
- Definition and Overview
- Components of Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
- Integration of Physical and Digital Worlds
- Examples of CPS in Industry
- Applications in Healthcare, Transport, and Defense
- Communication Protocols in CPS
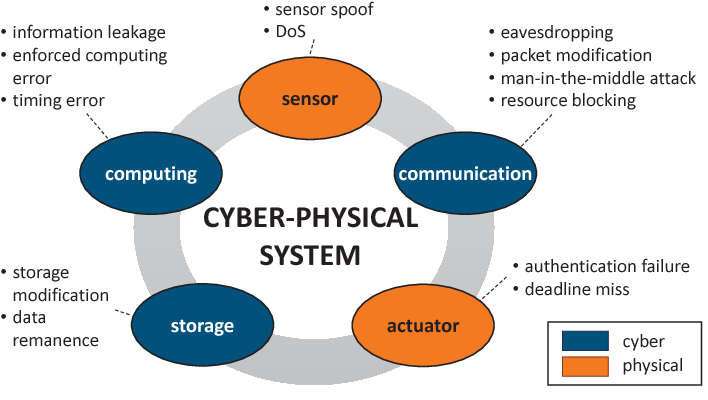
- Security Concerns in CPS
- Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Definition and Overview
A Cyber-Physical System (CPS) is an integrated system that combines computation, networking, and physical processes to create intelligent mechanisms capable of interacting with the real world in real-time. These systems are at the core of modern innovations like smart grids, autonomous vehicles, and advanced manufacturing. Cyber-Physical Production Systems (CPPS), a subset of CPS, specifically refer to the fusion of cyber and physical components in industrial environments, enabling flexible, efficient, and adaptive production processes. As these systems become more interconnected, Cyber Security Training becomes essential to safeguard sensitive data, ensure system integrity, and protect against potential cyber threats that could disrupt production workflows. With the increasing connectivity and automation in such systems, Cyber Physical Systems Security becomes critical, as any breach can lead to real-world consequences like equipment failure or safety hazards. As we transition into a highly digital world, global perspectives on CPS highlight the importance of international collaboration, standardization, and regulation to ensure safety, scalability, and ethical implementation. From smart homes to medical devices, CPS impacts every sector, demanding robust architectures that account for both technological advancement and societal impact. The integration of sensors, actuators, embedded systems, and network protocols within CPS not only optimizes performance but also sets the stage for innovations that can reshape industries and daily life. Understanding CPS through this lens allows us to appreciate its role in the evolving technological landscape and its influence on global digital transformation.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cybercrime Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Components of Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)
- Sensors and Actuators: These are the bridge between the physical and digital worlds, collecting real-time data and acting on decisions made by the system.
- Embedded Systems: These are microprocessors or controllers programmed to perform specific tasks, crucial for interpreting sensor data and controlling actuators. Ensuring Non-Repudiation in Cyber Security within these components helps verify the authenticity and origin of data transmissions, preventing unauthorized actions and enhancing system accountability.
- Communication Networks: Reliable and fast data transmission is vital in CPS Cyber environments, often using wireless, IoT, or industrial Ethernet technologies.
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are foundational to today’s digitised world, blending physical processes with computational intelligence to drive automation, connectivity, and smart decision-making. These systems are especially vital in sectors like healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing where Smart Factory CPS and CPS Smart Factory concepts are revolutionizing how machines and data interact. A deeper understanding of CPS starts with knowing its essential components, which together enable a seamless connection between the cyber and physical realms.
- Computational Intelligence: This includes algorithms, AI, and data analytics used to process inputs, predict outcomes, and make real-time decisions.
- Control Systems: Feedback loops ensure system stability and accuracy, particularly essential in dynamic environments like Smart Factory CPS.
- Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI): HMIs allow human operators to monitor, control, and intervene, ensuring that the CPS Smart Factory remains efficient and user-friendly.
Integration of Physical and Digital Worlds
The integration of the physical and digital worlds marks a pivotal shift in how modern systems operate, blending tangible, real-world processes with intelligent computational capabilities. At the heart of this transformation lie Cyber Physical Production Systems, where machinery, sensors, and software seamlessly interact to enable real-time monitoring, decision-making, and automation. This convergence is reshaping industries from manufacturing and healthcare to energy and transportation, creating smarter, more adaptive environments. However, as the lines between the physical and digital realms blur, ensuring robust Cyber Physical Systems Security becomes increasingly vital. A strong foundation in Understanding Cybercrime and its Implications is essential to anticipate potential threats, mitigate risks, and develop resilient CPS frameworks. The complexity of interconnected devices and data flows makes these systems vulnerable to cyber threats that can impact real-world operations. Therefore, security strategies must evolve alongside technological advancements to protect both information integrity and physical safety. Viewed through Digital World Global Perspectives, this integration goes beyond local or industrial boundaries; it represents a worldwide movement toward innovation, efficiency, and interconnected ecosystems. Countries and corporations alike are investing in frameworks that ensure safe, scalable, and ethical implementation of CPS technologies. As the digital and physical realms continue to merge, the success of this integration depends not just on technological innovation but also on global collaboration and a deep commitment to secure, sustainable progress.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Examples of CPS in Industry
- Automated Manufacturing Lines: In a Smart Factory CPS, robotic arms and conveyor systems work in sync, monitored and adjusted in real-time through CPS networks to ensure precision and adaptability.
- Smart Grids: These energy systems use CPS Cyber technologies to balance electricity supply and demand, integrate renewable sources, and prevent outages through predictive analytics. As these systems become increasingly digital and interconnected, Cyber Security Training is vital to equip professionals with the skills needed to protect critical infrastructure from cyber threats and ensure resilient energy operations.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Combining sensors, AI, and real-time data exchange, CPS enables self-driving cars to navigate safely, reacting instantly to changing road conditions.
In today’s digitised world, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) have become essential across various industries, driving automation, efficiency, and real-time decision-making. These systems merge physical components with computational intelligence, forming the backbone of Industry 4.0. From energy to manufacturing, CPS applications are redefining operational standards. The rise of Smart Factory CPS and CPS Smart Factory models showcases how integrated systems are transforming production landscapes. Below are six key examples of Cyber Physical systems in industry:
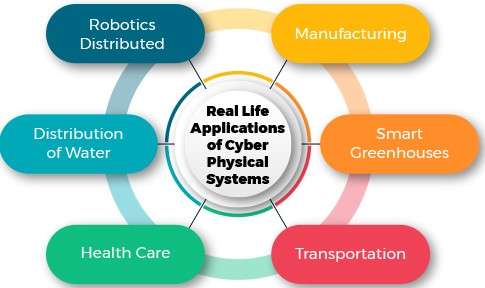
- Healthcare Monitoring Systems: CPS is used in wearable devices that track patient vitals and send data to medical professionals for timely interventions.
- Aerospace Control Systems: Advanced aircraft rely on CPS for flight stabilization, fault detection, and performance optimization during missions.
- Agricultural Automation: Smart farming tools use Cyber Physical systems to monitor soil, weather, and crop health, automating irrigation and harvesting processes efficiently.
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): Lightweight and efficient, MQTT is ideal for low-bandwidth networks and is widely used in IoT-based CPS applications.
- OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture): Designed for industrial automation, this protocol supports secure and reliable data exchange in CPS Smart Factory environments.
- Modbus:A widely used protocol in Cyber Physical industrial systems for simple, real-time communication between devices like PLCs and sensors. To ensure the security and reliability of these communications, Network Penetration Testing is often employed to identify vulnerabilities, assess potential threats, and strengthen the system’s defenses against cyber attacks.
- EtherCAT (Ethernet for Control Automation Technology): Known for its speed and precision, EtherCAT is vital in time-critical Smart Factory CPS operations.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): Common in automotive and transportation CPS, CAN enables microcontrollers to communicate without a host computer.
- Zigbee: A low-power, wireless protocol used in CPS Cyber systems for home automation and healthcare applications.
Applications in Healthcare, Transport, and Defense
In the rapidly evolving digitised world, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are playing a transformative role in critical sectors such as healthcare, transport, and defense. These systems, built on the seamless integration of physical components with computational logic, are reshaping how services are delivered and decisions are made. In healthcare, CPS Cyber technologies power smart medical devices and remote monitoring tools that collect real-time patient data, enabling timely diagnosis, personalized treatment, and reduced hospital stays. To secure this sensitive data, especially when transmitted or stored in the cloud, leveraging Top Cloud Security Tools is essential for maintaining privacy, ensuring compliance, and preventing cyber threats. In the transportation sector, CPS enhances the safety and efficiency of intelligent traffic systems, autonomous vehicles, and railway monitoring solutions by allowing dynamic route adjustments and predictive maintenance. Meanwhile, in defense, Cyber Physical solutions provide real-time surveillance, drone operations, advanced battlefield communication, and automated threat detection, increasing both situational awareness and response capabilities. While the Smart Factory CPS and CPS Smart Factory concepts are more manufacturing-focused, their underlying principles of automation, data exchange, and system responsiveness are now being adapted in these high-stakes domains. The success of CPS in these fields relies heavily on reliability, security, and interoperability demonstrating that these advanced systems are not just revolutionizing industries but also safeguarding human lives and national security in an increasingly connected global environment.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Communication Protocols in CPS
In the digitised world, effective communication within Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) is crucial for ensuring seamless data exchange between sensors, controllers, and actuators. These systems rely on robust and real-time communication protocols to maintain accuracy, safety, and efficiency especially in environments like the Smart Factory CPS. Whether in manufacturing, transportation, or healthcare, the role of communication protocols in Cyber Physical systems cannot be overstated. Below are six key communication protocols commonly used in CPS Cyber frameworks:
These protocols enable CPS to thrive in an interconnected, real-time digitised world.
Security Concerns in CPS
As Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) become more embedded in critical infrastructure and industrial environments, Cyber Physical Systems Security emerges as a top concern. These systems, which tightly integrate computing, networking, and physical processes, are widely used in sectors like energy, healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. However, the very features that make CPS powerful interconnectivity, automation, and real-time responsiveness also expose them to a wide range of cyber threats.In Cyber Physical Production Systems, any breach can lead to not just data loss but real-world consequences such as equipment damage, production halts, or even threats to human safety. A clear Overview of Cybersecurity Threats is essential to understand potential attack vectors, anticipate vulnerabilities, and implement proactive security measures to protect these critical systems. Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in sensors, communication protocols, or embedded software to manipulate system behavior or cause disruptions. As the digital world expands and global dependence on CPS increases, the importance of robust security frameworks becomes more evident. From encryption and access control to anomaly detection and real-time monitoring, multiple layers of defense are essential to safeguard CPS environments. Viewing these challenges through digital world global perspectives, it’s clear that collaboration across industries and borders is vital to developing standardized, scalable, and adaptive security solutions. Protecting CPS is not only about securing information but also about ensuring the safety and stability of the physical world they control.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Real-Time Monitoring and Control
In today’s digitised world, real-time monitoring and control are at the heart of Cyber Physical Systems (CPS), enabling seamless interaction between physical assets and digital intelligence. These systems continuously collect data from sensors, process it through embedded software, and respond instantly to changes in the environment creating highly adaptive and responsive operations. In the context of Smart Factory CPS, this capability allows manufacturers to detect faults, adjust production parameters, and optimize workflows in real-time, significantly boosting efficiency and reducing downtime. To maintain the reliability and safety of these connected systems, Cyber Security Training is crucial for personnel to identify vulnerabilities, respond to threats, and ensure secure operations. Whether it’s monitoring temperature fluctuations in a chemical plant or tracking the performance of autonomous vehicles, real-time control ensures safety, accuracy, and system integrity. In CPS Cyber environments, latency must be minimal, and decisions must be executed with precision, as even slight delays can lead to system failure or safety hazards. The concept of CPS Smart Factory further elevates this by integrating AI and predictive analytics to not only react to issues but also anticipate them before they occur. Across industries, real-time monitoring and control are reshaping how systems operate enhancing productivity, minimizing risk, and driving smarter decision-making. As CPS continues to evolve, this dynamic capability is key to unlocking the full potential of cyber-physical integration in our interconnected world.




