
- What is Virtual Reality?
- History and Evolution
- How VR Works: Key Components
- Types of Virtual Reality
- VR Devices and Hardware
- Software Development in VR
- Applications of VR in Industries
- Ethical Considerations
- Future of VR
- Getting Started with VR Development
- Conclusion
What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality (VR) is a simulated experience that immerses users in a three-dimensional, computer-generated environment where they can interact using sensory feedback such as sight, sound, and sometimes touch. Unlike traditional interfaces, VR places the user inside the experience, making it feel as if they are truly “there.” The goal of VR is to create an artificial world that feels real through technology. This is achieved using headsets, motion controllers, sensors, and specialized software. Whether it’s exploring a digital world, training for a high-risk job, or enjoying immersive entertainment, VR bridges the gap between imagination and experience.
Ready to Get Certified in Machine Learning? Explore the Program Now Machine Learning Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
History and Evolution
The evolution of immersive environments spans decades of technological innovation, starting with Morton Heilig’s groundbreaking Sensorama in 1956. This device offered a multi-sensory experience that greatly surpassed traditional media. In 1968, Ivan Sutherland created the first head-mounted display, the Sword of Damocles. Its design was awkward, as it had to be suspended from the ceiling. As the concept developed, Jaron Lanier introduced the term “Virtual Reality” in the 1980s. Around the same time, organizations like NASA looked into using VR for specific training. Early commercial efforts by Sega and Nintendo struggled due to technology limitations. However, the 2000s brought a significant comeback fueled by improvements in computing and graphics. A key moment came with the launch of the Oculus Rift in 2012. This product renewed consumer interest and drew major tech companies such as HTC and Sony. Today, standalone VR headsets and growing use in education, healthcare, and metaverse development show the technology’s ability to transform our experiences. We are now entering a new era of immersive digital experiences that continue to expand the way we interact and perceive the world.
How VR Works: Key Components
Creating a convincing virtual environment requires the integration of several core technologies:
- VR headsets use stereoscopic displays to present 3D images to each eye.
- Lenses focus and reshape the image to simulate depth perception.
- Head Tracking: Sensors like gyroscopes and accelerometers detect head movements.
- Positional Tracking: External or internal cameras track movement in space (6 degrees of freedom or 6DoF).
- Handheld devices or gloves detect user input, gestures, and finger movements.
- Haptics provide tactile feedback.
- Spatial audio enhances immersion by adjusting sound direction based on head orientation.
- VR engines like Unity and Unreal render the virtual environment in real-time.
- Processing is handled either by a connected computer, console, or built-in hardware.
-
Non-Immersive VR:
- Screen-based simulations (e.g., flight simulators, video games on monitors).
- User remains aware of the physical environment.
- Projection systems like CAVE (Cave Automatic Virtual Environment).
- Offers partial immersion with limited movement and interaction.
- VR headsets with full head and motion tracking.
- Provides the most realistic and interactive experience.
- Shared virtual spaces where users interact with avatars.
- Used in education, remote meetings, and gaming.
- Medical Training: Simulated surgeries and emergency response.
- Therapy: Exposure therapy for PTSD, anxiety treatment.
- Rehabilitation: Motor skill training for stroke patients.
- Virtual classrooms, historical reconstructions, immersive STEM lessons.
- Increased engagement and improved retention.
- Virtual walkthroughs of buildings pre-construction.
- Enhanced visualization for clients and architects.
- Prototyping and assembly line training in virtual settings.
- Reduces cost and time-to-market. Entertainment and Gaming:
- Immersive games, VR cinemas, and interactive storytelling.
- Platforms like SteamVR and Meta Horizon Worlds offer extensive content.
- Combat simulations, equipment training, drone operation.
- Safer and more cost-effective training.
- Virtual fitting rooms and interactive product demos.
- Increases customer engagement and reduces returns.
- Addiction and Escapism: Overuse of immersive environments can lead to withdrawal from reality.
- Privacy: VR systems collect biometric and behavioral data (eye tracking, body movements).
- Psychological Effects: Blurring lines between virtual and real may impact perception, especially in children.
- Inclusion and Bias: Experiences should be accessible to people of all abilities and avoid gender, racial, or cultural stereotypes in avatars and environments.
- Data Ownership: User data generated in VR should be protected from misuse.
- Addiction and Escapism: Overuse of immersive environments can lead to withdrawal from reality.
- Privacy: VR systems collect biometric and behavioral data (eye tracking, body movements).
- Psychological Effects: Blurring lines between virtual and real may impact perception, especially in children.
- Inclusion and Bias: Experiences should be accessible to people of all abilities and avoid gender, racial, or cultural stereotypes in avatars and environments.
- Data Ownership: User data generated in VR should be protected from misuse.
Display and Optics:
Motion Tracking:
Controllers and Inputs:
Sound:
Rendering and Processing:
To Explore Machine Learning in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Machine Learning Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Types of Virtual Reality
VR Categories Based on Immersion and Interaction:
Semi-Immersive VR:
Fully Immersive VR:
Collaborative VR (Social VR):
VR Devices and Hardware
Virtual reality (VR) experiences have changed a lot thanks to various devices that reshape digital interactions. At the forefront of the market, Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) like Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR provide immersive visuals and improved motion tracking. Mobile VR headsets offer a cheaper way in by using smartphones as screens, but they have limited performance. Standalone systems such as Meta Quest 3 are at the cutting edge. They include built-in processing and battery technology, which means users do not need external computers or consoles. Users can enhance their experience with advanced motion-sensing controllers, haptic gloves, and foot trackers for precise input. Innovative treadmills and haptic suits boost immersion by mimicking physical movement and providing touch feedback. This growing range of VR devices continues to expand what digital experiences can offer. They make more realistic and interactive virtual environments available to users with various tech needs and budgets.
Software Development in VR
In the fast-changing world of virtual reality development, professionals use a wide range of tools and platforms to create immersive experiences. Unity and Unreal Engine are top development environments that give developers strong capabilities for cross-platform design and high-quality visual rendering. By using platform-specific SDKs like OpenXR, Oculus, and SteamVR, developers build VR applications that ensure broad compatibility. They focus on important design aspects that prioritize user comfort. They implement strategies to reduce motion sickness with high frame rates and develop easy-to-use interaction models that include techniques like gesture recognition, voice commands, and gaze tracking. Developers work with programming languages such as C#, C++, Python, and JavaScript to support their work, especially focusing on spatial audio and environment design to improve realism and help users navigate. By balancing technical skills with user-focused design principles, VR developers create engaging and immersive experiences that stretch the limits of digital interaction and technology.
Looking to Master Machine Learning? Discover the Machine Learning Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Applications of VR in Industries
VR has transformed operations across diverse sectors:
Healthcare:
Education:
Architecture and Real Estate:
Manufacturing and Design:
Military and Defense:
Retail and E-Commerce:
Ethical Considerations
As with any emerging tech, VR raises ethical questions:
Developers and companies must build responsible and inclusive VR systems.
Preparing for Machine Learning Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Machine Learning Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Future of VR
As with any emerging tech, VR raises ethical questions:
Developers and companies must build responsible and inclusive VR systems.
Getting Started with VR Development
Aspiring virtual reality developers should start their journey into VR application development with a clear plan. First, they need to understand VR concepts, hardware, and interaction models. After that, they should choose a solid development platform like Unity or Unreal Engine, both of which offer user-friendly environments and strong community support. Getting a development kit, such as the Oculus Quest 2, is essential because it allows them to gain hands-on experience with important SDKs and development tools.
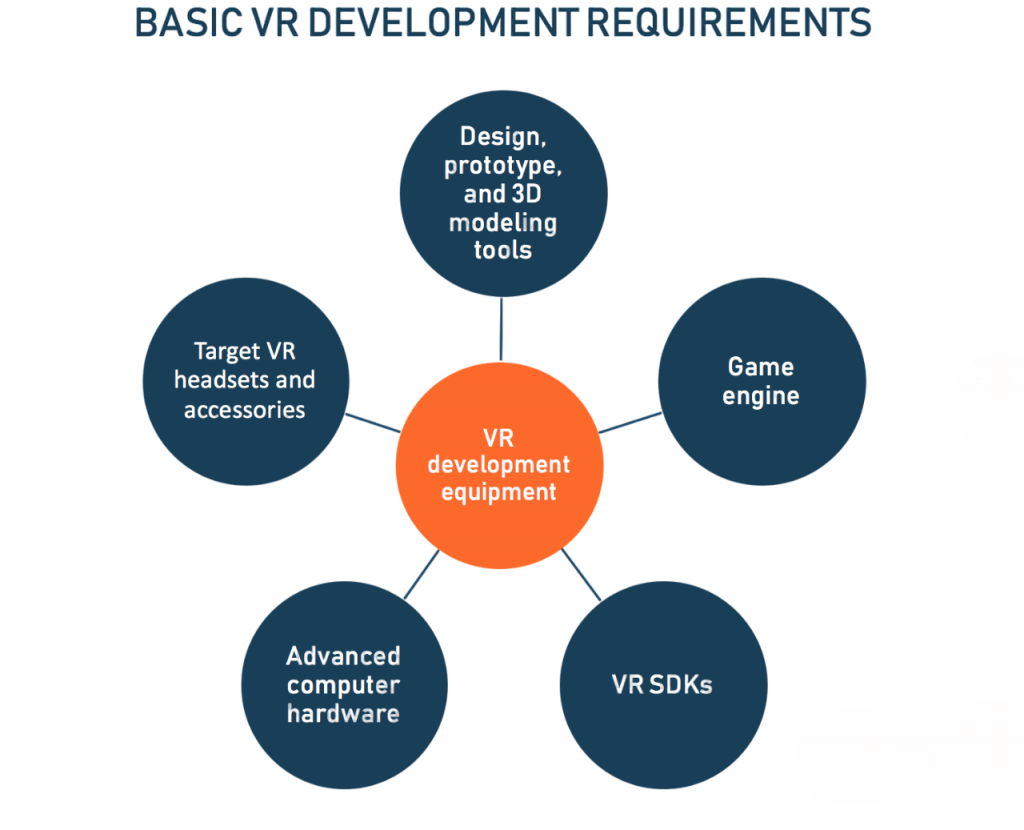
To speed up their learning, they can explore online tutorials, take structured courses from websites like Coursera and Udemy, and gradually build practical projects that improve their skills in room navigation and object interaction. At the same time, they should connect with VR developer communities on Reddit, Discord, and Stack Overflow to network, seek advice, and keep up with new trends. As they create their applications, they need to adopt a mindset of continuous improvement by collecting user feedback and considering publishing their work on platforms like the Oculus Store or SideQuest.
Conclusion
Virtual Reality is redefining the boundaries between digital and physical worlds. From immersive storytelling and revolutionary education tools to transforming healthcare and redefining collaboration, VR holds the key to a more interactive and intelligent future. As technology continues to evolve, so will the opportunities. Whether you’re a curious learner, developer, or business strategist, understanding VR today prepares you for tomorrow’s immersive world. VR is the key to a more interactive and smarter future. As technology improves, new opportunities will arise. The possible uses are expanding every day. You might be someone who enjoys learning. You could also be a software developer building these worlds. Or you may be a business leader preparing for what comes next. Understanding VR now is important. It gets you ready for this new world. A world based on immersive experiences. This is the future in development.


