
- Node.js Versions
- Understanding LTS and Current Releases
- How to Check Your Node.js Version
- Installing and Updating Node.js
- Node.js Versioning Policy
- Key Features in Different Node.js Versions
- Breaking Changes Between Major Versions
- Best Practices for Upgrading Node.js
- Node.js Security Updates and Patches
- Performance Improvements in Recent Versions
- Choosing the Right Node.js Version
- Conclusion
Node.js Versions
React Native, developed by Facebook in 2015, is a cross-platform framework for building mobile applications using JavaScript and React. Unlike traditional native development, which requires separate coding for Android (Kotlin/Java) and iOS (Swift/Objective-C), React Native allows developers to write a single codebase that runs on both platforms. The framework uses native components under the hood, which means that apps built with React Native achieve performance close to native apps while offering the flexibility and speed of JavaScript development. React Native’s popularity has surged because it combines the speed of web development with the capabilities of mobile apps. Companies like Facebook, Instagram, UberEats, and Shopify have leveraged React Native to build high-performance mobile apps that scale efficiently across platforms.
Understanding LTS and Current Releases
Node.js has two release types: Long-Term Support (LTS) and Current. Each one is for different needs in the development world. The current release has the newest features and upgrades. It’s good for developers who want to try out new stuff. Still, it can be a bit shaky sometimes, which might be an issue for some projects. After six months, a current release becomes an LTS version, with support for 30 months. LTS releases focus on stability, long support, and working well with other systems. This makes them useful for production setups where stability is very important. For example, Node.js 20 will be the active LTS version, and Node.js 21 will be the newest Current release. LTS versions get regular security and bug fixes, which ensures they stay reliable for a long time. This is key for companies and production use. This system lets developers pick between new features and stability, based on what they need for their projects.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Full Stack Developer? Sign Up For Our Full Stack Developer Training Today!
How to Check Your Node.js Version
It’s essential to know which Node.js version you’re running, especially when troubleshooting or ensuring compatibility with dependencies. You can check your current version using the terminal command:
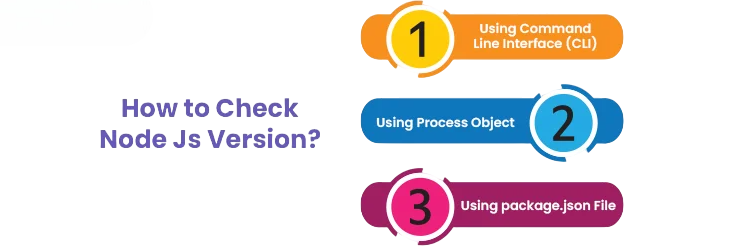
- npm -v
This command outputs a version string, such as v20.9.0. Similarly, to check your npm These version checks are vital during development, CI/CD pipeline setup, or when configuring environments across multiple machines.
Would You Like to Know More About Full Stack Developer? Sign Up For Our Full Stack Developer Training Now!
Installing and Updating Node.js
There are several ways to install or update Node.js depending on your operating system and workflow.
- For Windows and macOS: You can download installers directly from the official Node.js website. The installer includes both Node.js and npm by default.
- For Linux users: You can use package managers like apt, yum, or dnf:
- Updating Node.js: To update Node.js manually, download the latest version or use NVM
- Updating Node.js: To update Node.js manually, download the latest version or use NVM
Node.js Versioning Policy
Node.js uses Semantic Versioning (SemVer), with versions numbered as MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH. The MAJOR version changes when there are incompatible updates, like going from version 18 to 20. The MINOR version adds new, backward-compatible features, such as moving from version 20.1 to 20.2. The PATCH version fixes bugs or improves performance without breaking compatibility, for example, updating from version 20.2.1 to 20.2.2. This planned policy gives developers and businesses confidence when managing updates. Each Long-Term Support (LTS) version of Node.js has different phases: Active, Maintenance, and End-of-Life (EOL). It’s key for developers to watch the EOL dates to make sure they are using current versions. Older versions stop getting security updates, which are needed to keep applications safe and secure.
Key Features in Different Node.js Versions
Node.js updates bring improvements that change how we code. For example, version 14 gave us optional chaining and better reporting tools. These help make coding easier and debugging better. Version 16 then added good support for Apple’s M1 chip, made the Timers Promises API stable, and updated the V8 engine for better speed and compatibility. Version 18 included the Fetch API, Web Streams, and global structuredClone support. These allow developers to handle data and asynchronous tasks in a better way. In version 20, an updated permission model, a better V8 engine, and a stable test runner API gave developers additional testing ability. The newest version, 21, has faster startup times, better WebAssembly support, and some experimental upgrades to the permission model. By paying attention to these changes, developers can use new features and stay compatible with current web standards and JavaScript features, which improves their process.
Preparing for Full Stack Development Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Full Stack Development Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Breaking Changes Between Major Versions
Major Node.js releases often introduce breaking changes that may affect existing applications. These include:
- Removed Deprecated APIs: Older functions like require.extensions or outdated buffer constructors are removed for security reasons.
- Updated Default Behaviors: Certain features, such as module resolution or default TLS configurations, may behave differently.
- Changes in ECMAScript Module (ESM) Support: Some versions enhance or modify ESM handling, affecting import/export syntax.
- Runtime Deprecations: Libraries relying on outdated Node APIs may break if not updated.
Before upgrading, developers should review the official release notes and test applications in staging environments. Tools like nvm or containerized setups help mitigate risks during version transitions.
Best Practices for Upgrading Node.js
Upgrading Node.js should be approached strategically to minimize disruption. Here are best practices:
- Check compatibility: Review the release notes for deprecated APIs or behavior changes.
- Test in staging: Always verify your application in a non-production environment before upgrading.
- Update dependencies: Run npm outdated and update packages that rely on specific Node.js APIs.
- Use NVM: Manage multiple versions safely without affecting global configurations.
- Monitor performance: After upgrading, benchmark CPU and memory usage.
- Maintain backups: Before major updates, ensure that your application data and configurations are backed up.
Following these practices ensures a smooth transition between versions while minimizing downtime and bugs.
Node.js Security Updates and Patches
When handling Node.js versions, security is very important. To fix weaknesses, the Node.js team puts out Security Patch Releases when problems are found. These patches are key to stopping different kinds of exploits like prototype pollution and privilege escalations. Long-Term Support (LTS) versions get these updates quickly, which makes them more secure. Current versions might drop old, unsafe modules.
To stay safe from threats, sign up for Node.js Security Mailing Lists to get the newest updates. Also, running npm audit often will help you find and fix weaknesses in your dependencies. Using the newest LTS release is also a good idea because it has tested security patches. By keeping your Node.js versions updated, developers protect their applications and meet data protection rules, which makes the development environment more secure.
Performance Improvements in Recent Versions
Node.js continuously improves its speed and efficiency through optimizations in its underlying V8 JavaScript engine and the libuv library. Some of the recent performance upgrades include:
- Faster Startup Times: Newer versions pre-load essential modules to reduce initialization delays.
- Improved Garbage Collection: Optimized memory management helps applications run smoother under heavy load.
- Better Asynchronous Handling: The AsyncLocalStorage API and updated event loop algorithms enhance scalability.
- Native Test Runner: Introduced in Node.js 18 and stabilized later, reducing dependency on external testing tools like Mocha or Jest.
- HTTP/3 and QUIC support: Improving web server performance and security.
These improvements make modern Node.js versions more suitable for enterprise-grade microservices and large-scale API infrastructures.
Choosing the Right Node.js Version
Selecting the right Node.js version depends on several factors:
- For Production Use: Always prefer the latest LTS version for its stability, security, and community support.
- For Experimental Projects: Use the Current release to explore new features or test experimental APIs.
- For Legacy Projects: Stick to the version originally used until dependencies are updated.
- For Long-Term Projects: Choose a version that will remain supported for at least two years to minimize future migration issues.
As a rule of thumb, developers should align their Node.js version with their infrastructure requirements, dependency support, and long-term maintenance strategy.
Conclusion
Node.js version management is a crucial part of maintaining reliable, secure, and high-performing JavaScript applications. Each release whether LTS or current introduces valuable updates, optimizations, and security improvements. Understanding how to check, install, and upgrade Node.js versions ensures that your development environment remains efficient and future-proof. By following best practices, leveraging tools like NVM, and keeping up with release cycles, developers can harness the full power of Node.js to build scalable, performant, and secure applications. The key lies in balancing innovation with stability using current versions for learning and experimentation while relying on LTS versions for mission-critical deployments.



