
- Definition and Purpose
- Syntax of pass Statement
- Placeholder in Control Structures
- Use in Empty Functions and Classes
- Comparison with continue and break
- Real-World Examples
- Error Prevention with pass
- Style Guidelines
- Conclusion
Definition and Purpose
The Pass in Python statement in Python is a null operation when it is executed, nothing happens. It serves as a syntactic placeholder in code where a statement is required but no action is desired. The primary purpose of pass is to maintain the structure of the code during development, especially when the actual implementation is yet to be written.In Python, the pass statement is a null operation used when a statement is syntactically required but no action is needed. It serves as a placeholder in code blocks where logic will be added later or where no action is intended. Python does not allow empty blocks, Python Training so using pass prevents syntax errors during development. The primary purpose of pass is to allow the programmer to write structurally correct code without implementing the full logic immediately. This is especially useful in situations like defining empty functions, classes, loops, or conditional statements. For example, during initial development, you might define the structure of a function but choose to implement its logic later. In such cases, using pass keeps the code syntactically valid.
Syntax of pass Statement
The pass statement in Python is used as a placeholder where a statement is syntactically required but no action is to be performed Polymorphism in C++. Its syntax is simple:
- pass
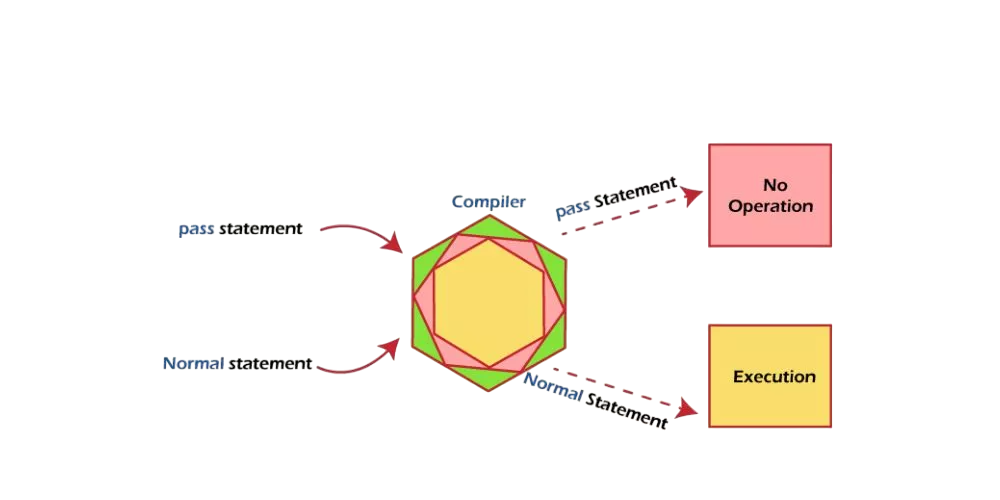
It can be used in functions, classes, loops, or conditional blocks to avoid syntax errors when no code is present. Pass in Python does not allow empty code blocks, so pass ensures proper structure without executing any operation. It is especially useful during the development phase when the logic is yet to be implemented. Although it does nothing, it maintains code readability and prevents indentation-related errors.
Interested in Obtaining Your Python Certificate? View The Python Developer Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Placeholder in Control Structures
- Used in if statements: Allows defining empty conditional blocks without causing syntax errors.
- if condition:
- pass
- Used in else and elif blocks: Handy when only one condition needs action, and others are intentionally left blank C++ Vectors.
- if x > 0:
- print(“Positive”)
- else:
- Pass
- Used in while loops: Helps define a loop structure without executing any logic yet.
- while condition:
- pass
- Used in for loops: Keeps loop structure valid when logic is to be added later.
- for i in range(5):
- pass
- Avoids Syntax Errors: Python does not allow empty blocks; pass acts as a legal no-operation placeholder.
- Enhances Code Planning: Helps lay out control flow before actual logic is implemented Python Training.
- Improves Readability: Signals to other developers that a block is intentionally left empty.
- Safe for Testing Structure: Allows testing of code structure without full implementation.
- def my_function():
- pass
- class MyClass:
- pass
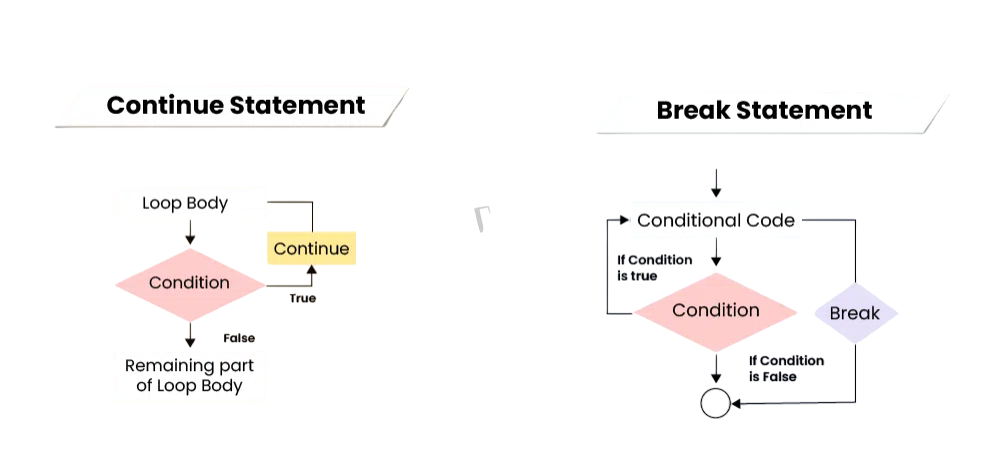
- The continue statement is used inside loops to skip the rest of the current iteration and move to the next one. Height of a Tree It is helpful when certain conditions should bypass part of the loop body.
- The break statement is used to exit a loop prematurely when a specific condition is met. Unlike continue, which moves to the next iteration, break stops the loop entirely.
- for i in range(5):
- if i == 2:
- continue
- print(i)
- for i in range(5):
- if i == 2:
- pass
- print(i)
- def process_data():
- pass
- if user_input:
- pass
- else:
- print(“No input provided”)
- class AbstractBase:
- def operation(self):
- pass
- def my_function():
- pass
- class MyClass:
- pass
- if condition:
- pass
- Use pass for Empty Code Blocks Only: Only use pass when no action is required, but the syntax demands a statement (e.g., in an empty function, class, or control structure) Minimum Spanning Tree.
- Avoid Overusing pass: Don’t use pass when actual logic or a more meaningful statement (like return or a comment) would be clearer.
- Comment When Necessary: If a block is intentionally left empty, use comments alongside pass to explain why.
- def process_data():
- pass
- Prefer Readable Structure: Keep your code clean and readable. Use pass to outline program structure during prototyping or while planning features.
- Don’t Use pass to Skip Logic in Loops: If you need to skip part of a loop, use continue, not pass.
- Use in Exception Handling with Caution: In try-except blocks, don’t suppress errors silently with pass unless absolutely necessary. Log or handle exceptions properly.
- try:
- risky_operation()
- except Exception:
- pass
- Conform to PEP 8: Python’s official style guide (PEP 8) allows pass for stubs and placeholders but recommends using it sparingly and clearly.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Python Developer by Enrolling in Our Python Master Program Training Course Now!
Use in Empty Functions and Classes
The pass statement is commonly used to define empty functions or classes when no implementation is provided yet. It prevents syntax errors by acting as a placeholder. This is useful during initial coding stages or when designing program structure. Without a pass, Python raises an error for empty blocks Backtracking Programming . It helps keep the code syntactically correct and readable.
Without a pass, an empty function or class will raise an IndentationError in Python.
Comparison with continue and break
In Python, pass, continue, and break are control flow statements, but they serve different purposes. The pass statement is a null operation used as a placeholder in empty blocks where code is syntactically required but no action is needed. It is often used in functions, classes, or loops during development.
These three statements help manage control flow, but only pass performs no operation at all.
Example:
Whereas:
Are You Preparing for Python Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Python Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Real-World Examples
Stub Functions:
Useful when laying out code architecture.
Incomplete Conditions:
Helps to outline logic without breaking the code.
Abstract Base Classes:
Indicates a method that should be overridden by subclasses.
Error Prevention with pass
In Python, the structure and indentation of code are critical for maintaining proper syntax. Unlike some other programming languages, Python does not allow empty code blocks. If a function, class, loop, or conditional statement is written without at least one valid statement inside its body, Python will raise an IndentationError or SyntaxError. To avoid these errors, the pass statement is used as a placeholder C Programming Examples. The pass statement is a null operation; it literally does nothing when executed. However, it plays an important role in ensuring that code blocks are syntactically correct. For example, if a developer wants to define a function or class for future use but hasn’t written the actual implementation yet, they can use pass to prevent the interpreter from throwing an error.
Example:
Similarly, in control structures like if, for, or while, if no action is required for a certain condition, using pass maintains the flow and prevents syntax issues:
Using pass helps during development by allowing the programmer to map out the structure of the program before filling in all the logic. It also improves collaboration by signaling to other developers that the block is intentionally left empty or will be implemented later.In summary, pass is a simple yet powerful tool in Python that helps prevent syntax-related errors in incomplete or intentionally empty code blocks. It ensures the code remains clean, runnable, and ready for future development.
Style Guidelines
Conclusion
The pass statement in Python is a simple yet powerful tool used to maintain code structure during development. It acts as a placeholder in loops, conditional blocks, functions, continue and break and class definitions, allowing the program to run without errors. While useful during initial development and design phases, over-reliance on pass should be avoided in finalized code. Understanding how and when to use pass effectively helps in writing clean, syntactically correct Python code while laying out a program’s architecture. The Pass in Python statement in Python is a simple yet powerful tool that plays an important role in writing clean, error-free, Python Training Error Prevention with pass and well-structured code Error Prevention. It acts as a placeholder in situations where the syntax requires a statement but no action is needed at the moment. Commonly used in empty functions, classes, and control structures, pass helps prevent syntax and indentation errors during development. While it does nothing during execution, pass is valuable for outlining program structure, planning features, or maintaining readability in incomplete sections of code. However, it should be used thoughtfully never as a way to silently ignore important logic or exceptions. By following best practices and style guidelines, developers can use pass effectively to write clean, maintainable, and well-organized Python code.





