
- Introduction to Load Balancing
- Why Load Balancing is Important in Distributed Systems
- Key Objectives of Load Balancing
- Types of Load Balancing (Static vs. Dynamic)
- Round Robin Algorithm
- Least Connections Algorithm
- Weighted Round Robin and Weighted Least Connections
- IP Hash and URL Hash Based Algorithms
- Conclusion
Introduction to Load Balancing
Load balancing is a critical technique in computer networking and distributed systems that distributes incoming network traffic or computation across multiple servers or resources. The primary goal is to improve system performance, maximize resource utilization, avoid overload on a single server, and ensure high availability and reliability. Load balancers act as intermediaries that decide how to route each request or task efficiently.Load balancing is a crucial technique in computer networks and distributed systems that ensures the efficient distribution of incoming traffic or workloads across multiple servers or resources Web Designing & Development Training. Its primary goal is to prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed, which can lead to reduced performance, increased latency, or even system failure. By intelligently distributing tasks, load balancers help maintain high availability and reliability of services. They monitor the health and performance of servers, directing traffic to the ones best suited to handle requests at any given time. This process not only enhances system performance but also ensures seamless user experiences, even during traffic spikes. Load balancing can be implemented using hardware appliances, software applications, or cloud-based solutions. It supports different algorithms like round-robin, least connections, and IP hash to determine how traffic is routed. In modern architectures like microservices and cloud computing, load balancing plays a vital role in scaling applications dynamically. It also adds a layer of fault tolerance, as traffic can be redirected if a server goes down. Overall, load balancing is essential for building scalable, resilient, and high-performing applications that serve users efficiently across the globe.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Why Load Balancing is Important in Distributed Systems
In distributed systems, multiple servers handle different parts of an application. Without proper load distribution, some servers may be overwhelmed while others remain underutilized. This imbalance leads to slower performance, increased latency, service downtime, and poor user experience. Load balancing ensures that no single node becomes a bottleneck, which is especially crucial in systems requiring horizontal scalability, such as large-scale web applications or cloud-based platforms.Load balancing is essential in distributed systems because it ensures optimal resource utilization, StringBuilder improves system responsiveness, and enhances reliability.
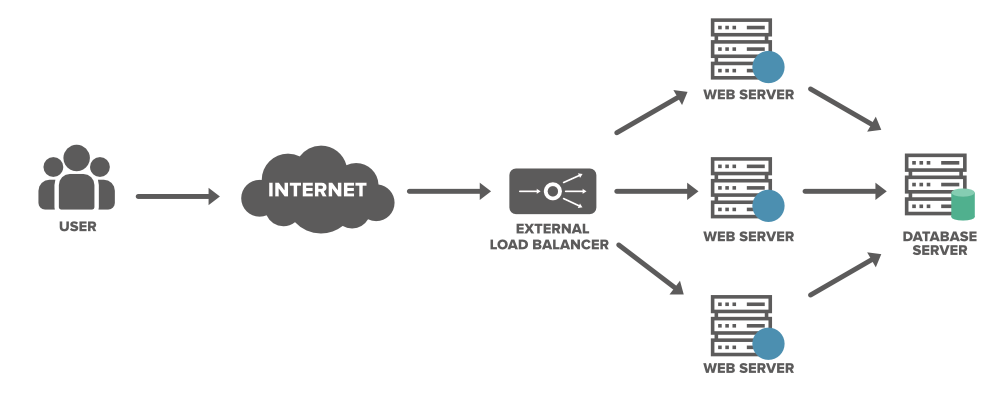
In a distributed environment, multiple servers or nodes work together to handle large volumes of tasks or user requests. Without proper load distribution, some nodes may become overloaded while others remain underutilized, leading to performance bottlenecks and potential system failures. Load balancing addresses this by evenly distributing workloads, preventing single points of failure and enabling the system to scale efficiently. It also supports fault tolerance by rerouting traffic in case a server goes down, ensuring continuous availability of services. Ultimately, load balancing is critical for maintaining the performance, scalability, and resilience of distributed systems.
Key Objectives of Load Balancing
- Even Distribution of Workload: To prevent any single server or resource from being overloaded while others remain underutilized.
- High Availability and Reliability: Ensures continuous operation of services by redirecting traffic in case of server failure or downtime.
- Scalability: Supports the ability to add or remove resources dynamically based on demand, Pointers in C enabling smooth system growth.
- Optimized Resource Utilization: Maximizes the use of available computing resources, improving overall system efficiency and performance.
- Reduced Latency and Faster Response Time: Directs user requests to the most responsive or geographically closest server, enhancing user experience.
- Fault Tolerance: Increases system resilience by automatically rerouting requests during failures or maintenance.
- Improved System Performance: Balances processing loads to maintain consistent performance, even during peak traffic periods.
- Static Load Balancing: Static algorithms use predefined rules and do not adapt to real-time traffic or server load. These are easier to implement and work well when workload and capacity are predictable. Examples include Round Robin and IP Hash.
- Dynamic Load Balancing: Dynamic methods monitor server health, workload, and response time to make intelligent routing decisions. These adapt to changing conditions and offer better performance in unpredictable environments Linux Operating System. Examples include Least Connections and Weighted Least Connections.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Types of Load Balancing (Static vs. Dynamic)
Each method has trade-offs; static is simpler but less flexible, while dynamic is smarter but often more complex.
Round Robin Algorithm
Round Robin is one of the simplest and most widely used static load balancing algorithms. It assigns incoming requests to servers in a cyclic order, ensuring that all servers get an equal number of requests over time.The Round Robin algorithm is one of the simplest and most commonly used load balancing techniques. It works by distributing incoming requests sequentially across a group of servers in a circular order Web Designing & Development Training. Once the last server in the list receives a request, the algorithm loops back to the first server and repeats the process. This method ensures that each server gets an equal share of the workload over time, assuming all servers have similar capabilities. While Round Robin is easy to implement and works well in environments with uniform server performance, it may not be ideal for systems with servers of varying capacities or workloads, as it does not account for the current load on each server. Despite its simplicity, it remains a popular choice for many load balancing scenarios, especially where resource demands are evenly distributed.
Example:
If you have three servers (A, B, C), the requests are distributed like: A → B → C → A → B → … Round Robin is easy to implement and works well when all servers have similar capacity and load-processing speed. However, it doesn’t account for real-time server load or response time.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Least Connections Algorithm
The Least Connections algorithm is a dynamic method that assigns new requests to the server with the fewest active connections. It is particularly effective when sessions are long-lived or vary in resource usage.The Least Connections algorithm is a dynamic load balancing method that distributes incoming requests based on the number of active connections each server is currently handling. Instead of rotating through servers in a fixed order like Round Robin, React Hooks this Load Balancing Algorithms assigns new requests to the server with the fewest active connections at that moment. This ensures that less busy servers handle more incoming traffic, Types of Load Balancing making it ideal for environments where requests vary in duration or resource usage. Least Connections is particularly effective in situations with uneven traffic loads, as it adapts in real time to balance the workload more efficiently. However, it may require more advanced tracking of server states compared to simpler algorithms, making it slightly more complex to implement.
Example:
If Server A has 5 active connections and Server B has 2, the next request is routed to Server B. This method ensures that heavily loaded servers are not overwhelmed further, resulting in more balanced and responsive systems. However, it requires continuous tracking of connection counts.
Weighted Round Robin and Weighted Least Connections
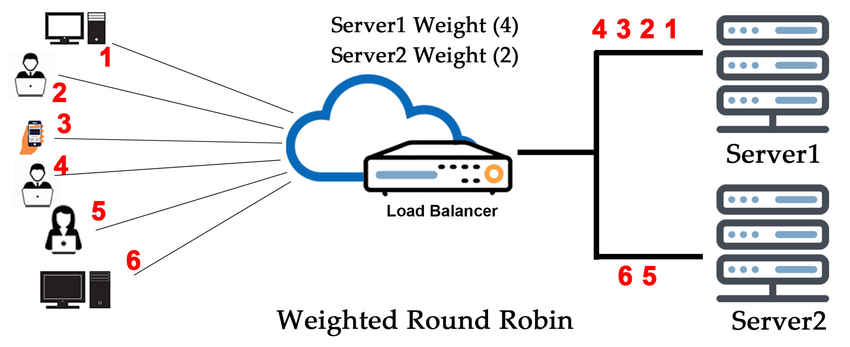
Weighted Round Robin (WRR):
This improves upon Round Robin by assigning weights to servers based on their capacity. A server with a higher weight receives more requests. For example, if Server A has weight 3 and Server B has weight 1, A receives 3 out of every 4 requests.
Weighted Least Connections (WLC):
Similarly, this variation of Least Connections considers both the current load and the weight of the server. Break and Continue In C Servers with higher weights are preferred when their connection count is similar to others. These algorithms provide more granular control and are especially useful in heterogeneous environments where servers differ in performance.
IP Hash and URL Hash Based Algorithms
IP Hash:
This static method uses the client’s IP address to determine which server should handle the request. The hash value of the IP is mapped to a specific server. This ensures that a client always connects to the same server (session stickiness), which is useful for applications that store user sessions locally Reverse a String .
URL Hash:
Similarly, URL hashing determines the server based on the hash of the requested URL or path. This is useful in content delivery networks (CDNs) to ensure consistency in content delivery and caching. These hashing techniques provide consistency but may cause uneven load if the hash distribution is not uniform.
Conclusion
In conclusion, load balancing algorithms play a vital role in ensuring efficient distribution of workloads across servers, enhancing the performance, scalability, and reliability of distributed systems. Whether it’s the simplicity of Round Robin, the adaptability of Least Connections, or the targeted approach of IP Hash algorithms Web Designing & Development Training , each method has its strengths and best-use scenarios. Understanding these algorithms helps in selecting the right strategy to meet specific system requirements and optimize resource utilization. As technology evolves, load balancing continues to be a cornerstone for building resilient and high-performing applications.





