysis. Business analysts interact with various stakeholders including clients, developers, testers, and management. They must communicate clearly and professionally to ensure that requirements are understood and issues are resolved promptly. Active listening, verbal articulation, and written communication are essential. Additionally, BAs must manage stakeholder expectations, build rapport, and resolve conflicts diplomatically. Communication isn’t just about conveying ideas, but also about interpreting and documenting what stakeholders need, even when they are not able to articulate it clearly themselves.
Analytical and Critical Thinking
- Analytical thinking is one of the most crucial skills for any Business analysts.
- This involves assessing problems, interpreting data, and synthesizing information to arrive at meaningful conclusions.
- BAs must distinguish between facts and assumptions, break down complex issues, and develop logical, data-driven recommendations.
- Critical thinking helps in identifying the root cause of problems and evaluating the potential impact of solutions.
- By developing strong analytical capabilities, BAs become adept at providing insights that drive business improvement and innovation.
- One of the core responsibilities of a BA is to gather requirements from stakeholders. This process must be thorough to ensure that nothing critical is missed.
- Techniques include interviews, surveys, workshops, document analysis, and observation. Each technique has its strengths depending on the context.
- For instance, workshops are excellent for collaborative environments, while document analysis is useful for reviewing existing systems.
- Business analysts interacting with various stakeholders must choose the right technique and follow a structured approach to extract clear, concise, and testable Requirement Gathering Techniques.
- Understanding project management methodologies is vital for Business analysts, as these frameworks dictate how work is structured and executed. Waterfall is a linear approach where each phase is completed before the next begins.
- Agile, Scrum and Waterfall Methodologies are iterative methodologies that emphasize flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback.
- Data Analysis and Visualization working in Agile environments must be adept at writing user stories, participating in sprint planning, and facilitating backlog grooming.
- Knowledge of these methodologies allows BAs to adapt to different organizational needs and improve project delivery.
- Today’s Business analysts are expected to have a basic understanding of technical concepts.
- Knowledge of SQL helps in extracting and analyzing data from databases. Familiarity with APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) is important when dealing with integrations between systems.
- Understanding data flows, system architecture, and backend logic enables Business analysts interact with various stakeholders to communicate effectively with technical teams and contribute more meaningfully to solution design.
- Technical proficiency also increases a BA’s credibility among developers and IT staff.
Requirement Gathering Techniques
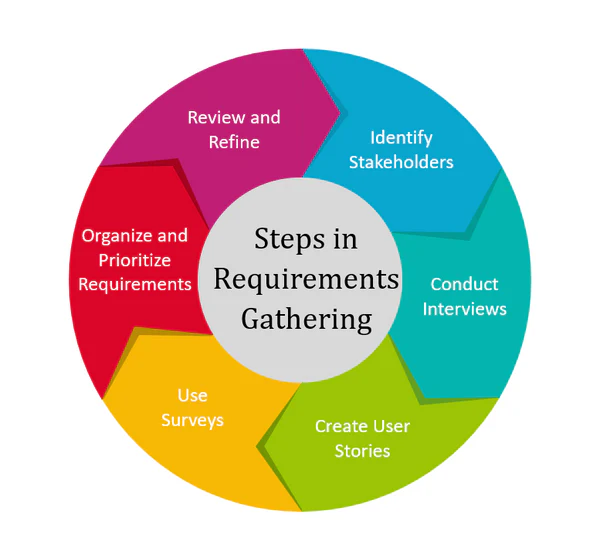
Are You Preparing for Business Analyst Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Business Analyst Interview Questions & Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Documentation and Modeling Tools
Once requirements are gathered, BAs must document them in a format that stakeholders and developers can easily understand. Common documents include Business Requirement Documents (BRD), Functional Requirement Documents (FRD), and Use Case Specifications. In addition to textual documentation, visual models such as flowcharts, data flow diagrams (DFDs), and entity-relationship diagrams (ERDs) help simplify complex processes. Familiarity with tools like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, and Draw.io is beneficial. Proper documentation ensures traceability and clarity throughout the project lifecycle.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Business Analyst? Enroll For Business Analyst Masters Program Training course Today!
Process Mapping and Use Case Creation
BAs often model business processes to understand the current state and propose improvements. Process mapping involves outlining each step of a workflow using standard symbols. This helps in identifying redundancies, inefficiencies, and bottlenecks. Use cases, on the other hand, describe how users will interact with a system. These are especially important in software projects. Creating clear and detailed use cases ensures that development teams understand how the software should function, leading to fewer misinterpretations and rework.
Agile, Scrum, and Waterfall Methodologies
Prototyping and Wireframing Tools
Prototypes and wireframes are visual representations of the user interface. They are used to demonstrate how a final product might look and behave. These are particularly useful in Agile projects where continuous feedback is essential. Tools like Balsamiq, Figma, Adobe XD, and Axure help BAs create low or high-fidelity mockups. By providing visual cues, business analyst skills can gather more accurate feedback from stakeholders early in the development process, reducing costly changes later.
Technical Skills (SQL, APIs, Data Flows)
Data Analysis and Visualization
Data Analysis and Visualization a central role in decision-making. BAs must be comfortable working with datasets, identifying trends, and presenting findings to stakeholders. Tools like Excel, Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio are commonly used for data visualization.
These tools allow BAs to convert complex data into charts, graphs, and dashboards that are easy to interpret. Effective data analysis helps stakeholders make informed decisions and measure the impact of implemented solutions.
Negotiation and Conflict Management
BAs often find themselves balancing competing interests. Stakeholders may have conflicting Requirement Gathering Techniques, or developers may face constraints that affect deliverables. In such situations, negotiation skills are essential. BAs must mediate between parties, propose alternatives, and strive for win-win outcomes. Conflict management also involves staying calm under pressure and defusing tensions before they escalate. Developing these interpersonal skills ensures smoother project execution and fosters a collaborative environment.
Continuous Learning and Certifications
The role of a BA is ever-evolving. As technology advances and business landscapes shift, continuous learning becomes indispensable. Pursuing certifications such as CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional), CCBA (Certification of Capability in Business Analysis), or PMI-PBA (Professional in Business Analysis) adds value to a BA’s profile. Online platforms like Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, and Udemy offer courses on emerging topics like Agile BA practices, data analytics, and AI in business analysis. Staying updated not only enhances employability but also enables BAs to offer innovative solutions.
Conclusion
Core Business analysts interact with various stakeholders skills encompass a combination of analytical thinking, technical knowledge, communication prowess, Data Analysis and Visualization and adaptability. A well-rounded business analyst is not just a requirement-gathering agent but a strategic partner who contributes to organizational success. By mastering these skills, BAs can effectively bridge the gap between business and technology, drive value across projects, and elevate their professional standing in any industry. The journey of becoming a proficient BA is continuous, and dedication to skill development is the key to long-term success in this dynamic field.




