
- Introduction to ReactJS
- Setting Up the Environment
- JSX Syntax
- Components and Props
- State Management
- Event Handling
- Conditional Rendering
- Lists and Keys
- Conclusion
Introduction to ReactJS
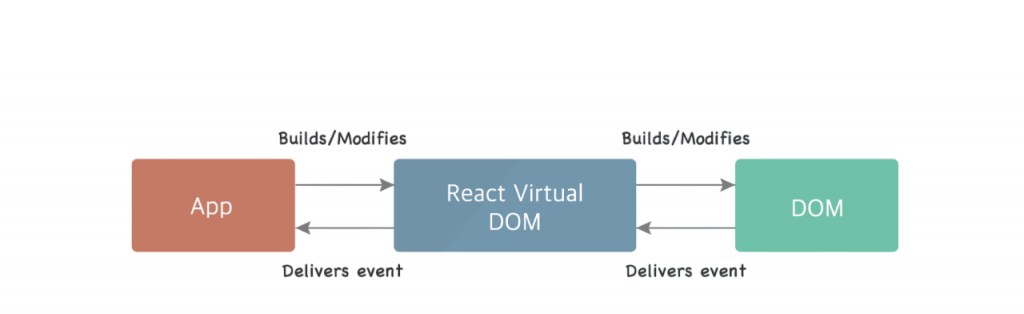
ReactJS Tutorial is an open-source JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building fast and interactive user interfaces for web and mobile applications. It allows developers to create large web applications that can update and render efficiently in response to data changes. React uses a component-based architecture and a declarative frontend programming style, making code more predictable and easier to debug. React focuses on building UI components. It uses a virtual DOM (Document Object Model) which is much faster than the real DOM. When a component’s state changes, only the affected elements in the virtual DOM are updated, which results in better performance. React is often used alongside other libraries like Redux for state management and React Router for navigation. Its ecosystem is vast and growing rapidly, making it a popular choice for front-end development.ReactJS is a popular JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building dynamic and responsive user interfaces, especially for single-page applications. It allows developers to create reusable UI components, making code more efficient and easier to maintain. React uses a virtual DOM (Document Object Model) to optimize rendering performance by updating only the parts of the page that change, rather than reloading the entire interface. With its component-based architecture and support for hooks and state management, Web Designing Training React enables developers to build fast, interactive, and scalable front-end applications. It’s widely used in modern web development due to its flexibility, performance, and strong community support.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Setting Up the Environment
- Install Node.js and npm – React requires Node.js and its package manager (npm) to manage dependencies.
- Install a Code Editor – Use a code editor like Visual Studio Code (VS Code) for efficient development.
- Use Create React App (CRA) – Set up a React project quickly using the npx create-react-app my-app command.
- Navigate to Project Folder – Java Web Development Use the terminal to go into your project directory: cd my-app.
- Start the Development Server – Run npm start to launch the app in your browser with hot-reloading.
- Folder Structure Review – Understand the default folder structure of CRA (e.g., src, public, node_modules).
- Install Additional Packages – Add tools like React Router, Axios, or Bootstrap if needed using npm or yarn.
- Set Up Version Control – Initialize Git for tracking changes and collaborating with others.
- Configure ESLint and Prettier – Optional tools to maintain code quality and consistency.
- Test Your Setup – Ensure everything is running smoothly by editing a component and seeing the changes reflect live.
JSX Syntax
JSX (JavaScript XML) is a syntax extension for JavaScript that plays a fundamental role in React development. It allows developers to write HTML-like code directly within JavaScript, making it much easier to build and understand user interfaces. While it may look like HTML, JSX is actually syntactic sugar for React.createElement() calls, which means every JSX element is eventually converted into plain JavaScript that the browser can understand, frontend usually with the help of a transpiler like Babel.JSX allows you to define components visually by combining markup and logic in one cohesive structure. For example, instead of writing verbose JavaScript code to create a heading element, you can simply write Hello, World! using JSX, Web Designing Training making the code much more readable.A major advantage of JSX is that it supports embedding JavaScript expressions directly within markup using curly braces {}.This allows for dynamic content rendering, such as displaying a variable value or running a function inside JSX. For example,{username} will render the value of the username variable. JSX also supports the use of conditional statements and loops (indirectly, using functions like map()), which makes it highly flexible and dynamic. Additionally, JSX encourages the use of components, where you can create reusable UI blocks like Header or Button, promoting clean and maintainable code.However, JSX comes with a few rules: for instance, components must return only a single parent element, so developers often use a div or React fragment (<>…) to wrap multiple elements.Also, some HTML attributes have different names in JSX, such as className instead of class, and htmlFor instead of for, due to JavaScript naming conflicts. In summary, JSX is an essential part of React that blends the structure of HTML with the flexibility of JavaScript, enabling efficient and intuitive UI development.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Components and Props
- Components are the building blocks of a React application.
- A component is a reusable piece of UI that can be rendered independently.
- Components can be functional or class-based.
- Functional components are simpler and use React Hooks for state and side effects.
- Components can return JSX to define how the UI should appear.
- React Hooks Props (short for “properties”) are used to pass data from a parent to a child component.
- Props are read-only, meaning child components cannot modify them.
- Props allow components to be dynamic and reusable with different data.
- A component can receive multiple props and use them within its JSX.
- Using components and props promotes modular, scalable, and maintainable code in React.
State Management
State management in React is a core concept that deals with how data is stored, updated, and passed throughout an application. In React, state refers to any value that can change over time such as user input, form data, fetched API results, or UI interactions like toggling menus or switching themes. React components can have their own local state, which can be managed using the built-in useState hook in functional components. When the state changes, React automatically re-renders the affected component, frontend keeping the UI in sync with the latest data. This is what makes React applications dynamic and interactive. However, as an application grows in size, managing state across multiple components becomes more complex. This is where global state management comes into play Node.js Frameworks. Global state allows different components in the app to access and update shared data without passing it manually through props (a process known as prop drilling). React provides tools like the Context API to handle this, making it easier to share state across the app in a more efficient way. For even more structured state handling, especially in large-scale applications, developers often turn to external libraries like Redux, MobX, or Zustand. These tools offer centralized state stores, predictable data flows, and powerful debugging features. Proper state management is crucial for maintaining clean, scalable, and maintainable code. It ensures that your application behaves consistently, avoids unnecessary re-renders, and makes it easier to debug and test. In summary, whether you’re managing simple local states or complex global ones, understanding how state works and how to control it is essential to becoming an effective React developer.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Event Handling
- Event handling in React is similar to handling events in regular HTML but uses camelCase syntax.
- React events are named using camelCase, such as onClick, onChange, and onSubmit.
- Event handlers in React are passed as functions, not strings.
- You can define event handler functions inside components React Slick or pass them as props.
- React uses a synthetic event system that wraps native browser events for cross-browser compatibility.
- To access event properties, use the event object passed to the handler function.
- In class components, event handlers often need to be bound to this to access component state.
- Functional components use hooks like useState to update state within event handlers.
- Prevent default behavior using event.preventDefault() in React event handlers.
- Proper event handling is essential for creating interactive and responsive user interfaces.
Conditional Rendering
Conditional rendering in React allows developers to display different UI elements or components based on certain conditions, making applications dynamic and responsive to user interactions or data changes. Instead of rendering the same content every time, React lets you use JavaScript conditions like if, else, ternary operators, or logical && to decide what gets shown on the screen. For example, you might display a loading spinner while data is being fetched and then show the actual content once the data is ready. Conditional rendering can be implemented directly within JSX, keeping the code clean and readable. This technique enhances user experience by ensuring that users see relevant information depending on the current state or props, such as showing error messages, login forms, or personalized content. It is a fundamental feature in React that helps create interactive, user-friendly web applications.Conditional rendering is a key feature in Create Microservices in Node.js that allows developers to render different UI elements or components based on specific conditions, making applications more dynamic and user-friendly. Instead of displaying the same content regardless of the situation, React lets you control what appears on the screen by using standard JavaScript conditions within JSX. This can be done using if statements, ternary operators (condition ? true : false), or logical && operators. For example, you might want to show a loading indicator while data is being fetched from an API, and then display the actual content once the data has loaded. Similarly, you can conditionally display error messages, user-specific content, or different navigation menus based on the user’s login status. This flexibility helps create a personalized experience for users and keeps the interface clean and relevant. Conditional rendering can be implemented directly inside the JSX, making the code more readable and easier to maintain. By leveraging this feature, developers can build responsive web applications that adapt seamlessly to changing data and user interactions, enhancing overall usability and engagement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ReactJS Tutorial offers a powerful and flexible framework for building dynamic, interactive, and scalable user interfaces. With core concepts like JSX, components and props, state management, event handling, and conditional rendering, React enables developers to create responsive applications that efficiently handle both data and user interactions. The component-based structure promotes reusability and cleaner code, while modern tools and practices such as React Hooks, Context API, Web Designing Training and frontend frameworks further enhance development capabilities. Whether you’re building a small interactive UI or a large-scale web application, understanding and applying these foundational concepts is essential for any web developer working with React.





