
- Introduction to Spring Framework
- Overview of Spring MVC Architecture
- Key Features of Spring MVC
- Model-View-Controller Design Pattern Explained
- Setting Up a Spring MVC Project
- Components of Spring MVC (DispatcherServlet, Controllers, Views, etc.)
- Handling Requests and Mapping URLs
- Conclusion
Introduction to Spring Framework
The Spring Framework is a powerful, feature-rich, open-source application development framework for Java. Its design philosophy revolves around the core principles of modularization, loose coupling, and separation of concerns. At its heart lies the support for dependency injection (DI) and aspect-oriented programming (AOP), which allows developers to build scalable and maintainable applications. Spring supports a range of modules like Spring Core, Spring AOP, Spring Data, Spring Security, and Spring MVC each catering to a specific need of enterprise application development. Among them, Spring MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a robust framework designed for building web applications that follow the MVC design pattern, offering flexibility and clean separation between presentation and business logic. The Spring Framework is a powerful, open-source framework for building enterprise-level Java applications. Designed to simplify the development process, Spring provides comprehensive infrastructure support for developing robust, scalable, and maintainable applications. To complement such backend architecture mastery with front-end expertise, exploring Web Designing & Development Training equips learners with skills in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and UI/UX design enabling them to build responsive, user-friendly interfaces that integrate seamlessly with enterprise-grade Java systems. At its core, Spring promotes loose coupling through Dependency Injection (DI) and supports Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) to separate cross-cutting concerns like logging and security. It offers a wide range of modules, including Spring MVC for web applications, Spring Data for database access, and Spring Boot for rapid application development. Widely used in the Java ecosystem, Spring helps developers build clean, testable, and efficient applications with minimal configuration.
Overview of Spring MVC Architecture
Spring MVC is built upon the Servlet API and leverages the core Spring functionalities to provide a structured web development experience. It is based on the Model-View-Controller design pattern, which segregates the application logic into three interconnected components. To complement such backend architectural clarity with front-end proficiency, exploring Web Designing & Development Training equips learners with essential skills in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and responsive design empowering them to build visually engaging interfaces that integrate seamlessly with Spring-based enterprise applications.
- Model: Represents application data and business logic.
- View: Renders the model data and presents it to the user.
- Controller: Intercepts user input, processes it, and returns an appropriate model and view.
- DispatcherServlet: The front controller that intercepts all incoming HTTP requests.
- HandlerMapping: Maps the request URL to appropriate controller methods.
- Controller: Annotated classes that handle requests and return responses.
- ModelAndView: Combines model data and logical view name.
- ViewResolver: Resolves view names to actual views like JSPs or Thymeleaf templates.
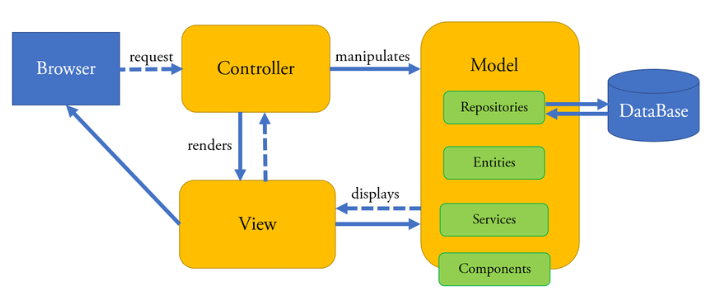
Main Components of Spring MVC Architecture:
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Key Features of Spring MVC
- Annotation-Based Programming: Use of annotations like @Controller, @RequestMapping, and @Autowired simplifies configuration.
- Flexible View Support: Integrates with various technologies such as JSP, Thymeleaf, Velocity, and FreeMarker. To complement such server-side templating flexibility with desktop interface development, exploring Python GUI Tkinter Module introduces a beginner-friendly toolkit for building interactive applications featuring widgets, layout managers, and event-driven programming that simplify the creation of responsive user interfaces in Python.
- Built-in Validation and Binding: Supports data binding and validation out-of-the-box.
- Exception Handling Mechanism: Easy configuration for centralized exception handling using @ControllerAdvice.
- RESTful Web Services Support: Seamless support for creating RESTful endpoints using annotations.
- Integration with Spring Security and ORM tools: Provides end-to-end enterprise solutions.
- Model: Represents the data layer. In Spring MVC, these are typically POJOs or entities managed by service and DAO layers.
- View: The presentation layer. It retrieves model data and displays it using JSP, Thymeleaf, or other view technologies.
- Controller: Acts as the coordinator between view and model. Accepts requests, invokes business logic, and returns a logical view name.
- User sends a request to the server.
- DispatcherServlet intercepts the request. To complement such centralized request handling with efficient graph traversal logic, exploring Minimum Spanning Tree introduces algorithms like Kruskal’s and Prim’s designed to connect all nodes in a network with minimal total edge weight.
- HandlerMapping identifies the corresponding controller.
- Controller processes the request and returns a ModelAndView.
- ViewResolver identifies the physical view.
- The response is rendered and returned to the user.
- Java Development Kit (JDK 8+)
- Maven or Gradle for dependency management streamlines the build process and ensures consistent project configuration across environments. To complement such automation tools with foundational coding logic, exploring C Programming Examples provides hands-on practice with variables, loops, conditionals, and functions equipping developers.
- IDE (Eclipse, IntelliJ)
- Tomcat Server (Optional if not using Spring Boot)
- src/main/java/com/example/controller
- src/main/java/com/example/model
- src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml
- src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/index.jsp
- <web-app>
- <servlet>
- <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name>
- <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
- <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
- </servlet>
- <servlet-mapping>
- <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name>
- <url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
- </servlet-mapping>
- </web-app>
- DispatcherServlet: Central controller of the MVC application. To complement such architectural coordination with algorithmic depth, exploring Height of a Tree introduces key concepts in binary tree traversal demonstrating how recursive and iterative methods compute the longest path from root to leaf.
- Controllers: Java classes annotated with @Controller, defining methods to handle requests.
- ModelAndView: Used by controllers to return model data and view name.
- ViewResolver: Determines the actual view (JSP, HTML, etc.).
- HandlerMapping: Maintains the mapping between request and controller method.
- @Controller
- public class HomeController {
- @RequestMapping(“/”)
- public String home(Model model) {
- model.addAttribute(“message”, “Welcome to Spring MVC”);
- return “index”;
- }
- }
- @RequestMapping
- @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping
- @PathVariable, @RequestParam
- @GetMapping(“/user/{id}”)
- public String getUser(@PathVariable int id, Model model) {
- model.addAttribute(“userId”, id);
- return “userDetails”;
- }
- }
- }
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Model-View-Controller Design Pattern Explained
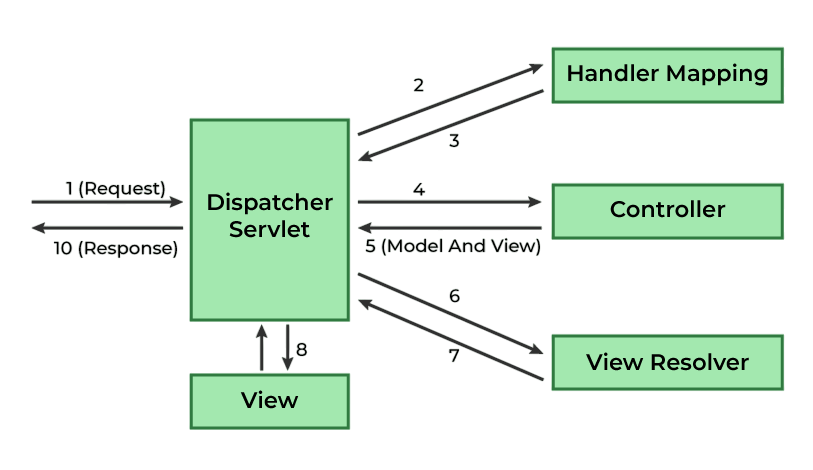
Request Flow in Spring MVC:
Setting Up a Spring MVC Project
Pre-requisites:
Project Structure:
web.xml Configuration:
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Components of Spring MVC
Sample Controller Code:
Handling Requests and Mapping URLs
Spring MVC offers a declarative way to map HTTP requests using annotations: To complement such structured request handling with recursive problem-solving techniques, exploring Backtracking Programming reveals how algorithms systematically explore solution spaces pruning invalid paths and incrementally building valid outcomes, ideal for solving puzzles, constraint satisfaction problems, and dynamic decision trees in scalable applications.
Example:
Conclusion
In conclusion, Spring MVC is a powerful and flexible web framework that follows the Model-View-Controller design pattern, making it easier to build well-structured and maintainable Java web applications. Its modular architecture, robust request handling, and seamless integration with other Spring modules make it a popular choice among developers. By understanding its core components and setup process, developers can build scalable, testable, and efficient web applications with ease. To complement such backend development expertise with front-end mastery, exploring Web Designing & Development Training equips learners with hands-on skills in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and UI/UX design empowering them to create responsive, visually engaging interfaces that integrate seamlessly with robust application architectures. Spring MVC continues to be a preferred choice for enterprise web application development. Its modular architecture, ease of integration with other Spring modules, and ability to build REST APIs make it ideal for both monolithic and microservices applications. By following best practices and leveraging its powerful features, developers can build robust, maintainable, and secure Java web applications.





