
- Introduction to SIEM
- Components of a SIEM System
- How SIEM Works
- Event Collection and Correlation
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
- Log Management and Analysis
- SIEM Deployment Models
- Use Cases and Benefits
- Popular SIEM Tools (Splunk, IBM QRadar)
- Integration with SOC
- Future of SIEM Technology
- Conclusion
Introduction to SIEM
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a comprehensive cybersecurity solution that provides real-time analysis, monitoring, and management of security events within an IT environment. By collecting, aggregating, and analyzing data from various sources like servers, firewalls, endpoints, and applications, SIEM tools help organizations detect, investigate, and respond to security threats. SIEM acts as a centralized security platform, playing a pivotal role in threat detection, compliance reporting, and incident response across modern digital infrastructures. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a comprehensive cybersecurity solution that provides real-time analysis, monitoring, and management of security events within an IT environment. By collecting, aggregating, and analyzing data from various sources like servers, firewalls, endpoints, and applications, SIEM tools help organizations detect, investigate, and respond to security threats. SIEM acts as a centralized security platform, playing a pivotal role in threat detection, compliance reporting, and incident response across modern digital infrastructures.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cybercrime Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Components of a SIEM System
A typical SIEM system comprises several key components: A Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system has several important parts that work together to keep an organization’s network safe. Data Collectors are the first step, gathering information from different places like servers, firewalls, and apps. This information is then handled by a Normalization Engine, which makes sure all the data is in the same format so it’s easier to work with.
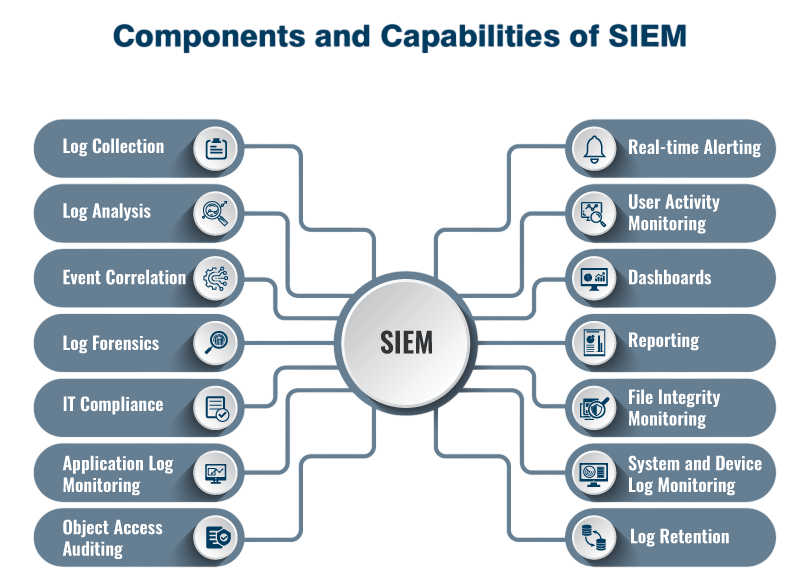
The Correlation Engine looks at this standardized data to find possible security issues by recognizing patterns and spotting unusual activity. An Alerting Module sends out timely messages based on set rules and how users typically behave, helping to respond to threats quickly. The Dashboard and Visualization tools let security experts see things clearly through charts and graphs, helping them watch what’s happening, look into problems, and make detailed reports. A strong Storage Layer keeps all the logs safe for long-term use, especially for investigations. Built-in Reporting Tools also help the organization follow rules like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, giving a full way to manage cybersecurity.
How SIEM Works
SIEM tools work by ingesting logs and event data from various sources across an organization’s network. The process generally includes the following steps:
- Data Collection: Logs and events are collected from endpoints, servers, applications, and network devices.
- Normalization and Parsing: Data is converted into a consistent format to ensure compatibility across diverse sources.
- Correlation: Events are analyzed using correlation rules to identify patterns that may signify a potential security breach.
- Alerting: If a pattern matches a rule indicating suspicious activity, an alert is generated.
- Visualization and Reporting: Security analysts use dashboards to review alerts, examine patterns, and initiate incident response.
This real-time processing enables quicker detection of threats, allowing security teams to act proactively.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Event Collection and Correlation
The core functionality of any SIEM lies in its ability to collect events from diverse sources and correlate them to detect threats:
- Operating Systems: Logs from Windows, Linux, or macOS environments.
- Web Servers: Logs from Apache, Nginx, IIS, etc.
- Firewalls: Records of allowed or denied traffic.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Alerts and events based on suspicious traffic patterns.
- Authentication Servers (e.g., Active Directory): Login attempts, account changes, and access controls.
Correlation engines then apply rules to these events to find relationships. For instance, if multiple failed logins are followed by a successful login from a suspicious IP address, the SIEM may flag it as a brute-force attack. This capability is critical for identifying multi-step attacks and reducing false positives.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
One of the standout features of SIEM is its ability to provide real-time monitoring and alerts. As logs are ingested, they are instantly analyzed against a set of correlation rules or machine learning models. This allows security teams to: Our security solution offers strong protection by detecting possible intrusions and constantly monitoring user activity. We use advanced algorithms to find and deal with insider threats while tracking potential policy violations. This layered approach ensures solid cybersecurity measures that protect organizational assets and keep critical digital infrastructure secure. Alerts can be customized based on severity levels and directed to the appropriate teams via dashboards, email, or integration with ticketing systems. This rapid detection is essential for minimizing dwell time and mitigating damage.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Log Management and Analysis
SIEM systems are highly effective at managing vast quantities of log data. They provide centralized storage and advanced search capabilities, enabling security analysts to: Our cybersecurity team conducts comprehensive forensic investigations that meticulously identify the root cause of security incidents while systematically tracking user activities and auditing system access and changes.
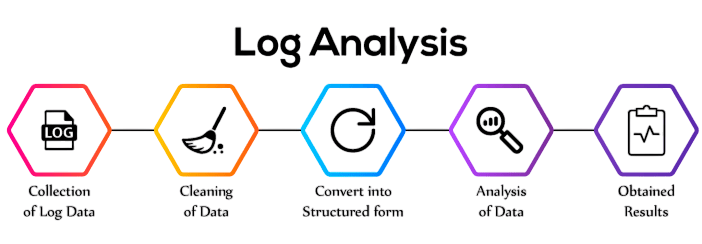
By employing advanced analytical techniques, we provide in-depth insights into potential vulnerabilities, enabling proactive threat detection and robust organizational security management. Logs can be retained for months or even years, depending on compliance requirements. The analytical capabilities of SIEM also support proactive threat hunting by allowing teams to query historical data and uncover hidden threats.
SIEM Deployment Models
Organizations can choose from several SIEM deployment models based on their needs, resources, and infrastructure:
- On-Premises SIEM: Installed within the organization’s own data center. Offers full control but requires significant resources for maintenance and scaling.
- Cloud-Based SIEM: Hosted by a third-party provider, offering scalability, reduced infrastructure costs, and easier updates.
- Hybrid SIEM: Combines on-premises and cloud-based components, offering flexibility and better data control.
- SIEM-as-a-Service: Fully managed SIEM offerings where the vendor handles configuration, updates, and monitoring.
Each model comes with its trade-offs in terms of cost, control, performance, and ease of management.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Use Cases and Benefits
SIEM tools serve multiple purposes within an organization’s cybersecurity framework. Common use cases include:
- Threat Detection: Identifies known and unknown threats through correlation and anomaly detection.
- Incident Response: Provides context-rich alerts that help analysts respond quickly to breaches.
- Compliance Management: Automates data collection and reporting to meet regulatory standards.
- Operational Visibility: Gives a unified view of security posture across the enterprise.
- Insider Threat Detection: Detects unusual behavior from internal users or compromised accounts.
The benefits of using SIEM tools include improved response times, reduced risk exposure, streamlined compliance, and enhanced security maturity.
Popular SIEM Tools (Splunk, IBM QRadar)
The use of encryption is often subject to legal regulations and ethical standards. Governments may require organizations to implement strong encryption for data protection, particularly for personal or financial information. Laws such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) mandate secure data handling practices, including encryption. However, encryption can also complicate law enforcement efforts when used to hide illegal activities. The balance between privacy and public safety is an ongoing debate, leading to discussions around encryption backdoors and lawful access.
Future of SIEM Technology
The future of SIEM lies in greater integration with artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cloud-native architectures. Emerging trends include:
- AI-Powered Analytics: Enhances threat detection by identifying complex patterns.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Focuses on behavioral baselines to detect anomalies.
- Cloud-Native SIEM: Designed for cloud environments with better scalability and performance.
- Integration with SOAR: Automates response actions to reduce time-to-resolution.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR): Combines SIEM with EDR and NDR for holistic threat detection.
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the evolution of SIEM will focus on automation, precision, and scalability to protect dynamic enterprise environments.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its benefits, encryption faces several challenges:
- Key Management Complexity: Maintaining and securing encryption keys can be difficult, especially at scale.
- Performance Overhead: Strong encryption can slow down systems, particularly in resource-limited environments.
- Legal Constraints: Some governments limit the use of strong encryption, complicating global deployment.
- Quantum Computing Threats: Quantum computers could potentially break existing encryption algorithms, prompting research into post-quantum cryptography.
Looking forward, encryption will continue to evolve with the development of quantum-safe algorithms, homomorphic encryption (which allows computations on encrypted data), and AI-enhanced security systems. As data continues to grow in volume and importance, encryption will remain a foundational element of digital trust and security.
Conclusion
SIEM systems have become an essential part of modern cybersecurity infrastructure, enabling organizations to monitor, detect, and respond to threats efficiently. From real-time event correlation to compliance reporting and forensic analysis, SIEM offers a centralized approach to managing security operations. Despite challenges in cost and complexity, its role continues to grow in importance, especially as digital landscapes expand and threats evolve. With continued advancements in AI and cloud technologies, SIEM is poised to become even more powerful, efficient, and indispensable in the cybersecurity domain. The heads of security also watch the tools closely. They see the promise in new technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud services. AI can help SIEM systems learn from past incidents, improve detection, and reduce false alarms. Cloud-based SIEM solutions offer flexibility, making it easier for companies to scale and access data from anywhere. These innovations will make SIEM systems more powerful, faster, and easier to use in the future.




