
- Introduction to Filling Algorithms
- What is the Boundary Fill Algorithm?
- Difference Between Boundary Fill and Flood Fill
- Types of Boundary Fill (4-connected vs 8-connected)
- Algorithm Logic and Step-by-Step Explanation
- Pseudocode for Boundary Fill Algorithm
- Recursive vs Iterative Implementation
- Applications in Computer Graphics and UI
- Limitations and Stack Overflow Issues
- Optimization Techniques for Boundary Fill
- Sample Code in C/C++ and Python
- Real-World Use Cases
- Summary
Introduction to Filling Algorithms
Filling algorithms form the backbone of many operations in computer graphics. Whether it’s a simple drawing application, a complex CAD system, or a sophisticated user interface, the ability to fill a closed region with a color or pattern is essential. Filling techniques help developers render shapes, manage textures, and even handle collision detection in some cases. To complement such graphical operations with language-level efficiency, exploring Kotlin vs Java offers a comparative view of two powerful languages highlighting Kotlin’s concise syntax and modern features versus Java’s stability and widespread adoption, helping developers choose the right toolset for building responsive, graphics-intensive applications. Among the available options like scan-line fill, flood fill, and boundary fill the boundary fill algorithm is widely appreciated for its logical simplicity and visual reliability.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
What is the Boundary Fill Algorithm?
The boundary fill algorithm is a region-filling algorithm used in computer graphics to fill a closed area defined by a boundary color. It starts from a given interior point (called the seed) and expands outwards in all directions until it encounters a boundary. To complement such algorithmic expansion with practical development expertise, exploring Web Developer Training equips learners with the skills to build interactive websites and full-stack applications covering HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and backend technologies that support scalable, user-driven experiences. During this expansion, it colors each pixel that is neither part of the boundary nor already filled. This algorithm is particularly beneficial in situations where the shapes or regions are irregular and not aligned to a specific coordinate grid.
Difference Between Boundary Fill and Flood Fill
Both boundary fill and flood fill algorithms aim to fill enclosed regions, but they differ in how they define the fill condition: To complement such graphical logic with structured programming principles, exploring What is Abstraction in Java reveals how abstract classes and interfaces help isolate essential behaviors enabling developers to focus on relevant properties while hiding implementation details, much like how fill algorithms selectively process pixels based on defined boundaries.
- Boundary Fill: The algorithm fills the area until it hits a specific boundary color. It does not depend on the color of the initial seed pixel.
- Flood Fill: The algorithm fills the area that has the same color as the initial seed pixel, regardless of any external boundary.
This distinction makes boundary fill ideal for artistic applications, where color boundaries separate regions, whereas flood fill is better suited for tasks like repainting areas of uniform color.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Types of Boundary Fill: 4-Connected vs 8-Connected
- 4-Connected Boundary Fill: The algorithm fills the four immediate neighbors up, down, left, and right.
- 8-Connected Boundary Fill: This includes the four diagonal neighbors in addition to the four cardinal ones.
4-connected fills are faster but may leave small gaps in diagonally connected areas. 8-connected fill provides better coverage, especially in irregularly bounded shapes. To complement such pixel-level connectivity logic with foundational programming structures, exploring What are the Important Data Structures introduces core concepts like arrays, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs each essential for managing spatial data, optimizing traversal, and implementing efficient fill algorithms in graphics and image processing.
Algorithm Logic and Step-by-Step Explanation
The steps involved in the boundary fill algorithm are: To complement such graphical algorithms with practical development expertise, exploring Web Developer Training equips learners with the skills to build interactive web applications covering HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and backend technologies that support dynamic rendering, user input handling, and real-time visual updates.
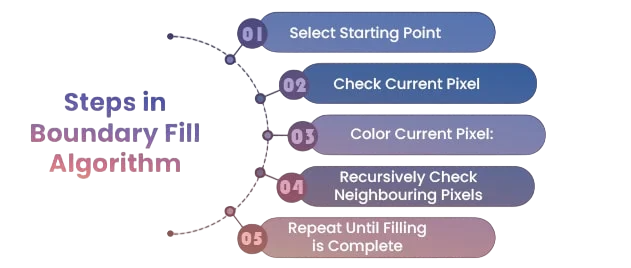
- Start from a pixel inside the boundary (seed pixel).
- Check the color of the pixel:
- If the pixel color is not the boundary color and not the fill color, change it to the fill color.
- Recursively apply this check to all connected pixels (based on 4 or 8 connectivity).
- Stop when all reachable pixels have been filled.
This recursive method ensures that no pixel within the boundary is left uncolored.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Pseudocode for Boundary Fill Algorithm
4-connected version:
- void boundaryFill(x, y, fillColor, boundaryColor) {
- if (getPixel(x, y) != boundaryColor && getPixel(x, y) != fillColor) {
- setPixel(x, y, fillColor);
- boundaryFill(x + 1, y, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill(x – 1, y, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill(x, y + 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill(x, y – 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- }
- }
8-connected version:
- void boundaryFill8(int x, int y, int fillColor, int boundaryColor) {
- if (getPixel(x, y) != boundaryColor && getPixel(x, y) != fillColor) {
- setPixel(x, y, fillColor);
- boundaryFill8(x + 1, y, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill8(x – 1, y, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill8(x, y + 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill8(x, y – 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill8(x + 1, y + 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill8(x – 1, y + 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill8(x + 1, y – 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill8(x – 1, y – 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- }
- }
Recursive vs Iterative Implementation
Recursive Method:
- Simple to implement.
- Easy to understand.
- Limited by stack size, which can lead to stack overflow errors on large regions.
Iterative Method:
- Uses an explicit data structure (like a stack or queue).
- Avoids stack overflow.
- Better suited for performance-critical applications.
Example (Python-like pseudocode):
- stack = [(x, y)]
- while stack:
- x, y = stack.pop()
- if getPixel(x, y) != boundaryColor and getPixel(x, y) != fillColor:
- setPixel(x, y, fillColor)
- stack.extend([(x + 1, y), (x – 1, y), (x, y + 1), (x, y – 1)])
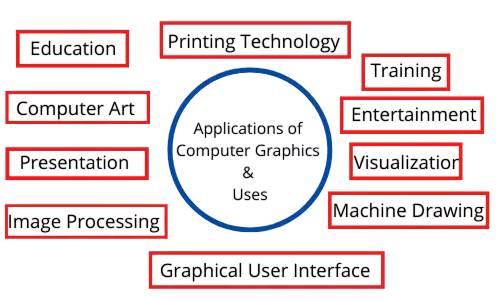
Applications in Computer Graphics and UI
- Drawing Software: Implements paint bucket tools for region filling.
- Game Development: Used for terrain painting and texture mapping.
- CAD Software: Enables filling of closed boundaries in 2D design layouts.
- Data Visualization: Highlights areas of interest in charts or geographic maps.
- UI Development: Supports theming and interactive component highlighting.
Limitations and Stack Overflow Issues
While the algorithm is conceptually simple, its recursive implementation is risky for large fill areas. Stack overflow errors may occur when too many recursive calls are made. This happens especially when filling large images or regions with complex shapes. To complement such recursion-heavy operations with language-level performance insights, exploring Go vs Python offers a comparative look at how each language handles memory, concurrency, and execution speed highlighting Go’s efficiency in managing stack frames and Python’s flexibility in prototyping complex algorithms. The performance may also degrade due to redundant checks or lack of optimization.
Optimization Techniques for Boundary Fill
- Use Iterative Approach: Avoids deep recursion and stack overflow issues.
- Check Visited Pixels: Prevents reprocessing by using a Boolean visited array.
- Bounding Box Optimization: Rejects pixels outside a predefined bounding region.
- Scan-Line Fill Integration: Combines horizontal line detection for faster processing.
These techniques not only enhance speed but also prevent crashes in production-level software. To complement such performance safeguards with robust communication protocols, exploring Soap vs Rest offers a detailed comparison between two major web service architectures highlighting SOAP’s strict standards and built-in security versus REST’s lightweight design and flexibility, helping developers choose the right approach for scalable, fault-tolerant systems.
Sample Code in C/C++
- void boundaryFill(int x, int y, int fillColor, int boundaryColor) {
- int currentColor = getPixel(x, y);
- if (currentColor != boundaryColor && currentColor != fillColor) {
- setPixel(x, y, fillColor);
- boundaryFill(x + 1, y, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill(x – 1, y, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill(x, y + 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- boundaryFill(x, y – 1, fillColor, boundaryColor);
- }
- }
Python Equivalent (Using a 2D Array)
- def boundary_fill(x, y, fill_color, boundary_color, canvas):
- if canvas[y][x] != boundary_color and canvas[y][x] != fill_color:
- canvas[y][x] = fill_color
- boundary_fill(x + 1, y, fill_color, boundary_color, canvas)
- boundary_fill(x – 1, y, fill_color, boundary_color, canvas)
- boundary_fill(x, y + 1, fill_color, boundary_color, canvas)
- boundary_fill(x, y – 1, fill_color, boundary_color, canvas)
Real-World Use Cases
- Medical Imaging: Highlighting tumor regions or tissues for diagnostic clarity.
- Geographic Mapping: Filling territories or zones on maps for visual distinction.
- Digital Painting: Creating complex vector artwork using region-based fills.
- Simulation Software: Representing filled areas to model physical or environmental phenomena.
Summary
Boundary fill is a basic technique used in computer graphics to fill an area defined by a specific color. This method has two types: 4-connected and 8-connected, which meet different application needs. While recursive implementations of this algorithm can be neat, they may lead to stack overflow issues with large datasets. To complement such algorithmic awareness with practical development expertise, exploring Web Developer Training equips learners with the skills to build scalable web applications covering HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and backend technologies that promote efficient, real-world problem solving. Therefore, iterative approaches are preferred in production settings because they are more reliable and efficient. Boundary fill is used in various areas, from video games to medical imaging, highlighting its versatility. By learning this algorithm, programmers and designers can improve their graphical tools and better understand region-based rendering.





