
- Business Analysis & Analytics Basics
- Business Analysis Explained
- Understanding Business Analytics
- Objectives and Focus Areas
- Core Skills Comparison
- Tools and Technologies
- Processes and Methodologies
- Role in Business Decision-Making
- Education and Certifications
- Key Differences: Business Analysis vs Business Analytics
- Future Trends and Career Outlook
- Conclusion
Business Analysis & Analytics Basics
In today’s data-driven corporate landscape, the terms Business Analysis and Business Analytics are often used interchangeably. However, they refer to two distinct yet complementary disciplines that play critical roles in improving organizational performance. Both involve understanding business needs and helping organizations make informed decisions, and Business Analyst Training equips professionals to handle these tasks, but they differ in focus, methodology, tools, and outcomes. Business Analysis primarily deals with identifying business requirements, improving processes, and ensuring successful implementation of solutions that meet organizational goals. In contrast, Business Analytics is centered around using data, statistics, and predictive modeling to uncover insights that drive decision-making. Understanding the difference between the two is crucial for professionals, students, and businesses seeking to harness the power of both domains for better efficiency and growth.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Business Analyst? Sign Up For Our Business Analyst Training Today!
Business Analysis Explained
Business Analysis (BA) is a systematic approach to understanding business needs, identifying challenges, and recommending solutions that enhance business processes and outcomes.
- It acts as a bridge between stakeholders and the technical team, ensuring that business requirements are effectively translated into functional solutions.
- A Business Analyst’s role extends beyond documentation and requirement gathering; they help define project scope, assess risks, develop strategies, and evaluate results, providing valuable skills for those aiming To Become an Entrepreneur .
- Their goal is to ensure that the organization’s solutions align with business objectives and deliver measurable value.
- Business Analytics professionals utilize tools like SQL, Python, R, Tableau, Power BI, and machine learning algorithms to analyze historical data and predict future trends, as a Bootcamp Explained can help beginners master these skills quickly.
- They support decision-making by providing actionable insights that optimize marketing strategies, pricing models, supply chains, and customer experiences.
- Business Analysis focuses on process improvement, change management, and solution design. Its main goals are to ensure that business needs are accurately captured, solutions are feasible, and implementation delivers expected benefits. It emphasizes understanding the business problem before finding a solution.
- Business Analytics, on the other hand, focuses on exploring data to derive insights and make predictions. Its objectives include identifying trends, forecasting outcomes, and quantifying the impact of business decisions. Analytics helps in measuring performance and optimizing operations based on evidence.
- Business Analysts need strong problem-solving, documentation, stakeholder management, and process modeling skills. They must understand frameworks like SDLC, Agile, and Waterfall and be proficient in tools like Microsoft Visio, JIRA, and Confluence. Communication and negotiation are essential, as they frequently interact with clients and developers.
- Business Analytics professionals, on the other hand, need expertise in mathematics, statistics, and data modeling. They work with tools and programming languages like Python, R, SQL, SAS, and Excel, as well as visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI. Critical thinking and data interpretation are vital for transforming raw numbers into actionable insights, especially when understanding the differences in BI vs BA .
- JIRA, Confluence, and Trello for project tracking and collaboration.
- Microsoft Visio for creating process flow diagrams.
- Balsamiq and Lucidchart for wireframing and modeling.
- MS Excel for simple data analysis and documentation. Business Analytics tools are more data-intensive, such as:
- SQL for database querying and data extraction.
- Python and R for statistical analysis and machine learning.
- Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView for data visualization.
- Excel and SAS for reporting and statistical modeling.
- BABOK (Business Analysis Body of Knowledge) standards.
- Agile and Scrum methodologies for iterative project management.
- SWOT Analysis and PESTLE Analysis for business environment assessment.
- Requirement Elicitation and Stakeholder Analysis for defining needs.
- CRISP-DM (Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining).
- Descriptive, Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prescriptive Analysis.
- Data Cleaning, Transformation, and Modeling techniques.
- Machine Learning and Statistical Analysis for predictive modeling.
- A Business Analyst facilitates decision-making by translating business problems into technical solutions. They gather requirements, validate feasibility, and ensure that implemented solutions deliver expected business value. Their decisions are often qualitative based on stakeholder feedback, market research, and organizational goals.
- A Business Analytics professional, meanwhile, supports data-driven decision-making. By analyzing patterns and predicting outcomes, they help management make informed choices about strategy, pricing, and operations.
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional)
- CCBA (Certification of Competency in Business Analysis)
- PMI-PBA (Professional in Business Analysis)
- Agile Analysis Certification (IIBA-AAC)
- Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
- Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate
- SAS Certified Data Scientist
- IBM Data Analyst Professional Certificate
- Tableau or Power BI Certifications
- Business Analysis is evolving to incorporate data literacy, agile methodologies, and cross-functional collaboration. As organizations adopt digital solutions, analysts must bridge business and technology even more efficiently. The rise of Digital Business Analysts and Product Analysts shows how the role is expanding into strategic digital transformation initiatives.
- Business Analytics, meanwhile, is advancing rapidly due to big data and AI integration. Predictive and prescriptive analytics are becoming vital for strategic planning, with demand rising for professionals skilled in machine learning, cloud computing, and data visualization.
In simpler terms, Business Analysis focuses on the “what” and “why” of business change: what needs to be improved, and why it should be improved. Analysts may not always work directly with data analytics tools but rely on qualitative assessments, process maps, and stakeholder feedback to drive solutions.
Understanding Business Analytics
Business Analytics (BA or BAn) is a data-centric field that uses statistical methods, predictive modeling, and data visualization to identify patterns, trends, and insights from data.
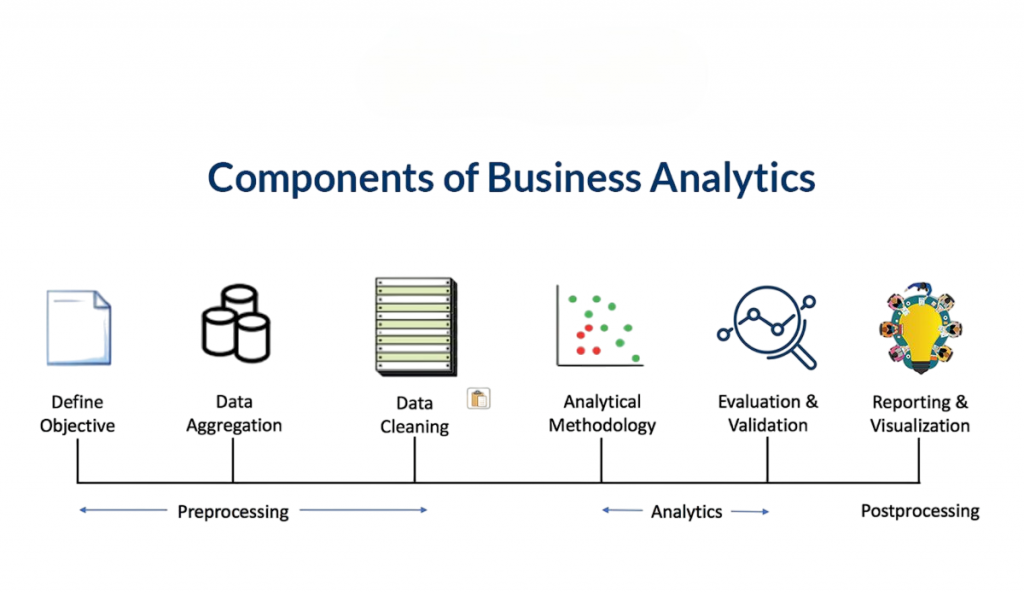
Unlike Business Analysis, which deals more with requirements and processes, Business Analytics emphasizes data-driven insights and measurable outcomes. It’s about transforming raw data into meaningful intelligence that supports strategic and operational decisions.
Objectives and Focus Areas
The objectives of Business Analysis and Business Analytics differ, though they overlap in supporting business growth.
In short, Business Analysis is more qualitative and strategic, while Business Analytics is quantitative and data-focused. Together, they provide a 360° view of business performance one defining what needs to change and the other explaining how and why it should change, a perspective highly valued by Educational Tech Companies .
Core Skills Comparison
While both fields require analytical thinking and communication skills, the core competencies differ significantly.
In essence, Business Analysts focus on the business process and solution design, while Business Analytics professionals focus on data and performance insights.
Tools and Technologies
The tools used in each discipline reflect their distinct functions.
- Business Analysis tools and technologies
While both may use Excel, the depth of use differs: Business Analysts use it for requirement tracking or summaries, while Business Analyst Training teaches them to use it for complex data analysis and reporting.
Processes and Methodologies
The methodology followed in each field defines their workflow and end goals. Business Analysis relies heavily on project management and process improvement methodologies. Analysts follow frameworks such as:
The methodical conversion of unprocessed data into useful insights that facilitate well-informed company decisions is the process of business analytics. First, pertinent data is gathered from multiple sources, and then it is cleaned and prepared to guarantee correctness and consistency. After that, analysts use statistical techniques and visualization tools to examine the data in order to find trends, patterns, and connections, skills that are essential for Jobs After BA . Business Analytics employs data-centric methodologies, such as:
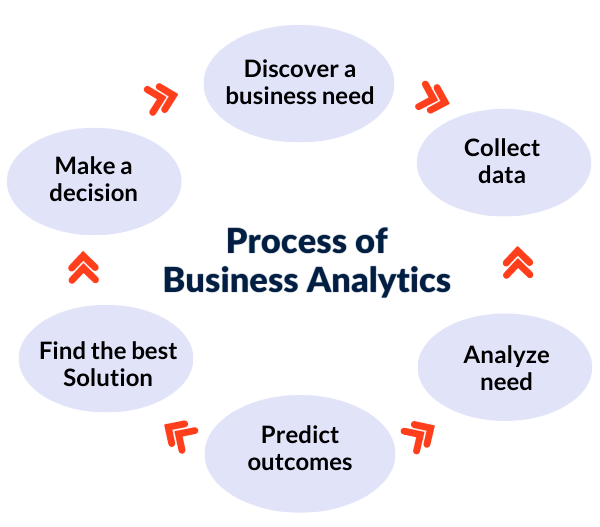
Thus, Business Analysis focuses on improving systems and processes, whereas Business Analytics focuses on optimizing decisions through data.
Looking to master Business Analyst? Sign up for ACTE’s Business Intelligence Master Program Training Course and begin your journey today!
Role in Business Decision-Making
Both Business Analysis and Business Analytics play integral roles in decision-making, but they approach it differently.
Their work is quantitative, relying on metrics, trends, and statistical inference. For example, if sales are declining, a Business Analyst with a Masters in BA might analyze process inefficiencies or system bottlenecks, while a Business Analytics expert might examine sales data to identify underperforming products or customer segments. Together, their combined insights help leaders make balanced decisions.
Education and Certifications
Both professions require a mix of academic qualifications and professional certifications to advance in their careers. For Business Analysis, a bachelor’s degree in Business Administration, Management, or Information Systems is ideal. Professionals often pursue certifications such as:
For Business Analytics, a degree in Statistics, Mathematics, Computer Science, or Economics is common. Leading certifications include:
While Business Analysis emphasizes understanding business systems, Business Analytics focuses on technical proficiency in handling data and statistical models.
Preparing for Business Analyst interviews? Visit our blog for the best Business Analyst Interview Questions and Answers
Key Differences: Business Analysis vs Business Analytics
To clearly distinguish between the two, here’s a concise summary of their core differences:
| Aspect | Business Analysis | Business Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Identifying business needs and improving processes | Analyzing data to extract insights |
| Approach | Qualitative and process-driven | Quantitative and data-driven |
| Goal | Define problems and suggest solutions | Predict outcomes and support decisions |
| Tools Used | JIRA, Visio, Confluence, Excel | SQL, Python, R, Tableau, Power BI |
| Primary Skills | Requirement gathering, documentation, stakeholder management | Data modeling, statistics, visualization |
| Output | Business requirements, workflows, process improvements | Reports, dashboards, forecasts |
Both are essential for organizational success, and many modern companies integrate both functions to ensure data-informed and process-aligned decisions.
Future Trends and Career Outlook
The future of Business Analysis and Business Analytics is deeply intertwined with digital transformation, artificial intelligence, and automation.
According to global reports, demand for data-related roles, including Business Intelligence , will continue to outpace supply. Similarly, the need for Business Analysts remains strong, especially in sectors like finance, healthcare, IT, and government. In the coming years, hybrid professionals who can combine both analytical and business process skills known as Business Data Analysts will be highly sought after. They will act as the bridge between insight generation and solution implementation.
Conclusion
In essence, Business Analysis and Business Analytics are two sides of the same coin. Business Analysis focuses on identifying and solving business problems, ensuring that systems and processes align with goals. Business Analytics focuses on analyzing data to provide insights that inform decisions. While one interprets what needs to be done, Business Analyst Training helps the other interpret what the data says. Both are essential for organizational success in the modern business ecosystem. As technology evolves, professionals who understand both perspectives will play a crucial role in shaping data-driven, efficient, and agile organizations.





