
- Introduction to Web Development
- Setting Up Development Environment
- CSS Styling
- JavaScript Essentials
- DOM Manipulation
- Responsive Design with CSS
- Frontend Framework Basics
- Backend Integration
- Hosting a Website
- Debugging and Optimization
- Final Project Walkthrough
- Conclusion
Introduction to Web Development
Web development is the process of building and maintaining websites or web applications that run in a browser. It combines creative design with technical expertise and includes several components like frontend, backend, databases, and hosting an integrated approach taught in Web Designing Training, where learners build full-stack applications using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, and MySQL. By mastering both client-side and server-side technologies, developers can create dynamic, scalable websites and deploy them across platforms with confidence. A strong understanding of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks is essential. In this guide, you’ll learn the key concepts and steps to create a functional, modern website from scratch. Web development can be broadly categorized into frontend (client-side) and backend (server-side). Frontend focuses on what users see, while backend handles data, authentication, server communication, and more. Modern web development often uses frameworks and libraries to speed up development, improve code quality, and enhance maintainability. The web ecosystem is dynamic, with frequent updates and innovations. Understanding the foundations helps you stay adaptable and ready to learn new tools and technologies as they emerge.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Setting Up Development Environment
Before starting, setting up the right environment is essential. Install a code editor such as Visual Studio Code (VS Code), which supports syntax highlighting, extensions, integrated terminal, and version control. You’ll also need a browser like Google Chrome or Firefox for testing and debugging basic tools emphasized in What is WordPress, where learners explore how this open-source CMS empowers users to build, customize, and maintain websites with ease. From theme selection to plugin integration, mastering WordPress development requires hands-on testing across browsers to ensure responsive design, accessibility, and performance consistency. Git is a popular version control tool used to track changes and collaborate on projects. Setting up Node.js is also useful, as it comes with npm (Node Package Manager) which allows you to install JavaScript libraries and tools. Install browser developer tools, such as Chrome DevTools, which let you inspect elements, monitor performance, and debug JavaScript. Setting up a local server using tools like Live Server extension in VS Code helps simulate real-time environment behavior. Ensure your system is up to date and consider using a terminal (Command Line Interface) for running commands efficiently. You may also set up linters like ESLint and formatters like Prettier to keep your code clean and consistent.
Backend Technologies (Node.js, Django, etc.)
Web pages are structured using HTML (HyperText Markup Language). To arrange content, it makes use of tags like html, head, body, div, h1 to h6, p, a, and img. For instance these foundational elements are covered in Become a Front End Developer, where learners explore how semantic markup, responsive design, and modern CSS techniques shape user-friendly interfaces. Mastering these tags is the first step toward building accessible, scalable websites that perform well across devices and browsers.
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>My First Web Page</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>Hello, World!</h1>
- <p>This is a paragraph.</p>
- <a href=”https://example.com”>Visit Example</a>
- <img src=”image.jpg” alt=”Image Description”>
- </body>
- </html>
You should understand semantic tags like article, section, nav, header, and footer for better accessibility and SEO. Forms are also crucial in HTML. You can collect user input with form, input, textarea, and button. Always ensure your HTML is well-structured and validated using tools like the W3C HTML Validator.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
CSS Styling
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is used to style HTML content. It allows you to change colors, fonts, spacing, layouts, and more. You can use inline styles, internal stylesheets, or external stylesheets. CSS rules are made up of selectors and declarations. For instance these styling fundamentals are covered in Web Development Languages To Learn, where learners explore how CSS integrates with HTML to create visually engaging, responsive websites. Mastering these techniques is essential for building modern web interfaces that adapt across devices and screen sizes.
- body {
- background-color: #f0f0f0;
- font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
- }
- h1 {
- color: navy;
- margin-top: 20px;
- }
CSS supports box model principles, including margins, padding, borders, and content areas. Understanding display properties (block, inline, flex, grid) is important for layout. Use developer tools to inspect CSS in real-time. Learn to manage specificity, use classes effectively, and leverage preprocessors like SASS or LESS for advanced CSS management. CSS frameworks like Bootstrap can speed up design using prebuilt components and grid systems.
JavaScript Essentials
JavaScript (JS) adds interactivity to websites. It allows you to handle user inputs, perform calculations, make dynamic changes to the page, and more. Key concepts include variables (let, const, var), data types, operators, loops, functions, arrays, objects, conditionals, and events core skills emphasized in Web Development Roadmap, where learners progress from foundational syntax to advanced DOM manipulation and asynchronous programming. Mastering these concepts is essential for building responsive, user-centric web applications.
- let userName = “John”;
- function greetUser(name) {
- alert(`Welcome, ${name}!`);
- }
- document.querySelector(“button”).addEventListener(“click”, () => greetUser(userName));
You’ll also learn about scoping, closures, and hoisting. Modern JavaScript (ES6+) includes features like arrow functions, destructuring, template literals, and promises. Using tools like Babel can help you write modern JS while maintaining compatibility. JavaScript forms the core of dynamic web applications.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
DOM Manipulation
The DOM (Document Object Model) represents the structure of an HTML page as a tree of objects. JavaScript can access and manipulate these elements using methods like getElementById, querySelector, innerHTML, classList, and appendChild core techniques contextualized in Understanding Render in ReactJS, where learners explore how React abstracts direct DOM manipulation through its declarative rendering model. By leveraging the virtual DOM and JSX, developers achieve efficient UI updates while maintaining clean, maintainable code structures.
- const title = document.getElementById(“title”);
- title.innerText = “New Title”;
- title.classList.add(“highlighted”);
DOM manipulation enables creating interactive components like image sliders, form validations, modal popups, and dynamic content updates. Event handling (onclick, onchange, addEventListener) plays a crucial role in building responsive UIs. Libraries like jQuery simplify DOM manipulation but modern JavaScript offers native, efficient methods.
Responsive Design with CSS
Responsive design ensures your website looks good on all screen sizes, from phones to desktops. Use flexible grids, relative units (%, em, rem), and media queries core techniques covered in Web Designing Training, where learners build adaptive layouts using fluid containers, scalable typography, and breakpoint-driven styling. By mastering these tools, developers create seamless experiences that adjust gracefully across devices and resolutions.
- @media (max-width: 768px) {
- .container {
- flex-direction: column;
- }
- }
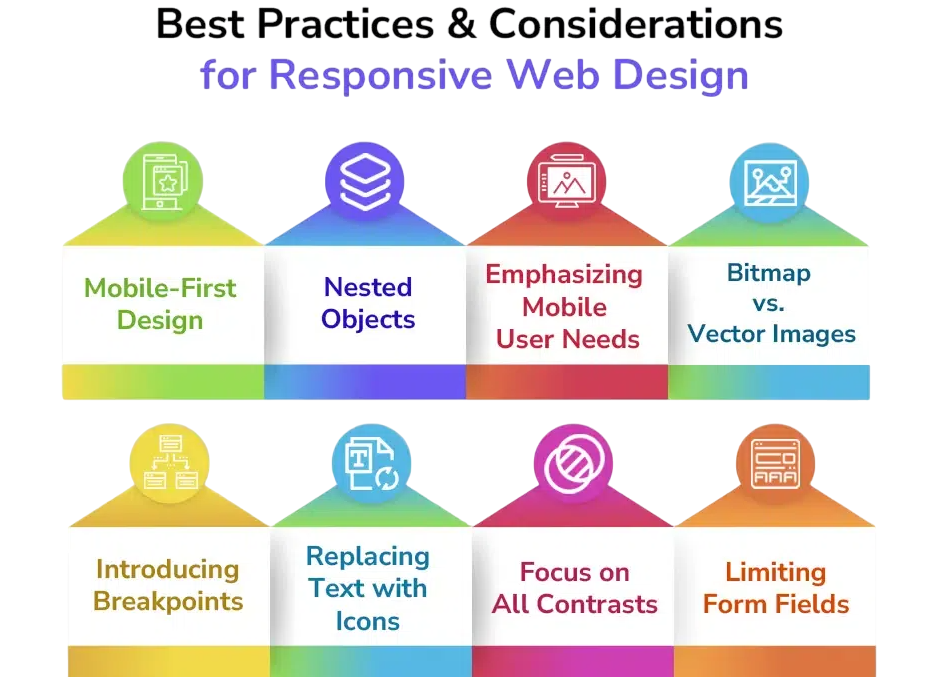
Tools like Flexbox and CSS Grid Layout help align items and build responsive layouts. CSS frameworks like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS provide responsive classes out of the box. It’s essential to test across devices and use tools like Chrome DevTools to simulate screen sizes.
Frontend Framework Basics
Frontend frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue help build scalable, maintainable applications. They introduce components, routing, state management, and modular architecture. Example React component:
- function Welcome({ name }) {
- return <h1>Hello, {name}!</h1>;
- }
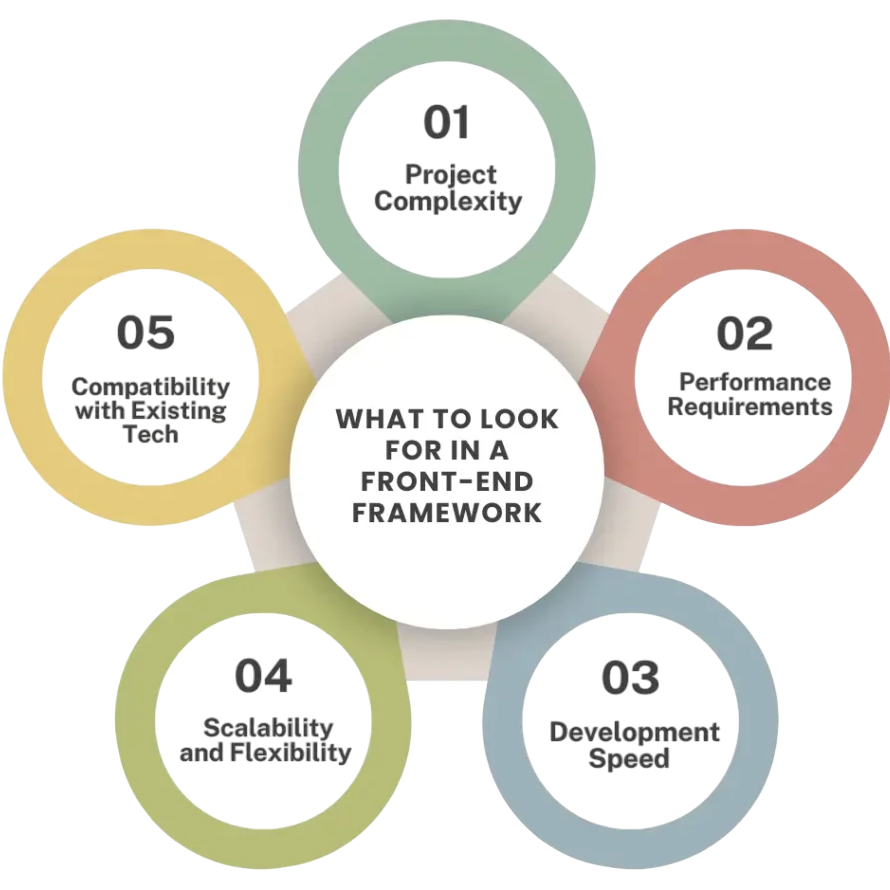
React uses JSX and virtual DOM for efficiency. Angular uses TypeScript and a full MVC structure. Vue is lightweight and flexible. Choose based on project needs. Learn component lifecycles, props, state, and hooks (React) to build reusable and efficient UI parts. Frameworks enhance productivity in large-scale applications.
Backend Integration
The backend powers features like data storage, user authentication, and complex logic. Technologies include Node.js, Express, Python (Flask, Django), Ruby on Rails, and PHP. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) allow frontend to communicate with backend. Example:
- fetch(“https://api.example.com/users”)
- .then(res => res.json())
- .then(data => console.log(data));
Backend integration includes CRUD operations, authentication (JWT, OAuth), and database interactions. RESTful APIs follow HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE). You may use tools like Postman for testing APIs. Backend frameworks simplify routing, middleware, and database access.
Hosting a Website
Once development is complete, hosting makes your site accessible online. Free platforms like GitHub Pages, Netlify, and Vercel are ideal for static sites. For dynamic sites, use Heroku, Firebase, or traditional hosts like Bluehost. Steps to host:
- Push code to GitHub
- Link repository to Netlify or GitHub Pages
- Configure domain and build settings
- Deploy site and test live version
Purchase a custom domain via Namecheap or GoDaddy. DNS settings link your domain to the hosting platform. SSL certificates (HTTPS) improve security and trust.
Debugging and Optimization
Debugging involves identifying and fixing issues using browser dev tools, console logs, breakpoints, and network monitoring. Common tools: Chrome DevTools, ESLint, and debugging extensions. Optimization includes minifying code, compressing images, using lazy loading, caching, and CDN delivery. Tools like Lighthouse provide performance reports practices that align with SCM in Software Engineering, where learners explore how Software Configuration Management ensures consistency, traceability, and performance across development environments. SCM tools like Git and Jenkins integrate with optimization workflows to streamline version control, automate builds, and maintain high-quality software delivery. Reduce unused CSS/JS, enable GZIP compression, and avoid layout shifts for better performance and SEO.
Final Project Walkthrough
- HTML: Create index.html with sections (Header, About, Projects, Contact).
- CSS: Style with style.css using Flexbox/Grid and media queries.
- JavaScript: Add scroll effects, modal popups, and interactive project cards for dynamic UX.
- Responsive Design: Ensure seamless adaptation across mobile and desktop viewports.
- Hosting: Push to GitHub and deploy via Netlify or GitHub Pages for free and fast hosting.
You can expand this with a contact form, animations using CSS or libraries like AOS, and integrate backend (contact form submissions via API or Google Forms).
Conclusion
Web development combines creativity with coding to build interactive, responsive, and scalable websites. By mastering HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and integrating frameworks and backend, you can create impressive web applications an end-to-end skillset developed through Web Designing Training, where learners build responsive interfaces, implement dynamic logic, and connect to databases using technologies like React, Node.js, and MongoDB. This full-stack approach empowers developers to deliver scalable, secure, and visually engaging digital experiences. Regular practice, building projects, and staying updated with trends are key to success. Whether you’re creating personal portfolios or business platforms, this foundational knowledge will set you on the right path.





