
- Introduction to OOP in PHP
- What is Inheritance?
- Types of Inheritance in PHP
- Syntax and Structure
- The extends Keyword
- Method Overriding
- Constructor Behavior in Inheritance
- Using parent:: to Access Base Class
- Conclusion
Introduction to OOP in PHP
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in PHP is a programming paradigm that uses “objects” to design and structure code. Unlike procedural programming, where the focus is on functions and sequences of steps, OOP emphasizes modeling real-world entities using classes and objects. A class is a blueprint that defines the properties (variables) and behaviors (methods) of an object, while an object is an instance of a class. PHP began supporting OOP from version 4, but its full-fledged support came with PHP 5 Web Designing & Development Training and has since evolved significantly. Core concepts of OOP in PHP include encapsulation (restricting direct access to object data), inheritance (allowing a class to use properties and methods of another class), and polymorphism (using a single interface to represent different data types). These principles promote code reusability, modularity, and ease of maintenance. For example, instead of writing separate functions for similar entities like cars and bikes, you can create a Vehicle class and extend it. PHP also supports advanced OOP features such as interfaces, traits, abstract classes, and magic methods. By using OOP, developers can write more organized, scalable, and secure applications. It is widely used in frameworks like Laravel, Symfony, and CodeIgniter, making it essential for modern PHP development.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
What is Inheritance?
Inheritance is a fundamental concept in Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) that allows a class to inherit properties and methods from another class. The main purpose of inheritance is to promote code reusability and establish a natural hierarchy between classes. In inheritance, the class that provides its properties and methods is called the parent class (or base class or superclass) Minimum Spanning Tree, while the class that inherits from it is known as the child class (or derived class or subclass).
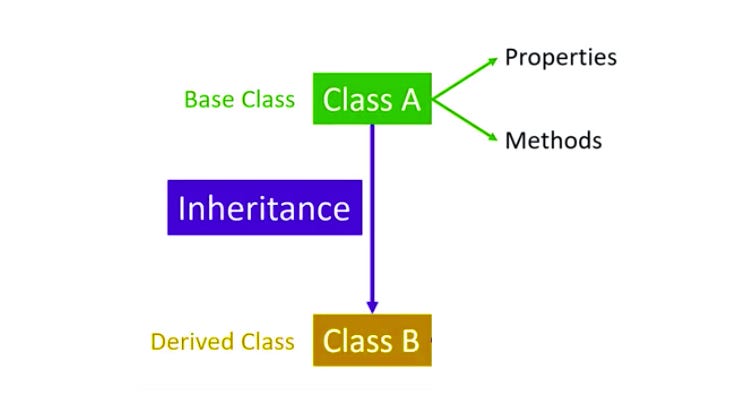
The child class can use all the accessible methods and properties of the parent class, and it can also have its own unique features or override the inherited ones. This allows developers to write general functionality once in a base class and extend or customize it in multiple subclasses.d override the makeSound() method to provide their specific. In PHP and other OOP languages, inheritance simplifies code maintenance and supports the design of flexible, scalable systems. Overall, inheritance enhances the organization of code by modeling relationships between classes based on shared behavior and characteristics.
Types of Inheritance in PHP
GUI Tkinter Module While PHP does not support multiple inheritance through classes (i.e., a class cannot extend more than one class), it offers the following:
Single Inheritance:
One class inherits from one parent.
- class Animal {
- public function speak() {
- echo “Animal speaks\n”;
- }
- }
- class Dog extends Animal {
- public function bark() {
- echo “Dog barks\n”;
- }
- }
Multilevel Inheritance:
A class inherits from a derived class.
- class LivingBeing {
- public function isAlive() {
- return true;
- }
- }
- class Animal extends LivingBeing {}
- class Cat extends Animal {}
Hierarchical Inheritance:
Multiple classes inherit from one base class.
- class Shape {
- public function draw() {
- echo “Drawing shape\n”;
- }
- }
- class Circle extends Shape {}
- class Square extends Shape {}
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Syntax and Structure
Basic structure of inheritance in PHP:
- class ParentClass { // Properties and methods
- }
- class ChildClass extends ParentClass { // Additional properties and methods
- }
Reverse C++ Vector The extends keyword establishes the inheritance relationship.
The extends Keyword
The extends keyword in PHP is used to create a child class from a parent class.It allows the child class to inherit properties and methods of the parent class Data Structures & Algorithms. This promotes code reusability and supports object-oriented principles like inheritance.
Example:
- class Vehicle {
- public $type = “Generic”;
- public function start() {
- echo “Vehicle started\n”;
- }
- }
- class Car extends Vehicle {
- public function drive() {
- echo “Driving a car\n”;
- }
- }
- $myCar = new Car();
- $myCar->start(); // Inherited method
- $myCar->drive(); // Own method
The Car class now has access to both start() and its own drive() method.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Method Overriding
Method Overriding occurs when a subclass provides a specific implementation of a method that is already defined in its parent class.It allows the subclass to modify or extend the behavior of the inherited method Web Designing & Development Training.The method name, parameters, and return type must be the same as in the parent class.This is useful for customizing functionality in a child class while maintaining a consistent interface.
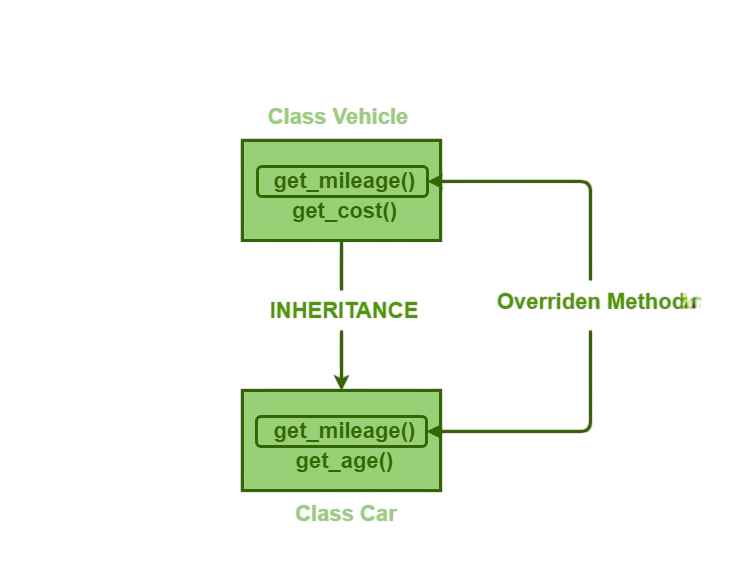
Example:
- class ParentClass {
- public function greet() {
- echo “Hello from parent\n”;
- }
- }
- class ChildClass extends ParentClass {
- public function greet() {
- echo “Hello from child\n”;
- }
- }
- $obj = new ChildClass();
- $obj->greet(); // Output: Hello from child
This allows customization of behavior while retaining structure.
Constructor Behavior in Inheritance
When a child class defines its own constructor, the parent Constructor Behavior in Inheritance is not called automatically. In PHP, when a child class inherits from a parent class, it does not automatically call the parent’s constructor unless explicitly done using parent::__construct(). If the parent class has a constructor and the child class defines its own, the parent’s constructor must be manually invoked if needed Paging in Operating Systems. This allows the child class to perform its own initialization while still reusing the setup from the parent. If the child class has no constructor, the parent’s constructor is called by default during object creation.
Example:
- class Base {
- public function __construct() {
- echo “Base constructor\n”;
- }
- }
- class Derived extends Base {
- public function __construct() {
- parent::__construct(); // Call base constructor
- echo “Derived constructor\n”;
- }
- }
- $obj = new Derived(); // Output: // Base constructor // Derived constructor
If the child doesn’t define a constructor, the parent’s constructor will be used by default. Attempting to access private members from a child class results in an error.
Using parent:: to Access Base Class
You can use parent:: to call parent methods or constructors even if they’ve been overridden. The parent:: keyword in PHP is used to access methods or properties from the parent (base) class within a child class IPO Cycle. It is commonly used to call the parent class’s constructor (parent::__construct()) or to reuse overridden methods. This helps maintain the behavior of the base class while extending or customizing it in the child class.
Example:
- class ParentClass {
- public function sayHi() {
- echo “Hi from parent\n”;
- }
- }
- class ChildClass extends ParentClass {
- public function sayHi() {
- echo “Hi from child\n”;
- parent::sayHi(); // Call parent method
- }
- }
- $obj = new ChildClass();
- $obj->sayHi();
Output:
- Hi from child
- Hi from parent
Conclusion
Inheritance is a foundational OOP feature that makes your PHP applications organized, scalable, and reusable. By extending classes using extends, reusing properties and methods, and overriding functionality, PHP allows you to build complex applications with ease. While inheritance simplifies code, it should be used judiciously alongside composition, traits, and interfaces to ensure modularity and maintainability Web Designing & Development Training. Inheritance is a key feature of Object-Oriented Programming in PHP that promotes code reuse, modularity, and cleaner application structure. By allowing child classes to inherit properties and methods from a parent class, developers can avoid code duplication and build scalable systems with shared functionality. Concepts like method overriding, constructors in inheritance, and the use of keywords like extends and parent:: provide flexibility in customizing class behavior. Understanding inheritance is essential for writing efficient, organized, and maintainable PHP code, especially when working with large applications or frameworks.





