
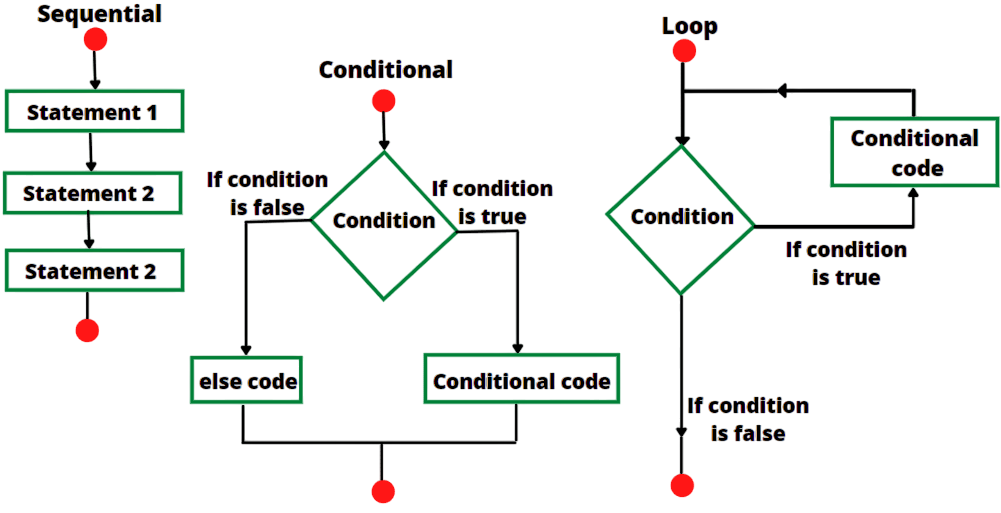
- Introduction to Control Statements
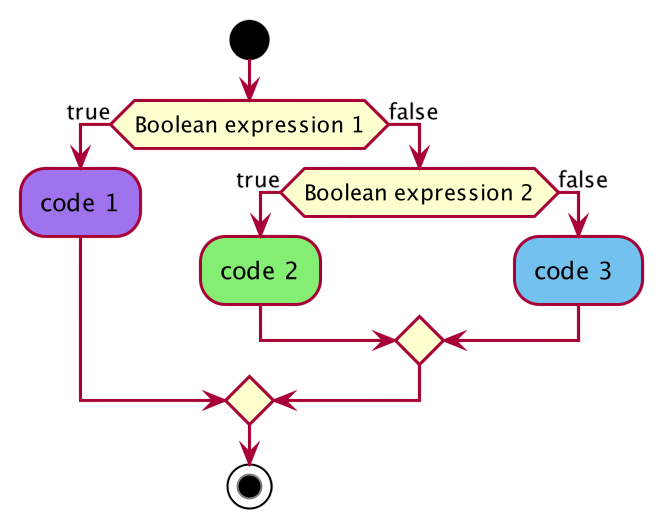
- If, If-else, and Nested if Statements
- Switch-Case Statements
- Loops in C (for, while, do-while)
- Break and Continue Keywords
- Goto Statement (Use with Caution)
- Conditional Operator (?:)
- Infinite Loops and Exit Conditions
- Practical Scenarios Using Control Statements
- Logical Operators and Their Role
- Common Errors and Debugging
- Conclusion
Introduction to Control Statements
In programming, Control Statements refers to the order in which individual instructions, functions, and statements are executed or evaluated. In C, control statements play a vital role in determining how a program proceeds through its logic based on specific conditions or repeated operations. These structures make C a powerful language capable of handling decision-making, looping, and branching. To complement such low-level control with high-level design capabilities, exploring Web Developer Training equips learners with the tools to build responsive, visually engaging websites using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern UI frameworks bridging logic with aesthetics in web development. Whether you’re building a calculator, a menu-driven program, or handling user authentication, control statements allow your program to react and respond dynamically to various inputs and situations.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
If, If-Else, and Nested if Statements
The if statement is a basic programming tool that lets you check a condition and run specific code only when that condition is true. For example, if you check whether a number is greater than zero using if (x > 0), and that turns out to be true, the program will show x is positive. This simple check is not just a technical detail, it is essential for validating user inputs, following business rules, and ensuring security in applications. The if-else statement adds flexibility by giving an option for what to do when the condition isn’t met. To complement such decision-making logic with career-oriented insights, exploring Functional Programming vs OOP reveals top tech roles like Data Scientist, DevOps Engineer, and AI Architect highlighting the skills, salaries, and growth paths that align with today’s competitive software landscape. Imagine having an if-else structure that checks the same condition: if x is positive, it prints x is positive, but if it is zero or negative, it returns x is zero or negative. This setup helps programmers manage different outcomes effectively, creating a smooth and logical flow in the code. Understanding these conditional statements opens up more complex decision-making processes in programming.
Nested if Statements
Allow multiple conditions in a hierarchy. Useful when decisions depend on prior checks. To complement such decision structures with efficient data handling, exploring Linked List In Data Structure introduces specialized data types like enhancing performance, readability, and flexibility in complex Python workflows.
- if (x > 0) {
- if (x % 2 == 0) {
- printf(“x is a positive even number\n”);
- }
- }
Use indentation and braces to make nested conditions clear and manageable.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Switch-Case Statements
The switch statement offers a multi-way decision structure and is an efficient alternative to lengthy if-else-if ladders. To complement such branching logic with cleaner iteration patterns, exploring Data Structure Definition reveals how assigning indices to iterable items streamlines loop control making your code more readable, efficient, and Pythonic when handling lists, tuples, or strings.
- switch (choice) {
- case 1:
- printf(“Option 1 selected\n”);
- break;
- case 2:
- printf(“Option 2 selected\n”);
- break;
- default:
- printf(“Invalid choice\n”);
- }
Switches are typically used in menu-driven programs, state machines, and configurations. Always use the break statement to prevent fall-through errors, unless intentional.
Loops in C (for, while, do-while)
Loops allow code to execute repeatedly based on a condition. There are three primary types: To complement such control structures with front-end development skills, exploring Web Developer Training equips learners with the ability to build dynamic, responsive interfaces using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript bridging logic-driven execution with visually engaging user experiences.
For Loop
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- printf(“%d\n”, i);
- }
Ideal for traversing arrays, counting, or executing a block a fixed number of times.
While Loop
Check the condition before executing the block.
- int i = 0;
- while (i < 5) {
- printf(“%d\n”, i);
- i++;
- }
Best for input validation or conditions with unpredictable bounds.
Do-while Loop
Executes the block at least once before checking the condition.
- int i = 0;
- do {
- printf(“%d\n”, i);
- i++;
- } while (i < 5);
Useful in menu systems or when the code must run at least once.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Break and Continue Keywords
Break Statement
Immediately terminates the enclosing loop or switch.
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- if (i == 5) break;
- printf(“%d\n”, i);
- }
Commonly used to exit a loop based on a condition, saving time and resources.
Continue Statement
Skips the current iteration and proceeds with the next.
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- if (i == 5) continue;
- printf(“%d\n”, i);
- }
Ideal for filtering out certain data within a loop. To complement such control flow techniques with long-term career planning, exploring How to Become a Software Engineer outlines the essential steps from choosing a programming language and learning to code, to pursuing internships, certifications, and specializations that align with today’s most in-demand software roles.
Goto Statement (Use with Caution)
The `goto` statement is an interesting feature in programming that lets you jump to a specific spot in the code without any conditions. For example, when you encounter instruct the program to jump directly to label:, where the code continues to run. This can be useful in certain situations, like breaking out of complex nested loops or handling errors.However, be careful! While the `goto` statement can quickly fix specific problems, misusing it often leads to what programmers jokingly call ‘spaghetti code’ a complex mess that is difficult to read and maintain. To complement such control flow discussions with scalable software development practices, exploring Load Balancing Algorithms showcases how Java powers everything from enterprise systems and mobile apps to embedded devices and cloud platforms emphasizing structure, maintainability, and cross-platform reliability. So, even though it might be an appealing tool in your programming toolbox, it’s wise to use `goto` sparingly and carefully consider your code’s structure. By understanding its impact, you can keep your projects clear and avoid confusion.
Conditional Operator (?:)
A ternary operator that offers a compact syntax for conditionally assigning values. To complement such concise logic with robust text manipulation, exploring Introduction to Algorithms reveals how immutable objects support operations like comparison, concatenation, splitting, and formatting making them foundational for building readable, maintainable, and efficient Java applications.
- int max = (a > b) ? a : b;
- // Equivalent to:
- if (a > b) max = a;
- else max = b;
This operator is often used in expressions that need to return a value quickly.
Infinite Loops and Exit Conditions
An infinite loop occurs when the exit condition is never satisfied.
- while (1) {
- // runs forever
- }
- for (;;) {
- // infinite loop
- }
Useful in servers, background processes, or embedded systems, but must be managed with proper exit conditions or signals.
Practical Scenarios Using Control Statements
- ATM Machine Simulation: Use switch-case for handling operations like withdrawal, deposit, or viewing balance.
- User Authentication System: Use if-else to validate user credentials and implement retry logic with while.
- Student Grading System: Use nested if statements to determine grades based on marks.
- Menu-driven Calculator: Combine while and switch to allow continuous calculation until the user exits.
- Data Filtering: Use for loops to skip undesired values while processing data.
Logical Operators and Their Role
Logical operators allow multiple conditions to be evaluated:
- && (Logical AND)
- || (Logical OR)
- ! (Logical NOT)
Example:
- if (age >= 18 && hasLicense) {
- printf(“You are eligible to drive.\n”);
- }
They are essential in complex decision-making and validation logic.
Common Errors and Debugging
- Omitting break in switch: Can lead to unintended fall-through behavior across cases.
- Assignment Instead of Comparison: Using = instead of == in conditions causes logic errors.
- Forgetting Braces in Nested if: May result in ambiguous or incorrect control flow.
- Infinite Loops: Verify loop conditions and ensure they can eventually evaluate to false.
- Incorrect Loop Incrementation: Ensure the loop variable changes correctly to avoid infinite execution.
Use debuggers like gdb, print statements, and logical tracing to identify and fix these issues.
Conclusion
Control Statements in C are essential tools that determine the logical flow of programs. Whether it’s making decisions using if-else, selecting among alternatives using switch, or repeating actions using loops, control structures offer flexibility, efficiency, and clarity in coding. Understanding these structures deeply not only makes your code functional but also more efficient and adaptable to change. To complement such foundational coding skills with front-end expertise, exploring Web Developer Training offers hands-on experience in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and UI/UX design empowering learners to build responsive, visually engaging websites aligned with modern development standards. Through hands-on practice and real-world examples, developers can master control statements and write robust, bug-free programs with greater confidence.





