
- What are Java Frameworks?
- Benefits of Using Java Frameworks
- Spring Framework Overview
- Hibernate ORM Framework
- Struts MVC Framework
- JSF (JavaServer Faces)
- Play Framework
- Dropwizard for Microservices
- JavaFX for Desktop UI
- Popular Projects and Real-World Use Cases
- Conclusion
What are Java Frameworks?
Java Frameworks is a robust platform consisting of pre-written code, libraries, and tools that serve as a foundation for building Java applications. Frameworks streamline the development process by providing a standard structure and best practices. They help manage common functionalities such as database access, session management, security, configuration, and more, allowing developers to focus on business logic. To complement backend efficiency with front-end expertise, exploring Java Training equips learners with the skills to create visually engaging, responsive interfaces using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern UI/UX principles bridging the gap between structure and design. Frameworks are different from libraries in that a framework often calls your code to perform specific functions (inversion of control), whereas libraries are called by your code. This inversion of control gives frameworks greater control over application behavior and flow.
To Earn Your Java Training Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Java Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Java Training Today!
Benefits of Using Java Frameworks
In today’s fast-paced development landscape, using frameworks can greatly improve productivity and efficiency. They cut down on the amount of boilerplate code developers need to write, which allows for faster project turnarounds. Most frameworks follow proven architectural patterns, like the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design. This helps keep a clear separation between different parts of the application. It leads to a more organized codebase and promotes consistency across the project. To complement such architectural clarity with language-level design choices, exploring Software Development highlights key differences in typing, concurrency, and performance helping developers choose the right tool for scalable systems, rapid prototyping, or data-intensive workflows. Many frameworks also include built-in security features, providing important protections like authentication and input validation. These are crucial for keeping applications safe. Developers can benefit from the support of the community and detailed documentation available for established frameworks, making troubleshooting and learning new techniques much easier.
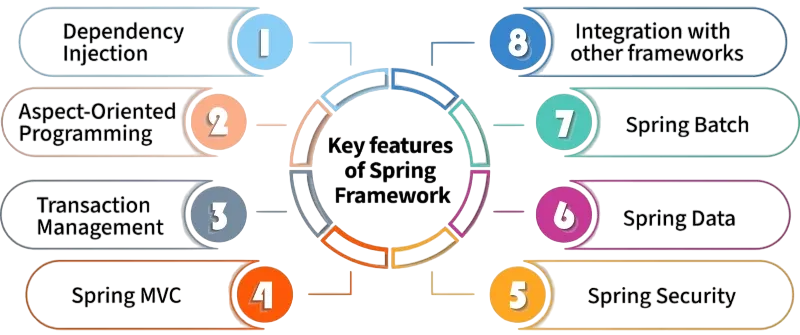
Spring Framework Overview
Spring Framework is the most popular and comprehensive Java framework. It provides a full suite of tools for developing Java applications across different layers of architecture: To complement such backend mastery with end-to-end development skills, exploring How to Become a Full Stack Developer outlines the essential technologies, tools, and workflows needed to build scalable applications from front-end interfaces to server-side logic and cloud deployment strategies.
- Dependency Injection (DI): Manages object creation and dependency resolution.
- Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP): Allows separation of cross-cutting concerns.
- Spring MVC: Supports web application development using the MVC design pattern.
- Spring Boot: Offers auto-configuration, embedded servers, and production-ready features.
- Spring Security: Manages application security.
- Spring Data: Simplifies database interaction.
Spring Framework is widely used in enterprise environments, microservices architecture, and cloud-native applications.
Would You Like to Know More About Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Now!
Hibernate ORM Framework
Hibernate is a leading Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) tool in Java. It allows developers to map Java objects to relational database tables using simple annotations or XML. To complement such backend integration with broader development roles, exploring Full Stack vs Front End vs Back End clarifies the distinctions between client-side, server-side, and cross-functional responsibilities helping developers choose the right path based on their interests, skillsets, and career goals.
Key Features:
- Transparent persistence
- HQL (Hibernate Query Language)
- Automatic dirty checking
- Lazy loading
- First-level and second-level caching
Advantages:
- Removes the need for verbose SQL
- Improves data integrity
- Provides database independence
Hibernate is widely used in combination with Spring and is suitable for data-centric applications with complex relationships.
Struts MVC Framework
Apache Struts was once a leading framework for Java EE web applications. It introduced the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture that many developers still use today.
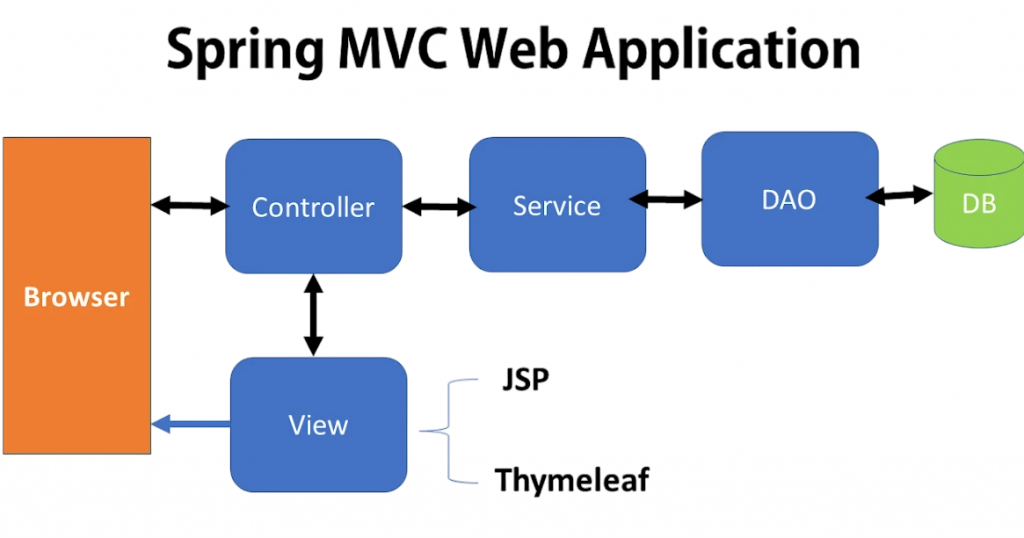
To complement such architectural patterns with front-end expertise, exploring Java Training equips learners with the skills to craft visually engaging, responsive interfaces using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern design principles bridging the gap between structure and user experience. The essential components of Struts include ActionForm, which captures user input, and ActionServlet, the important controller that directs requests. The Action Class manages the business logic, and the struts-config.xml file acts as a central place for configuration. This file is crucial for guiding the application. Struts has its advantages, such as solid support for legacy systems and a clear divide between business logic and presentation.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Java Training? Sign Up For Our Java Training Today!
JSF (JavaServer Faces)
JavaServer Faces (JSF) is an interesting technology for anyone who wants to build dynamic user interfaces for web applications using Java. At its core, JSF offers a component-based approach. This allows developers to create visually appealing and interactive UIs easily. Its Managed Beans and Facelets templating system simplify the development process. This is why it is a popular choice for enterprise environments that follow Java EE standards. To complement such enterprise-grade tooling with broader language versatility, exploring Best Programming Languages highlights top choices like Python, Java, and JavaScript each offering unique strengths in scalability, community support, and application domains from web development to data science. The event-driven model ensures a responsive user experience, while a rich set of UI components improves functionality. However, it is important to note that JSF has a steeper learning curve and is not as popular as other frameworks in modern web development.
Preparing for Java Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Java Training Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Play Framework
Play is a modern, high-performance framework for building web applications and RESTful APIs. It supports Java and Scala. To complement such framework-level capabilities with foundational language mastery, exploring Java Programming provides access to curated tutorials, hands-on projects, and expert-led courses empowering developers to build scalable applications with clean architecture and robust backend logic.
Features:
- Asynchronous and non-blocking
- Built-in JSON support
- Hot code reloading
- RESTful by default
Benefits:
- Rapid development
- Great for real-time apps
- Powerful routing mechanism
Play is a solid choice for startups and companies looking to build scalable web applications or APIs with reactive support.
Dropwizard for Microservices
Dropwizard is a minimalist Java framework optimized for building high-performance RESTful web services and microservices. To complement such backend efficiency with streamlined Python development, exploring Java Projects introduces one of the most popular Python IDEs offering features like intelligent code completion, debugging tools, and project navigation that accelerate productivity for both beginners and experienced developers.
Technology Stack:
- Jetty (web server)
- Jersey (REST framework)
- Jackson (JSON processor)
- Metrics (monitoring)
Benefits:
- Easy to get started
- Comes bundled with production-ready features
- Good performance and scalability
Ideal For:
- Microservices
- Lightweight REST APIs
- Applications requiring quick startup time
JavaFX for Desktop UI
JavaFX is an exciting platform for developing cross-platform desktop applications in Java. It offers key components that simplify UI design. The Scene Graph allows for a hierarchical way to create user interfaces. Developers will find FXML, an XML-based markup language, very useful for defining layouts. CSS helps keep applications visually appealing with easy styling. For those looking to add multimedia content, JavaFX provides strong support through Media and WebView. To complement such front-end and UI capabilities with scalable backend design, exploring Node JS Architecture reveals how the single-threaded event loop, non-blocking I/O, and V8 engine work together to handle concurrent requests efficiently making Node.js ideal for building fast, lightweight, and real-time web applications. This modern platform also includes features like 2D and 3D graphics, hardware acceleration, and various built-in charts and UI controls.
Popular Projects and Real-World Use Cases
- Netflix: Uses Spring Boot and Spring Cloud for microservices architecture.
- Amazon: Employs Spring and Hibernate for scalable backend systems.
- LinkedIn: Uses Play Framework for scalable, high-traffic web applications.
- Coursera: Built using Play and Hibernate for content delivery.
- Trading Platforms: Use JavaFX for real-time dashboards and charts.
Conclusion
Java Frameworks are essential tools that streamline development, reduce complexity, and improve code quality. They encapsulate proven design patterns and provide robust solutions for common programming problems. From building enterprise-level REST APIs to lightweight microservices and desktop applications, Java has a framework tailored for every use case. To complement backend expertise with front-end mastery, exploring Java Training provides hands-on experience in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and UI/UX principles equipping developers to build visually compelling and responsive interfaces that align with modern design standards. Understanding and mastering these frameworks not only makes you a more efficient developer but also enhances your ability to choose the right tools for the right tasks. As the software industry evolves, frameworks will continue to abstract lower-level tasks, enabling developers to focus more on innovation and less on plumbing.





