
- Overview of Online Threats
- What is Phishing?
- What is Pharming?
- Technical Differences
- Delivery Methods
- Target Audience and Impact
- Detection Techniques
- User Education and Awareness
- Real-World Scenarios
- Role of DNS in Pharming
- Preventive Measures
- Summary
Overview of Online Threats
In the digital age, the internet has become an integral part of daily life, enabling communication, commerce, and information exchange. However, it also serves as a breeding ground for cybercriminals who exploit users through various methods. Among these, phishing and pharming are particularly dangerous because they rely on user manipulation or system compromise to deceive victims. While phishing involves tricking users into voluntarily providing information, pharming silently redirects users to malicious sites Without their knowledge, recognizing these threats and understanding their distinctions is essential in Cyber Security Training to develop effective defenses.Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and among the most deceptive forms are detecting phishing and pharming . These two attacks may appear similar because they both aim to steal sensitive data, such as login credentials, financial information, and personal identification details. However, they differ significantly in execution, technical mechanisms, and prevention strategies. Understanding the nuances between phishing and pharming is crucial for individuals, businesses, and cybersecurity professionals aiming to protect sensitive information and maintain secure systems.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cybercrime Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a cyberattack method that involves sending deceptive messages often through email, text, or social media to lure victims into revealing In discussions about What Is Cyber Trolling, it’s important to recognize that personal information theft or clicking malicious links often happens through messages that appear to come from legitimate sources such as banks, e-commerce platforms, or employers. Phishing attacks exploit human psychology, Detection using fear, Online Threats, surgency, or curiosity to manipulate users into taking harmful actions. Once the victim clicks a link or enters information into a fake site, Target Audience and Impact the attacker captures sensitive data that can be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or unauthorized access.
What is Pharming?
Pharming is a more technically sophisticated attack that manipulates the way users reach legitimate websites. Instead of tricking users with fake emails, pharming redirects them to malicious websites by compromising DNS (Domain Name System) servers or altering local host files.
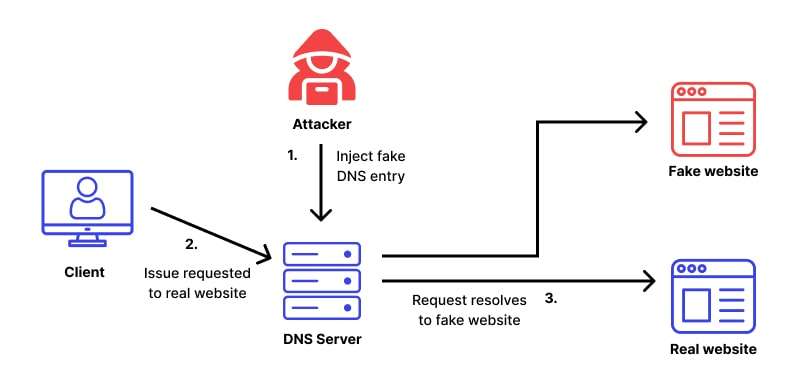
This means that even if a user types the correct web address into their browser, they may unknowingly land on a fraudulent site. Because it operates silently Understanding What is Data Classification helps organizations prioritize security measures, especially since pharming operates in the background, is harder to detect than phishing attacks, and can affect multiple users simultaneously if DNS infrastructure is compromised.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Technical Differences
The core difference between phishing and pharming lies in their technical execution:
- Phishing uses social engineering tactics to deceive individuals. It requires user interaction clicking a link, downloading a file, or submitting a form.
- Pharming on the other hand, involves manipulating network settings or DNS servers to redirect users without their awareness.
In Cyber Security Training, it’s emphasized that phishing attacks are usually short-lived and target specific individuals or groups, while pharming attacks can persist for longer periods and have broader impacts. particularly when DNS systems are targeted. Because of these differences, the two require distinct detection and prevention approaches.
Delivery Methods
Detecting phishing and pharming differ in how they reach and affect their victims:
- Phishing typically uses email, SMS (smishing), voice calls (vishing), or social media to deliver malicious links or attachments. The message often includes urgent language to prompt immediate action.
- Pharming The Guide to Multi-Factor Authentication that some attacks do not require direct user interaction through messages. Instead, they rely on DNS poisoning, host file manipulation, or rogue DNS servers to silently redirect users from trusted websites to malicious ones.
- Phishing often targets individuals through mass campaigns or spear-Phishing attacks, which are personalized attacks aimed at specific people or organizations.
- Pharming can affect entire networks or communities, especially if the attacker compromises an ISP’s DNS server or a widely used website.
- Phishing Detection: Anti-Phishing attacks tools analyze incoming messages for suspicious links, sender authenticity, and content red flags. Spam filters, email authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC), and browser warnings are commonly used to prevent phishing and spoofing attacks, much like how classical encryption methods such as the Vigenere Cipher were early attempts to secure communication.
- Pharming Detection: Since pharming alters the system or network settings, detecting it involves monitoring DNS traffic, checking host file integrity, and verifying the authenticity of digital certificates. Network monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems (IDS) are essential.
- Phishing Example: In a major phishing campaign, Cyber threats sent fake emails pretending to be from a well-known bank. The emails asked users to update their account information, directing them to a fake website that looked identical to the bank’s site—a common phishing tactic highlighted inCertified Cloud Security Professional(CCSP) training. Thousands of users entered their credentials, which were then used for unauthorized transactions.
- Pharming Example: A well-documented pharming attack in Brazil involved the compromise of DNS settings on users’ routers. When users attempted to visit banking websites, they were silently redirected to fake sites that harvested their credentials. Because the attack occurred at the network level, even security-conscious users were affected.
- Use spam filters and anti-phishing toolbars.
- Train employees to recognize suspicious messages.
- Employ two-factor authentication (2FA) for all sensitive accounts.
- Verify links and email senders before responding. For Pharming:
- Use antivirus and anti-malware programs that check for host file changes.
- Monitor DNS traffic for unusual activity.
- Keep routers and network firmware up to date.
- Use DNSSEC and secure DNS providers.
Phishing is generally more visible and detectable by users, while pharming operates covertly and may go unnoticed without proper cybersecurity tools.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Target Audience and Impact
Both phishing and pharming can target individuals, businesses, and institutions, but their impact varies:
The consequences of both attacks include data theft, unauthorized transactions, identity fraud, and loss of trust. However, pharming’s broader reach can cause widespread damage quickly and requires more technical effort to remediate.
Detection Techniques
Detecting phishing and pharming requires different strategies:
Users and administrators must stay vigilant and employ a combination of software solutions and manual checks to detect these threats early.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
User Education and Awareness
Education is a powerful tool in preventing detecting phishing and pharming attacks. Users who are aware of the signs of phishing such as misspelled domain names, suspicious links, and urgent requests for sensitive information are less likely to fall victim. Likewise, Online Threats educating users about the risks of pharming, such as being redirected to fake websites even when URLs are typed correctly, is essential. Regular training programs, simulated phishing tests, and security awareness campaigns can significantly reduce the likelihood of successful Cyber threats. Encouraging users to report suspicious activity and consult IT professionals when in doubt fosters a proactive cybersecurity culture.
Real-World Scenarios
Several real-world examples highlight the dangers of phishing and pharming:
These examples show how phishing and pharming exploit different vulnerabilities but lead to similar outcomes unauthorized access and data theft.
Role of DNS in Pharming
The DNS (Domain Name System) plays a central role in pharming attacks. DNS is responsible for translating human-friendly domain names into IP addresses that computers understand. By compromising DNS servers or altering DNS entries in a user’s system, Cyber threats can redirect traffic to malicious sites.
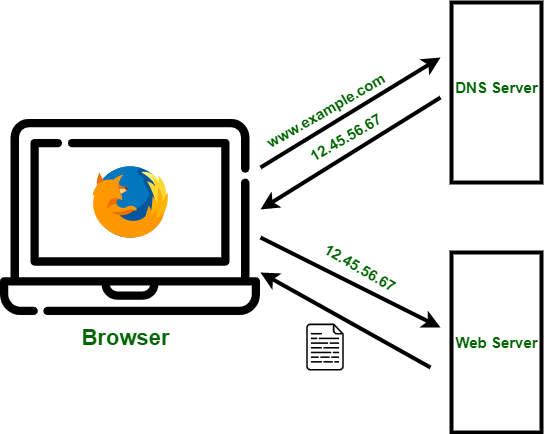
DNS poisoning or cache poisoning corrupts the DNS server’s records, allowing the attacker to redirect multiple users to fraudulent websites. This makes pharming a particularly dangerous threat, as it affects users regardless of their individual behaviors. Secure DNS protocols, DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions), and vigilant DNS management are crucial in preventing pharming.
Preventive Measures
To defend against Detecting phishing and pharming , users and organizations must implement layered security strategies:
For Phishing:General best practices include regularly updating software, avoiding public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions, and using VPNs to secure connections.
Summary
Between phishing and pharming are two distinct but equally dangerous cyber threats. While phishing exploits human psychology through deceptive messages, pharming manipulates internet infrastructure to redirect users to malicious sites. Understanding their differences helps in crafting effective defense mechanisms. In Cyber Security Training making education and awareness crucial, pharming which targets domain names and represents a more technical and silent online threat—requires robust network monitoring and secure DNS management to effectively protect users.In a connected world, no single solution guarantees complete protection. A multi-layered cybersecurity approach combining technical tools, user education, and organizational policies is essential to stay ahead of evolving threats. By understanding how phishing and pharming operate, individuals and businesses can better prepare, detect, and defend against these pervasive attacks.




