
- Introduction to Java Projects Development
- Setting Up Java Environment
- Simple Calculator
- Student Management System
- Library Management System
- Online Banking Simulation
- Inventory Management App
- Chat Application
- E-commerce Backend
- File Handling Project
- Project Structure and Design Patterns
- Final Deployment
- Conclusion
Introduction to Java Projects Development
Setting up a Java development environment is the first step in your journey. This includes installing the Java Development Kit (JDK), configuring environment variables, and choosing an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA. The JDK provides the necessary libraries and tools to compile and run Java programs, while the IDE offers features like syntax highlighting, debugging, and project management. To master these tools in a real-world development environment, exploring Java Training reveals how integrated development environments and Java toolkits are used to streamline coding, testing, and deployment across full-stack applications. Once the environment is set up, familiarize yourself with basic commands such as compiling (javac) and running (java) programs from the terminal. Understanding how the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) works also enhances your ability to write efficient and portable code. Maven or Gradle can be used to manage project dependencies and build automation.
To Earn Your Java Training Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Java Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Java Training Today!
Setting Up Java Environment
Setting up a Java development environment is the first step in your journey. This includes installing the Java Development Kit (JDK), configuring environment variables, and choosing an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA. The JDK provides the necessary libraries and tools to compile and run Java programs, while the IDE offers features like syntax highlighting, debugging, and project management. To understand how these tools support modular design and clean architecture, exploring What is Abstraction in Java reveals how developers use abstract classes and interfaces to simplify complexity, hide implementation details, and build scalable applications. Once the environment is set up, familiarize yourself with basic commands such as compiling (javac) and running (java) programs from the terminal. Understanding how the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) works also enhances your ability to write efficient and portable code. Maven or Gradle can be used to manage project dependencies and build automation.
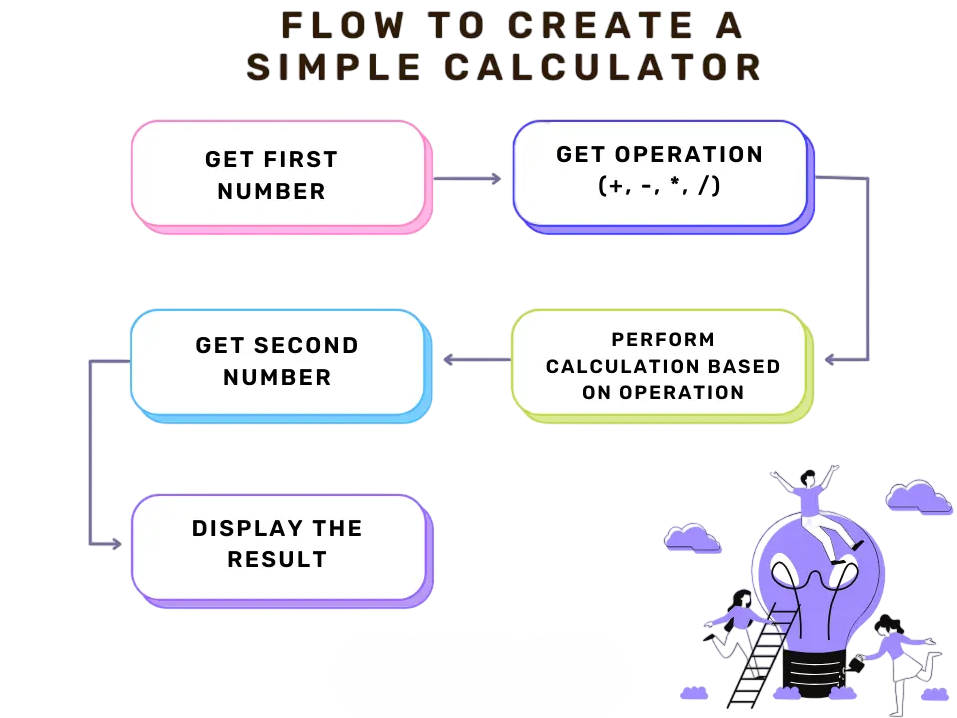
Simple Calculator
- A Simple Calculator project is ideal for beginners to get comfortable with Java syntax, classes, and control statements. This project involves building a basic arithmetic calculator that performs addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- The GUI can be built using Swing or JavaFX to enhance interactivity. Key learning outcomes include using conditional statements, loops, and GUI components. Exception handling can be implemented to manage divide-by-zero errors. This project introduces event-driven programming and the MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern.
- An Online Banking Simulation allows users to create accounts, check balances, transfer funds, and view transaction histories. This project incorporates security concepts, such as user authentication, encrypted passwords, and session management.
- Developers gain experience in handling complex data structures, implementing business logic, and managing concurrent transactions. Real-world scenarios like transaction failures and audit trails are also explored. Advanced learners can use Spring Boot to build a RESTful backend for this application.
- An Inventory Management App is designed to monitor product stocks, suppliers, and sales. This project involves designing tables for inventory tracking, setting reorder levels, and generating stock reports.
- Through this project, you will understand real-time data updates, data visualization using Java charts, and integration with barcode scanners or QR codes. This is an ideal project for learning multi-threading, input/output streams, and report generation using JasperReports.
- File Handling projects help you learn how to read from and write to files, perform data validation, and manage file directories. Projects may include creating a text editor, file encryption tool, or log file analyzer.
- Java’s File, BufferedReader, BufferedWriter, and Scanner classes are used extensively. Exception handling, stream management, and file format conversions (e.g., CSV to JSON) are important learning areas.
- Understanding project structure and implementing design patterns are crucial for writing maintainable code. Projects should follow organized packages, naming conventions, and separation of concerns (SoC).
- Commonly used design patterns in Java include Singleton, Factory, Observer, and DAO (Data Access Object). Incorporating these patterns improves code readability, scalability, and testability. This section also emphasizes writing unit tests using JUnit.
Would You Like to Know More About Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Now!
Student Management System
The Student Management System project focuses on managing student data such as name, ID, grades, and attendance. This project teaches how to implement CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations using file handling or databases like MySQL. You will learn how to design user-friendly interfaces and store/retrieve data efficiently. To master these skills in a professional development environment, exploring Java Training reveals how Java developers build responsive UIs, connect to databases, and implement seamless data flow across full-stack applications. The system can be expanded to include search and filter options, login authentication, and report generation. This project introduces the concept of persistence and modular coding.
Library Management System
A Library Management System simulates the operations of a library, such as book check-in/check-out, inventory updates, and member registration. The project may include modules for book categorization, late fee calculation, and issuing alerts. This intermediate-level project enhances your knowledge of Java collections, object serialization, and database interactions. JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is used to integrate Java with relational databases. To understand how these components align with core programming principles, exploring Important Data Structures and Algorithms reveals how lists, maps, trees, and graphs support efficient data handling, persistence, and retrieval in real-world Java applications. Emphasis is placed on maintaining data integrity and user roles (admin vs. user).
Are You Interested in Learning More About Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Today!
Online Banking Simulation
Inventory Management App
Preparing for Java Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Java Training Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Chat Application
Building a Chat Application introduces the concepts of networking in Java. This project involves creating a client-server architecture where multiple clients can send and receive messages in real time. You will learn socket programming, multi-threading, and GUI design.
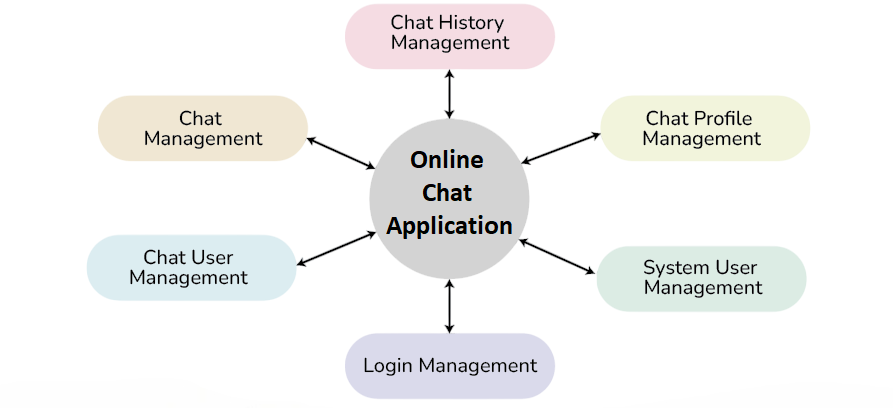
Advanced features like message encryption, chat history, and file sharing can be included. To choose the right language for implementing these capabilities, exploring Go vs Python reveals how Go’s concurrency model and performance stack up against Python’s simplicity and rich libraries helping developers align their project goals with the most suitable toolset. The chat application server handles multiple connections, ensuring secure and smooth communication.
E-commerce Backend
The E-commerce Backend project focuses on building the server-side logic for an online shopping platform. Key features include product listings, user authentication, shopping carts, and order processing. Using Java Servlets and JSP, or frameworks like Spring and Hibernate, you can design scalable and maintainable backend systems. To choose the right communication protocol for such architectures, exploring Soap vs Rest reveals how REST’s lightweight, stateless design compares with SOAP’s structured, feature-rich approach helping developers align protocol choice with system requirements and integration goals. Database integration, RESTful APIs, and MVC architecture are core aspects of this project. Performance optimization and secure payment processing are advanced considerations.
File Handling Project
Project Structure and Design Patterns
Final Deployment
Once the project is complete, the final step is deployment. For desktop applications, you can create executable .jar files. For web applications, WAR files can be deployed to servers like Apache Tomcat. Learning deployment involves configuring server environments, managing build tools, and monitoring application performance. To streamline this process during development, exploring Python IDEs and Code Editors reveals how modern editors support syntax validation, plugin integration, and deployment automation making it easier to manage full-stack workflows efficiently. Cloud platforms such as AWS or Heroku can be used for hosting. Version control systems like Git and CI/CD pipelines using Jenkins ensure smooth delivery.
Conclusion
Java project development provides a balanced experience that improves both your technical skills and soft skills. Working on projects development, from making simple calculators to creating complex enterprise solutions, is crucial for your growth as a developer. Each project boosts your coding skills and helps you prepare for interviews, internships, and real-world software challenges. By practicing regularly and committing to ongoing learning, exploring Java Training equips you with the knowledge and confidence needed to succeed in Java development covering everything from core syntax and OOP principles to advanced frameworks and deployment strategies. Completing these projects deepens your understanding of the language and encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are essential traits for a successful developer. Whether you’re working alone or collaborating with others, each project contributes to your journey toward expertise in Java.





