SAP’s sales and distribution function is part of the logistics area. The module contains processes that help a company integrate with its customers.Sales & Distribution (SD) is one of the main and most used modules of SAP R / 3 products alongside the Financial (FI), Controlling (CO), Material Management (MM) and Production Planning (PP) modules.The Sales and Distribution module (SD) consists of different components, also called sub-modules.
The main areas covered by this module and the sub modules are:
- Pre-sales activities, including Inquiry and Quotation creation.
- Sales Order processing, including Sales Order (SO) creation.
- Shipping, including Outbound Delivery document creation.
- Billing, including Billing document and invoice creation.
Sales & Distribution (SD) is a highly integrated module with other SAP modules like FI, CO, MM, PP and more. This can make SD a complex module, so as part of this introduction we will also attempt to detail a normal sales process and how the activities fit and are covered by this module.These processes include:
- Providing quotations to customers:
The cost and the product details are provided through the quotations.
- Receiving sales order via phone, internet or EDI:
Ones teh quotation is approved, sales order is received through phone, internet or through other networks.
- Shipping the finished goods:
After getting the order, the finished goods are being transported at the final destination.
- Billing the customer for the goods received:
As soon as the good are received, billing process takes place and money is transferred.
QUALIFICATIONS & EXPERIENCE:
Experience:
8 to 10 years systems and business analysis experience. Apparel experience highly preferred.
5 plus years of experience working with SAP Sales & Distribution / SAP SD Certification.
Education:
Bachelor’s Degree or equivalent required.
Skills:
Must have excellent partnership skills and must be able to work with a highly diverse workforce, domestically and internationally.
Must possess excellent written and verbal communication skills and presentation skills.
Proficient in Microsoft Office suite.
Proficient in Visio.
Proficient in Microsoft Project.
Key Components of SAP Sales and Distribution:The fundamental components of SAP SD module include:
- Sales Support
- Master Data (of both the customers and the vendors)
- Transporting the goods
- Billing and invoicing system
- Shipping of materials
- Finance handling
- Management of contracts
- Foreign trade functionality
Like every other SAP ECC modules, SAP SD is mostly centred on the master data which is kept in centralised master data tables. In SD the types of master data include data related to consumers, price and materials. In ECC overall, there are two other types of data that exist, namely transactional data and customizing data. The transactional data is created from the master data- hence creating, for example, sales orders in SD or purchase order in MM. On the other hand, customizing data is created only when a business decides to customize SD to serve its particular and unique needs.
Sub Components of SAP SD (Sales and Distribution)- Material Master / Customer Master Data: accumulates and maintains client product data bases, preferences, customer orders, shipping details, addresses and all other data appertaining to the department of sales and distribution.
- Availability check: keeping a track of the availability of product in the inventory, placement of back orders and so forth.
- Sales: sales forecast, marketing, advertisements and management of the overall sales information system.
- Billing and invoice: generation of invoices, bills, statements for orders as well as product deliveries.
- Credit Management: setting of credit limits and management of customer specific credit issues.
- Batch and serial number management: issue and management of product serial numbers.
- Pricing and taxation: product pricing, evaluation and maintenance of price lists and other allied data.
- Shipping and transportation: shipping, order delivery processing, transportation and associated personnel.
The sales documents you create are individual documents but they can also form part of a chain of inter-related documents. For example, you may record a customer’s telephone inquiry in the system. The customer next requests a quotation, which you then create by referring to the inquiry. The customer later places an order on the basis of the quotation and you create a sales order with reference to the quotation. You ship the goods and bill the customer. After delivery of the goods, the customer claims credit for some damaged goods and you create a free-of-charge delivery with reference to the sales order. The entire chain of documents – the inquiry, the quotation, the sales order, the delivery, the invoice, and the subsequent delivery free of charge – creates a document flow or history. The flow of data from one document into another reduces manual activity and makes problem resolution easier. Inquiry and quotation management in the Sales Information System help you to plan and control your sales.
The following graphic shows how the various types of sales documents are inter-related and how data subsequently flows into shipping and billing documents.
- Works with minimal direction from the technical lead and with customer nominated representatives to accomplish assigned tasks. Contributes to design for specific deliverables and assists in the development of technical solutions
- Participates as part of a team and maintains good relationships with team members and customers. Understands HP strategy and the role that the individual players
- Uses knowledge tools and reuses information for the benefit of projects, and of professional development. Uses and contributes to technical forums within the HP environment and local professional communities and technical user groups. Focuses on single customer
- Expertise in Execute Unit, Integration & Regression testing to validate that the business requirements are met by the SAP system and document the test results & provide training sessions to the SAP Power Users to operate any customized solutions and prepare program/process documentation & End user training material
- Account Determination
- Customer / Material Master Data
- Forms and Enhancements (User Exits, Function Modules etc.)
- Advanced understanding of Software Test methodologies, test scripting and testing tools
- Desirable business analysis skills
- Demonstrated technical leadership skills
- To support SAP projects, enhancements and Help Desk Tickets through analysis, configuration, and knowledge transfer
- To understand and support multiple business requirements from various business models and global initiatives
- To harmonize processes and configurations in a global model
- To support all aspects of the Order to Cash (OTC) & EDI in SAP supporting the objective to role out and support SAP in all of major manufacturing and distribution facilities
- Collaborate with members of the Business Process Integration groups (Sales and Marketing; Supply Chain; and Finance) to design solutions
- Provide Level III support of the SD/OTC/EDI module; Consult and assist with Level II issue resolution as required
- Identify root cause for recurring issues, make proposal for their elimination
- Assist or take responsibility for conducting development work end to end (requirement analysis, estimates, functional spec, testing, etc.)
- Build and test system solutions,
- 7-10 years of experience supporting OTC cycles and Logistics Execution processes in discrete and repetitive manufacturing environments
- 7-10 years of experience on SAP implementation in the SD and EDI Modules of SAP
- Experience, knowledge and understanding in the following areas
- Must possess a disciplined approach and commitment to delivering on Service Level Agreements (SLA’s)
- Willingness to adhere to a standard, global template and maintain the consistency of the global process model
The automotive industry and its associated suppliers very often make use of scheduling agreements. The process diagram below shows the document exchange sequence when using scheduling agreements.
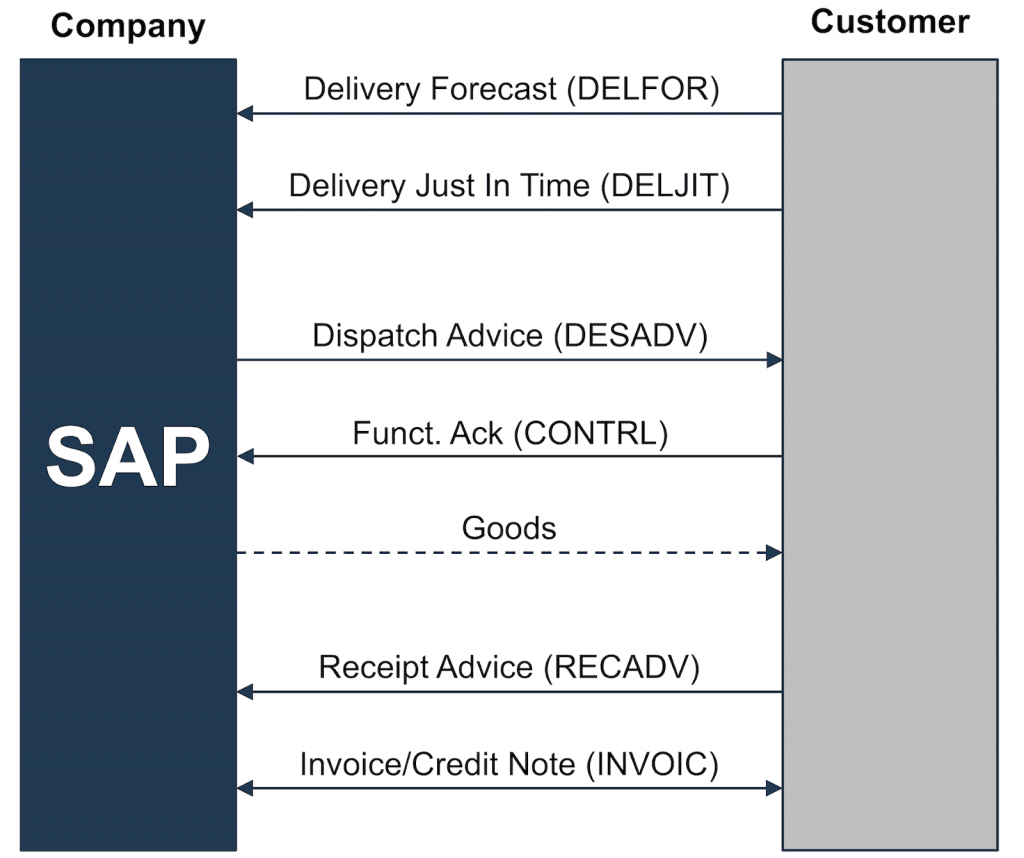
This process can be extended with additional transactions, such as the exchange of master data (based on PRICATs) or offer requests/offers.
However, the most important SAP SD processes for a delivery plan are:
- Customer sends a delivery forecast (DELFOR)
- Customer sends a just in time delivery forecast (DELJIT)
- Customer receives a dispatch advice (DESADV)
- Customer sends a receipt advice (RECADV)
- Customer sends a credit note (GSVERF)
- Customer receives an invoice (INVOIC)
Depending on the situation, confirmations can also be exchanged at business level, e.g., the client can send CONTRL files after receiving a dispatch advice.