
- Introduction to Linear Data Structures
- Definition of Stack
- Definition of Queue
- Differences in Operations (LIFO vs FIFO)
- Use Cases of Stack
- Use Cases of Queue
- Implementation Using Arrays
- Implementation Using Linked Lists
- Conclusion
Introduction to Linear Data Structures
Linear data structures are fundamental in the realm of computer science. They organize data in a sequential manner, which simplifies the process of traversing and manipulating the data. Among the most popular linear structures are stacks and queues. Their logical organization and behavior model real-world scenarios, making them indispensable in solving complex computing problems. By understanding the differences, applications, and implementations of these structures, developers and data scientists can optimize code efficiency and logic. Mastery of stacks and queues paves the way for mastering more advanced structures like trees and graphs.Linear data structures Python Training are a fundamental concept in computer science and programming, where data elements are arranged sequentially or linearly. In these structures, each element is connected to its previous and next element, forming a clear and organized order. The main types of linear data structures include arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues. Arrays are fixed-size structures that store elements of the same data type in contiguous memory locations. They allow fast access to elements using an index. Linked lists, on the other hand, are dynamic in size and consist of nodes, each containing data and a pointer to the next node. This makes insertion and deletion more efficient compared to arrays. Stack vs Queue are abstract data types that follow specific order principles. A stack operates on a Last In, First Out (LIFO) basis, meaning the most recently added item is the first to be removed. Queues follow a First In, First Out (FIFO) order, where the first item added is the first to be removed. Linear data structures are essential for solving many real-world problems efficiently. They are widely used in algorithm design, memory management, and process scheduling. Understanding these structures is a crucial step in mastering data structures and algorithms.
Interested in Obtaining Your Python Certificate? View The Python Developer Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Definition of Stack
A stack is a linear data structure that operates on the Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) principle. A Stack vs Queue is a linear data structure that follows the Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle, meaning the last element added is the first one to be removed. It can be visualized like a stack of plates where the top plate is removed first. Stacks support two primary operations: push, IT Engineer Salary in India which adds an element to the top, and pop, which removes the top element. An additional operation, peek or top, allows viewing the top element without removing it. Stacks are widely used in programming for function calls, expression evaluation, and backtracking algorithms due to their simple and efficient structure.This means the last element added is the first one to be removed. Picture a stack of plates or books adding or removing happens only at the top. Operations supported by stacks include:
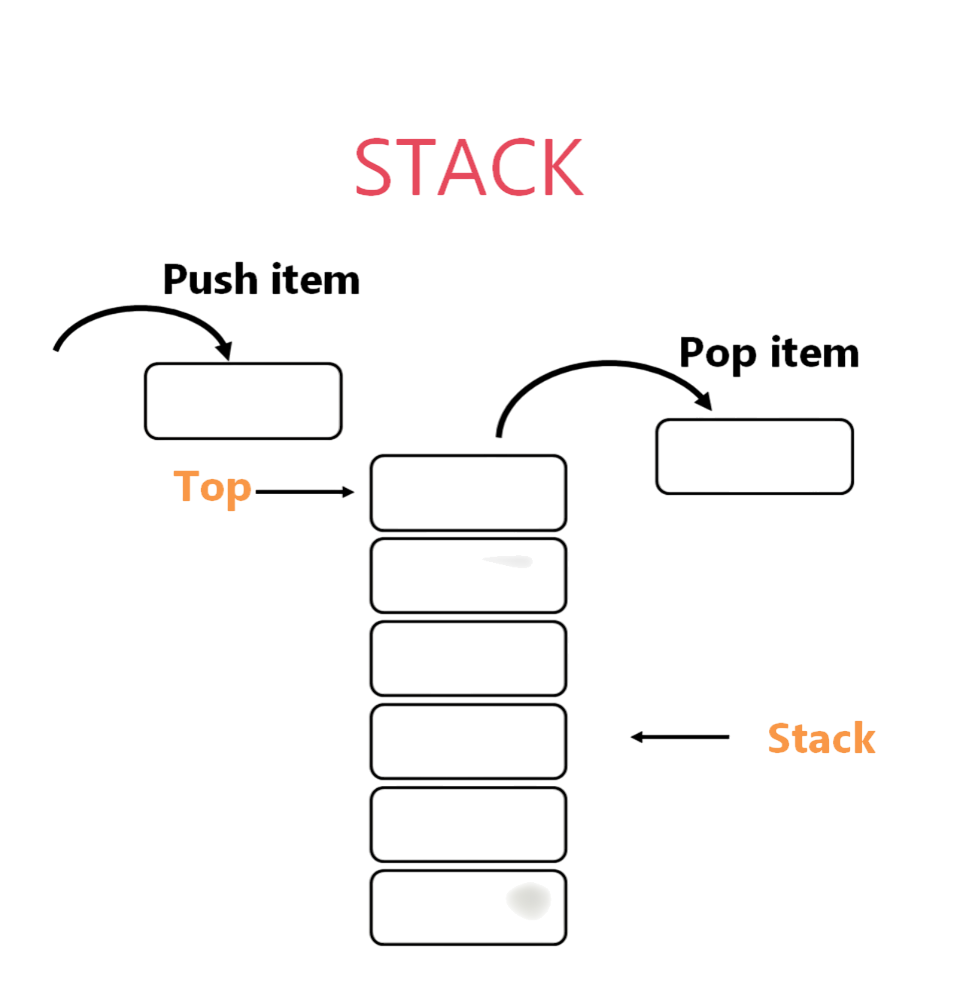
- Push: Add an element to the top.
- Pop: Remove the element from the top.
- Peek/Top: View the topmost element without removal.
- isEmpty: Check if the stack contains any elements.
Stacks can be implemented using arrays, linked lists, or through programming libraries. Their primary use is in scenarios that require tracking the most recent task or data.
Definition of Queue
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the First-In, First-Out (FIFO) method. The first element added is the first to be removed. This model resembles a line of people waiting for service. A queue is a linear data structure that follows the First In, First Out (FIFO) principle, meaning the first element added is the first one to be removed Best Software Development Courses . It is similar to a line of people waiting, where the person who arrives first is served first. A queue supports two main operations: enqueue, which adds an element to the rear, and dequeue, which removes an element from the front. Additional operations like peek allow viewing the front element without removing it. Queues are commonly used in scheduling, buffering, and managing resources in operating systems and network data transfers.
The operations include:
- Enqueue: Insert an element at the rear.
- Dequeue: Remove the element from the front.
- Front: Access the element at the front without removing it.
- isEmpty: Check if the queue is empty.
Queues are particularly useful in resource scheduling, task processing, and maintaining a sequence of operations where order matters.
Differences in Operations (LIFO vs FIFO)
Order Principle:
- Stack (LIFO): Last In, First Out
- Queue (FIFO): First In, First Out
- Stack: Insertion (push) happens at the top
- Queue: Insertion (enqueue) happens at the rear
- Stack: Become an IT Engineer Removal (pop) happens from the top
- Queue: Removal (dequeue) happens from the front
- Stack: Accesses the most recently added element
- Queue: Accesses the oldest added element
- Stack: Used in backtracking, function calls, undo operations
- Queue: Used in scheduling, buffering, and resource management
- Function Call Stack: Used to manage function calls and local variables.
- Undo/Redo Systems: Found in software like Microsoft Word and Photoshop.
- Parsing Expressions: Python Training Used in compilers to evaluate expressions or validate parentheses.
- Depth-First Search (DFS): Utilized in graph and tree traversal.
- Postfix Evaluation: Interpreting postfix or Reverse Polish Notation expressions.
- Print Queue: Manages jobs sent to a printer.
- CPU Scheduling: Operating systems manage process queues.
- Breadth-First Search (BFS): Graph and tree traversal techniques.
- I/O Buffers: Temporary storage for data exchange.
- Customer Support Systems: Handle tickets in order of arrival.
- stack = []
- stack.append(10)
- print(stack.pop())
- queue = []
- queue.append(10)
- print(queue.pop(0))
Insertion:
Removal:
Access:
Usage:
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Python Developer by Enrolling in Our Python Master Program Training Course Now!
Use Cases of Stack
Stacks are ubiquitous in computing for managing order-sensitive tasks:
Their simplicity makes stacks a go-to tool for temporary data storage where recent history matters.
Use Cases of Queue
Queues ensure orderly execution and are key in systems requiring fairness:
These real-world analogies help reinforce the FIFO behavior and make queues easier to understand and apply Complete Guide on System Software.
Are You Preparing for Python Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Python Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Implementation Using Arrays
Stacks and queues can be implemented using arrays What is Software Engineering:
Stack with Array:
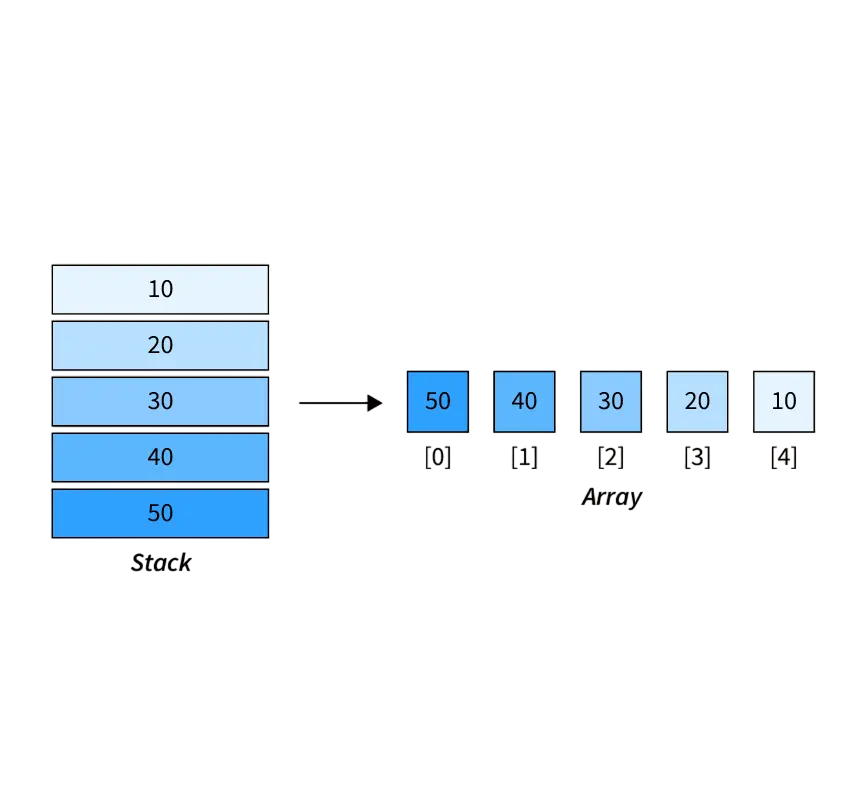
Queue with Array:
Using arrays is simple but has limitations, especially for queues where removing from the front causes shifting of all elements.
Implementation Using Linked Lists
Stacks and queues can be efficiently implemented using linked lists, which provide dynamic memory allocation and flexible data storage. In a stack implementation using a singly linked list, elements are added and removed from the head of the list. The push operation inserts a new node at the beginning, making it the new top of the stack, while the pop operation removes the node from the head, ensuring Last In, First Out (LIFO) behavior. This approach allows constant time operations Software Engineering Prototype without the need to shift elements, as in arrays. In contrast, a queue using a linked list requires two pointers: one pointing to the front and another to the rear of the queue. The enqueue operation adds a new node at the rear, and the dequeue operation removes the node from the front, maintaining the First In, First Out (FIFO) order. This setup ensures that both operations occur in constant time without shifting elements. Using linked lists for these structures eliminates the size limitations of arrays and enables efficient memory use. Linked list-based implementations are particularly useful in situations where the number of elements is unpredictable or changes frequently during runtime, offering both flexibility and efficiency.
Conclusion
Stack vs Queue form the core of linear data structures. While stacks follow the LIFO model, queues use FIFO. Their distinct behaviors lend themselves to specific use cases like memory management, process scheduling, and algorithm implementation. With Implementation Using Arrays and linked lists and support across all major programming languages, stacks and queues remain timeless in their relevance and utility. Mastering these basics is essential for anyone entering the field of software development Python Training or computer science. Understanding when and how to use stacks and queues optimizes logic flow, improves resource management, and contributes to building efficient and scalable systems. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the effective application of these structures will remain a crucial skill for developers, analysts, and engineers alike.





