
- What is Tkinter?
- Installing Tkinter
- Creating Your First Window
- Adding Buttons, Labels, and Entry Widgets
- Event Handling
- Layout Managers (pack, grid, place)
- Message Box and Dialogs
- Menu and Menubar
- Frames and Containers
- Canvas and Drawing
- Tips for GUI Development
- Conclusion
Python GUI – Tkinter Module
Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) are an essential part of modern software applications. Whether it’s a desktop app, a data visualization dashboard, or a small tool to automate tasks, GUIs help users interact with applications intuitively. In the Python ecosystem, the Python GUI Tkinter Module stands out as one of the simplest and most powerful libraries for GUI development. To complement these skills with front-end expertise, enrolling in Web Developer Training can help developers master layout design, styling, and user experience principles essential for modern application interfaces. This article explores the Python GUI Tkinter Module in depth, from installation to creating a complete GUI project.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
What is Tkinter?
Tkinter is the standard Python interface to the Tk GUI toolkit, which is one of the oldest and most widely used GUI toolkits. Tkinter comes bundled with most Python installations, making it highly accessible to developers without any extra dependencies. To understand how foundational class structures operate in other languages, exploring the Object Class in Java reveals how all Java classes inherit core methods like `toString()`, `hashCode()`, and `equals()`, forming the root of its object-oriented hierarchy. Tkinter allows developers to create windows, buttons, menus, labels, and much more with minimal code. It provides an object-oriented approach to building desktop applications, and it supports various layout managers and event-driven programming. Tkinter is especially suitable for beginners due to its simplicity and is used in many educational institutions to teach GUI programming.
Installing Tkinter
In most Python distributions, Tkinter is pre-installed. You can check if it’s available by opening your Python shell and typing. To better understand how Python scripts execute and where GUI logic should begin, exploring the Must-Know Main Function in Python helps clarify how to structure your code using `__name__ == “__main__”` for clean, modular execution.
- Efficient Code: Understanding DSA helps create optimized solutions in terms of speed and memory usage.
- Problem Solving: Most real-world problems require breaking down into smaller, manageable problems which are solved using algorithms and data structures.
- Interview Preparation: Most technical interviews for software engineering positions focus heavily on DSA.
- Competitive Programming: DSA is a core part of solving problems quickly under constraints.
Without a solid foundation in DSA, developers may struggle with writing high-performance applications.
Adding Buttons, Labels, and Entry Widgets
To make the GUI interactive, we can add various widgets like buttons, labels, and entry fields. Developers looking to enhance their interface design skills can benefit from Web Developer Training, which covers layout techniques, styling fundamentals, and user experience best practices.
Example:
- from tkinter import *
- root = Tk()
- root.title(“Widgets Example”)
- Label(root, text=”Enter your name:”).pack()
- entry = Entry(root)
- entry.pack()
- def greet():
- name = entry.get()
- Label(root, text=f”Hello, {name}!”).pack()
- Button(root, text=”Greet”, command=greet).pack()
- root.mainloop()
- Label: Displays text.
- Entry: Input field for user data.
- Button: Clickable button to trigger a function.
Tkinter allows easy chaining of widgets to create user-friendly interfaces.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Event Handling
Event handling is the process of responding to user actions, such as clicks or key presses. Tkinter uses callback functions to handle events. You can bind events using the .bind() method or assign a function to a widget’s command parameter. To build such interactive applications across both frontend and backend layers, mastering the Skills Needed for Full Stack Developers ensures you’re equipped with the versatility to handle UI logic, server communication, and database integration seamlessly.
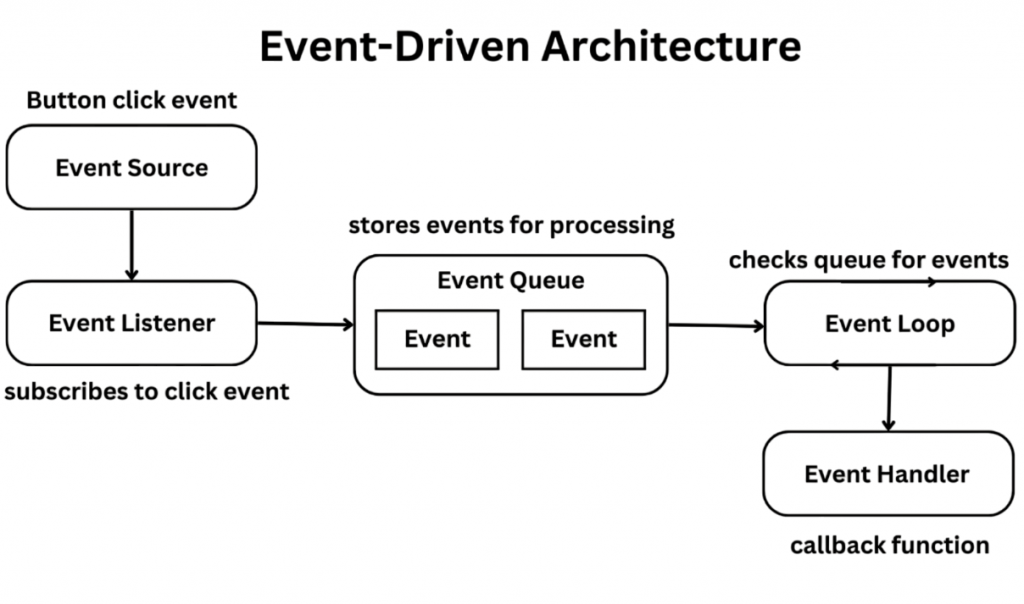
Example: Binding an Event:
- def on_keypress(event):
- print(“Key pressed:”, event.char)
- root = Tk()
- root.bind(“<Key>”, on_keypress)
- root.mainloop()
Layout Managers (pack, grid, place)
Tkinter, the powerful GUI toolkit for Python, offers three main layout managers to help you arrange your widgets easily. The first, `pack()`, lets you stack widgets vertically or horizontally in a simple way, making it perfect for straightforward interfaces.
For a more organized approach, `grid()` places your widgets in a table-like structure, which is ideal for forms where layout matters. To make these interfaces interactive, understanding What Is User Input in Python is essential, as it enables programs to capture and respond to user actions effectively using built-in functions like `input()`. You can label your input fields and align them neatly. Lastly, if you need complete control over where to place your widgets, `place()` allows you to position them at specific x and y coordinates.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Message Box and Dialogs
Tkinter supports various built-in dialogs and message boxes, which can be used for alerts, confirmations, and user input. To strengthen your programming fundamentals across languages, exploring Logical Programs in Java helps reinforce core algorithmic thinking through structured examples like Fibonacci series, palindrome checks, and prime number validation.
Example:
- messagebox.showinfo(“Info”, “This is an information box.”)
- messagebox.showwarning(“Warning”, “This is a warning.”)
- messagebox.showerror(“Error”, “This is an error message.”)
- response = messagebox.askyesno(“Confirmation”, “Do you want to continue?”)
These message boxes are useful for enhancing interactivity and guiding user actions.
Menu and Menubar
Menus provide navigational structure to GUI applications. To ensure these interfaces remain responsive under unpredictable load conditions, understanding What is Spike Testing is crucial it evaluates how software behaves during sudden surges or drops in user activity, helping developers design resilient systems that recover quickly from traffic spikes.
Example:
- from tkinter import *
- def open_file():
- print(“File opened.”)
- root = Tk()
- menu = Menu(root)
- root.config(menu=menu)
- file_menu = Menu(menu)
- menu.add_cascade(label=”File”, menu=file_menu)
- file_menu.add_command(label=”Open”, command=open_file)
- file_menu.add_separator()
- file_menu.add_command(label=”Exit”, command=root.quit)
- root.mainloop()
Menus enhance application professionalism and provide quick access to key functionalities.
Frames and Containers
Frames are containers that allow grouping of widgets. They are helpful in organizing complex layouts. To understand how structured components are managed in larger software ecosystems, exploring What is .Net FrameWork provides insight into Microsoft’s development platform, which supports modular design, language interoperability, and scalable application architecture.
- from tkinter import *
- root = Tk()
- frame = Frame(root)
- frame.pack()
- Label(frame, text=”Username”).grid(row=0, column=0)
- Entry(frame).grid(row=0, column=1)
- Label(frame, text=”Password”).grid(row=1, column=0)
- Entry(frame, show=”*”).grid(row=1, column=1)
- root.mainloop()
Using frames improves layout clarity and allows modular design, especially in larger apps.
Canvas and Drawing
Canvas is a powerful widget in Tkinter used for drawing shapes, graphs, and custom visuals. To ensure these graphical components function reliably across different environments, understanding Quality Assurance is essential it focuses on preventing defects and establishing standards that guarantee consistent performance and user satisfaction in software applications.
Example:
- from tkinter import *
- root = Tk()
- canvas = Canvas(root, width=300, height=200)
- canvas.pack()
- canvas.create_rectangle(50, 20, 250, 150, fill=”blue”)
- canvas.create_oval(80, 40, 220, 130, fill=”yellow”)
- root.mainloop()
Canvas is useful for building drawing apps, games, simulations, and custom animations.
Tips for GUI Development
Creating a polished GUI requires attention to both functionality and user experience. Here are some tips:
- Plan Your Layout: Use frames to divide your UI into logical sections before adding widgets.
- Be Consistent: Use consistent fonts, colors, and spacing to enhance usability.
- Use Meaningful Names: Name widgets and functions clearly to make your code readable.
- Separate Logic and UI: Keep your business logic in separate functions to avoid cluttering the GUI code.
- Test on Different Resolutions: Ensure your app is responsive and works well across screen sizes.
- Use Tooltips and Help Messages: Guide users by providing instructions or messages using Label or popups.
- Keep It Simple: Don’t overwhelm users with too many options. Build a minimal interface with essential features.
Conclusion
Tkinter is an excellent choice for Python developers looking to venture into GUI programming. The Python GUI Tkinter Module is beginner-friendly, well-documented, and powerful enough to build desktop applications ranging from simple tools to fully functional software. For those expanding into front-end development, exploring Web Developer Training can complement GUI skills by introducing layout principles, responsive design, and user experience fundamentals. With features like layout managers, events, menus, dialogs, and drawing capabilities, the Python GUI Tkinter Module equips you with everything needed to create interactive interfaces. Whether you are a student, a developer automating tasks, or someone prototyping a software tool, learning the Python GUI Tkinter Module adds immense value to your Python skill set. By understanding the fundamentals outlined in this article, you can now start building your own GUI applications confidently.





