
- Introduction to Multidimensional Arrays
- Syntax and Declaration of 2D Arrays
- Initialization Techniques
- Accessing and Modifying Elements
- Nested Loop Traversals
- Real-World Applications
- Matrix Operations (Addition, Multiplication)
- Conclusion
Introduction to Multidimensional Arrays
In the realm of programming, arrays are foundational data structures that allow developers to group multiple items of the same type together. Among these, the Two Dimensional Arrays is a particularly versatile tool. A 2D array is essentially an array of arrays, meaning each element of a 2D array is itself a one-dimensional array. This structure makes it possible to organize data in tabular format rows and columns allowing for more intuitive manipulation of structured data like matrices, tables, images, and even game boards. In languages such as C, C++, and Java, 2D arrays are widely used in applications that require matrix operations, grid-based problems, and data that naturally fits into a row-column structure. The ability to access data through two indices provides a natural and straightforward way to represent and work with structured datasets Web Designing & Development Training .Multidimensional arrays are data structures that allow the storage and organization of data in more than one dimension. While a one dimensional array stores a simple list of elements, a multidimensional array such as a two-dimensional array can represent data in the form of tables or matrices, with rows and columns. This makes them ideal for applications involving grids, images, or mathematical computations. In programming, multidimensional arrays are typically accessed using multiple indices; for example, array[i][j] accesses the element in the i-th row and j-th column of a 2D array. These arrays can extend to three or more dimensions, such as 3D arrays used in modeling volumetric data or simulations. Understanding how to declare, initialize, and traverse these structures is crucial for solving complex problems efficiently. Many programming languages, like C++, Java, Python, and JavaScript, support multidimensional arrays, although the syntax and internal implementation may vary. For instance, Python offers lists of lists to simulate multidimensional arrays, while NumPy provides powerful support for actual n-dimensional arrays. Efficient use of multidimensional arrays can significantly optimize algorithms in areas like scientific computing, graphics, data analysis, and machine learning. Mastering them is essential for developers and data scientists working with large and complex data sets.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Syntax and Declaration of 2D Arrays
The declaration of 2D arrays varies slightly depending on the programming language being used:
In C/C++:
- int matrix[3][4];
This line of code declares a matrix of integers with 3 rows and 4 columns.
In Java:
- int[][] matrix = new int[3][4];
Java allows more flexibility, IPO Cycle as arrays in Java are actually arrays of references to other arrays, meaning that each row can potentially be a different length (jagged arrays). In both cases, the array is zero-indexed, meaning the first element is at [0][0].
Initialization Techniques
There are several ways to initialize Two Dimensional Arrays . You can do it manually using loops, or Web Designing & Development Training Initialization Techniques the values directly when you declare the array.
C/C++ Example:
- int matrix[2][3] = {
- {1, 2, 3},
- {4, 5, 6}
- };
Java Example:
- int[][] matrix = {
- {1, 2, 3},
- {4, 5, 6}
- };
In both cases, the array has 2 rows and 3 columns. For larger arrays, it is often more practical to use nested loops to fill the array with data, especially if the values are generated at runtime.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Accessing and Modifying Elements
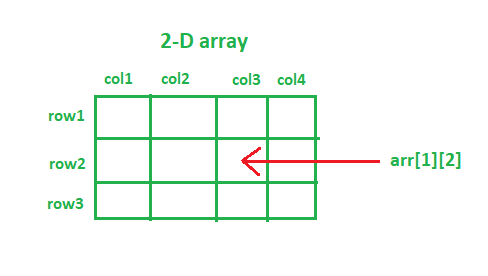
Accessing elements in a 2D array is done using two indices: one for the row and one for the column. To retrieve or change a value, you simply use:
- int val = matrix[1][2]; // Accesses the element in the second row, third column
- matrix[1][2] = 10; // Modifies the element to hold the value 10
It’s important to ensure that the indices are within the bounds of the array to avoid runtime errors such as ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException in Java or segmentation faults in C/C++Accessing and modifying elements in a multidimensional array involves using multiple indices to pinpoint the exact location of a value within the structure. For example, in a two-dimensional array, you use two indices one for the row and one dimensional array for the column such as array[i][j], where i refers to the row and j to the column. This allows you to directly retrieve or update a specific element. To modify an element, you simply assign a new value to that indexed position, like array[i][j] = newValue. The process is similar for arrays with more dimensions; you just add additional indices, such as array[i][j][k] for a three-dimensional array. It’s important to ensure that all index values are within the bounds of the array to avoid errors like index out of range Call a Function in Python. Traversing through a multidimensional array to access or modify each element typically involves nested loops, with one loop for each dimension. Understanding how to properly navigate and update elements is essential for performing calculations, updating data structures, and solving complex problems efficiently. Whether you’re working with matrices, grids, or multi-layered data, mastering element access and modification is a key skill in programming with arrays.
Nested Loop Traversals
2D arrays are typically traversed using nested loops:
- for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++) {
- System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + ” “);
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
In this example, Remove Duplicate Elements the outer loop iterates over the rows and the inner loop iterates over the columns.
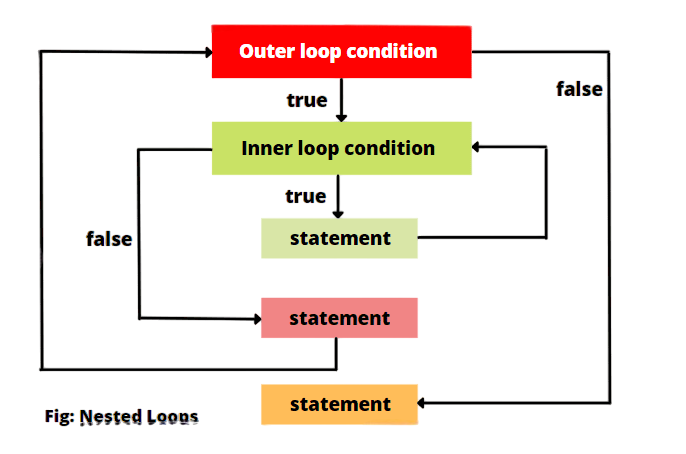
This pattern is used for accessing, modifying, or performing operations like summing all elements.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Real-World Applications
Two-dimensional arrays are ubiquitous in real-world applications. Some common examples include:
- Image Processing: Pixels of an image are stored in a grid format.
- Game Development: Games like chess or sudoku rely on a board, which is essentially a 2D array.
- Data Tables: Storing rows and columns of data, similar to a spreadsheet GUI Tkinter Module.
- Pathfinding Algorithms: Maps and grids used in AI often use 2D arrays.
- Scientific Computing: Simulations and numerical methods require matrices.
Matrix Operations (Addition, Multiplication)
Matrix operations are fundamental in various applications such as graphics, physics simulations, Data Structures & Algorithms and machine learning.
Addition of Two Matrices:
- for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
- result[i][j] = matrix1[i][j] + matrix2[i][j];
- }
- }
Multiplication of Two Matrices:
- for (int i = 0; i < rows1; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < cols2; j++) {
- result[i][j] = 0;
- for (int k = 0; k < cols1; k++) {
- result[i][j] += matrix1[i][k] * matrix2[k][j];
- }
- }
- }
These operations must conform to specific rules: For addition, matrices must have the same dimensions. For multiplication, the number of columns in the first matrix must equal the number of rows in the second.
Conclusion
Two-dimensional arrays are a critical concept in computer programming, especially when working with structured or grid-based data. They provide an organized way to store, manipulate, and retrieve data efficiently. Mastery of 2D arrays and one dimensional array paves the way for advanced concepts such as matrices in linear algebra, dynamic programming techniques, Web Designing & Development Training and multi-dimensional data visualization. By understanding how to declare, initialize, access, and manipulate Two Dimensional Arrays , programmers can build robust and efficient applications. Whether it’s for games, data analytics, scientific simulations, or just processing tabular data, 2D arrays are invaluable tools in your programming toolkit. Practice and experimentation are key. Try out various operations, solve matrix-based problems, and visualize your array’s structure to solidify your understanding. Once comfortable, explore higher-dimensional arrays and complex data structures built upon them like tensors or 3D matrices. Happy coding!





